Intro
Discover 5 ways vitamin B12 deficiency medication can improve health, alleviating fatigue, weakness, and neurological symptoms with supplements, injections, and dietary changes, addressing pernicious anemia and nutrient deficiencies.
Vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in the production of red blood cells, nerve function, and DNA synthesis. A deficiency in vitamin B12 can lead to a range of health problems, including anemia, fatigue, and neurological disorders. Fortunately, vitamin B12 deficiency medication is available to help alleviate these symptoms and restore optimal health. In this article, we will explore the importance of vitamin B12, the causes and symptoms of deficiency, and the various treatment options available.
Vitamin B12 deficiency is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including a vegetarian or vegan diet, gastrointestinal disorders, and certain medications. The symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency can be subtle, making it challenging to diagnose. However, if left untreated, a deficiency can lead to serious health complications. Therefore, it is essential to understand the importance of vitamin B12 and the various treatment options available.
The human body requires vitamin B12 to produce red blood cells, which carry oxygen to the body's tissues. It also plays a critical role in the maintenance of the nervous system and the synthesis of DNA. A deficiency in vitamin B12 can lead to a range of health problems, including anemia, fatigue, weakness, and neurological disorders. In severe cases, a deficiency can cause permanent damage to the nervous system, making it essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist.
Vitamin B12 Deficiency Causes and Symptoms
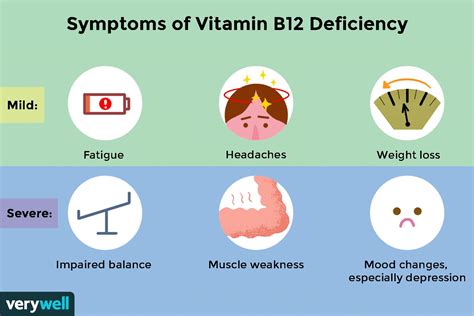
Types of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
There are several types of vitamin B12 deficiency, including: * Pernicious anemia: a condition where the body is unable to absorb vitamin B12 due to a lack of intrinsic factor, a protein in the stomach that helps absorb the vitamin. * Dietary deficiency: a condition where the diet is lacking in vitamin B12, often seen in vegetarians and vegans. * Gastrointestinal disorders: conditions such as celiac disease, Crohn's disease, and ulcerative colitis can lead to vitamin B12 deficiency. * Medication-induced deficiency: certain medications, such as proton pump inhibitors and metformin, can interfere with vitamin B12 absorption.Vitamin B12 Deficiency Medication Options

Benefits of Vitamin B12 Deficiency Medication
Vitamin B12 deficiency medication can provide numerous benefits, including: * Improved energy levels: vitamin B12 plays a critical role in the production of red blood cells, which carry oxygen to the body's tissues. * Improved neurological function: vitamin B12 is essential for the maintenance of the nervous system and the synthesis of DNA. * Improved heart health: vitamin B12 helps to reduce homocysteine levels, which can contribute to heart disease. * Improved cognitive function: vitamin B12 plays a critical role in the synthesis of neurotransmitters, which are essential for cognitive function.Vitamin B12 Deficiency Treatment Options
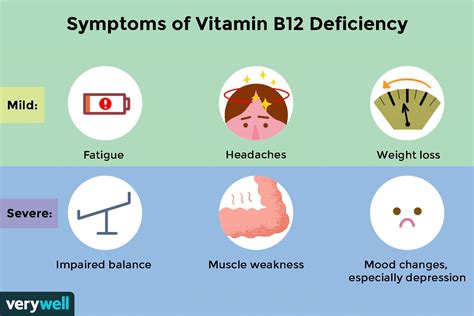
Preventing Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Preventing vitamin B12 deficiency is essential to maintain optimal health. Common prevention strategies include: * Eating a balanced diet: increasing vitamin B12 intake through dietary sources such as meat, fish, and dairy products. * Taking supplements: taking vitamin B12 supplements to increase levels. * Avoiding certain medications: avoiding medications that can interfere with vitamin B12 absorption. * Managing underlying conditions: managing underlying conditions such as gastrointestinal disorders to prevent vitamin B12 deficiency.Vitamin B12 Deficiency Diagnosis and Testing

Interpreting Test Results
Interpreting test results is essential to diagnose vitamin B12 deficiency. Common test results include: * Low vitamin B12 levels: indicating vitamin B12 deficiency. * Elevated MMA levels: indicating vitamin B12 deficiency. * Abnormal CBC results: indicating anemia or other blood disorders.Vitamin B12 Deficiency Complications and Risks
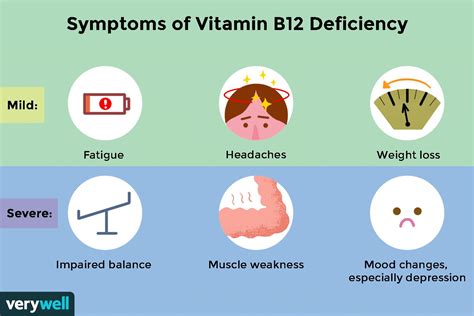
Managing Complications and Risks
Managing complications and risks is essential to prevent long-term damage. Common strategies include: * Seeking medical attention: seeking medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen. * Taking medication: taking vitamin B12 medication to increase levels and prevent complications. * Making lifestyle changes: making lifestyle changes such as increasing vitamin B12 intake through dietary sources and avoiding certain medications.What are the symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency?
+Common symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency include fatigue, weakness, pale skin, shortness of breath, and neurological problems such as numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness.
How is vitamin B12 deficiency diagnosed?
+Vitamin B12 deficiency diagnosis involves a physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests such as a complete blood count (CBC), vitamin B12 level test, and methylmalonic acid (MMA) test.
What are the treatment options for vitamin B12 deficiency?
+Treatment options for vitamin B12 deficiency include dietary changes, oral supplements, injections, and nasal sprays. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the deficiency, the underlying cause, and the individual's overall health.
Can vitamin B12 deficiency be prevented?
+Yes, vitamin B12 deficiency can be prevented by eating a balanced diet, taking supplements, avoiding certain medications, and managing underlying conditions such as gastrointestinal disorders.
What are the complications and risks of vitamin B12 deficiency?
+Vitamin B12 deficiency complications and risks can be severe if left untreated and include anemia, heart problems, and neurological disorders. It is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen.
In conclusion, vitamin B12 deficiency is a common condition that can have severe consequences if left untreated. Understanding the importance of vitamin B12, the causes and symptoms of deficiency, and the various treatment options available is essential to maintaining optimal health. By seeking medical attention, making lifestyle changes, and taking medication, individuals can prevent long-term damage and alleviate symptoms. We encourage readers to share this article with others, comment below with their experiences, and take action to prioritize their health and well-being.
