Intro
Discover densities and their significance in physics, exploring mass, volume, and buoyancy, to understand the fundamentals of density and its applications.
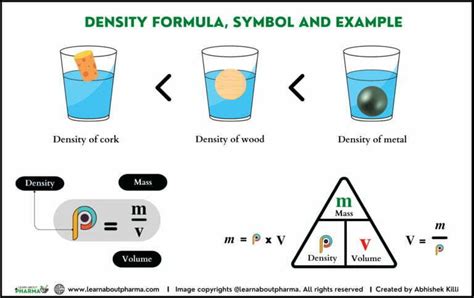
Densities are a fundamental concept in physics and engineering, and they play a crucial role in understanding the behavior of materials and objects in various environments. The density of a substance is defined as its mass per unit volume, and it is typically denoted by the symbol ρ (rho). In simpler terms, density is a measure of how much "stuff" is packed into a given amount of space. For example, a brick has a higher density than a balloon because it has more mass packed into a smaller volume.
The concept of density is essential in many fields, including physics, engineering, chemistry, and materials science. It helps us understand the properties of materials, such as their strength, buoyancy, and thermal conductivity. Density also plays a critical role in various industrial applications, including the design of buildings, bridges, and other structures. Furthermore, understanding densities is crucial in fields like geology, where it helps us understand the composition and behavior of rocks and minerals.
The study of densities has a rich history, dating back to ancient civilizations. The Greek philosopher Archimedes is credited with discovering the principle of buoyancy, which is closely related to density. He realized that the upward force exerted on an object immersed in a fluid is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object. This fundamental principle has had a profound impact on our understanding of densities and their role in various phenomena. Today, densities are used in a wide range of applications, from designing more efficient transportation systems to developing new materials with unique properties.
Types of Densities
There are several types of densities, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. Some of the most common types of densities include:
- Absolute density: This is the density of a substance relative to the density of water at a reference temperature and pressure. Absolute density is typically denoted by the symbol ρ and is measured in units of kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³) or grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³).
- Relative density: This is the density of a substance relative to the density of another substance, usually water. Relative density is also known as specific gravity and is denoted by the symbol SG.
- Apparent density: This is the density of a substance that is measured by displacing a fluid, such as water or air. Apparent density is often used to measure the density of porous or granular materials.
- Bulk density: This is the density of a substance that includes the volume of any pores or voids within the material. Bulk density is typically denoted by the symbol ρb and is measured in units of kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³) or grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³).
Applications of Densities
The applications of densities are diverse and widespread. Some of the most significant applications include:- Design of structures: Densities are used to calculate the weight and stress of buildings, bridges, and other structures.
- Materials science: Densities are used to understand the properties of materials, such as their strength, toughness, and thermal conductivity.
- Chemical engineering: Densities are used to design and optimize chemical processes, such as distillation and crystallization.
- Geology: Densities are used to understand the composition and behavior of rocks and minerals.
Measurement of Densities

The measurement of densities is a critical aspect of understanding the properties of materials and objects. There are several methods for measuring densities, including:
- Hydrometer: A hydrometer is a device that measures the density of a liquid by displacing a known volume of fluid.
- Pycnometer: A pycnometer is a device that measures the density of a solid or liquid by displacing a known volume of fluid.
- Density column: A density column is a device that measures the density of a substance by comparing it to a series of known densities.
- Digital density meter: A digital density meter is an electronic device that measures the density of a substance using a variety of techniques, including ultrasound and vibrational methods.
Factors Affecting Densities
There are several factors that can affect the density of a substance, including:- Temperature: Temperature can affect the density of a substance by changing its volume or molecular structure.
- Pressure: Pressure can affect the density of a substance by changing its volume or molecular structure.
- Composition: The composition of a substance can affect its density by changing its molecular structure or the arrangement of its molecules.
- Purity: The purity of a substance can affect its density by changing its molecular structure or the arrangement of its molecules.
Importance of Densities in Everyday Life

Densities play a crucial role in many aspects of everyday life, from the design of buildings and bridges to the development of new materials and technologies. Some of the most significant ways in which densities affect our daily lives include:
- Transportation: Densities are used to design and optimize transportation systems, including cars, airplanes, and ships.
- Construction: Densities are used to design and build structures, including buildings, bridges, and roads.
- Materials science: Densities are used to develop new materials with unique properties, such as strength, toughness, and thermal conductivity.
- Energy production: Densities are used to design and optimize energy production systems, including fossil fuel power plants and nuclear reactors.
Real-World Examples of Densities
There are many real-world examples of densities in action, including:- Buoyancy: The buoyancy of an object in water is determined by its density relative to the density of water.
- Floating objects: Objects that are less dense than water will float, while objects that are more dense will sink.
- Sinking objects: Objects that are more dense than water will sink, while objects that are less dense will float.
- Density columns: Density columns are used to separate substances based on their densities, such as in the separation of minerals and rocks.
Calculating Densities

Calculating densities is a straightforward process that involves measuring the mass and volume of a substance. The formula for calculating density is:
ρ = m / V
Where ρ is the density, m is the mass, and V is the volume.
There are several units that can be used to express density, including:
- Kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³): This is the most common unit of density and is used to express the density of solids, liquids, and gases.
- Grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³): This unit is often used to express the density of small objects or substances.
- Pounds per cubic foot (lb/ft³): This unit is often used to express the density of substances in the United States.
Common Density Values
There are several common density values that are useful to know, including:- Water: The density of water is approximately 1 g/cm³ or 1000 kg/m³.
- Air: The density of air is approximately 0.0012 g/cm³ or 1.2 kg/m³.
- Steel: The density of steel is approximately 7.9 g/cm³ or 7900 kg/m³.
- Wood: The density of wood is approximately 0.5 g/cm³ or 500 kg/m³.
Challenges and Limitations of Densities
While densities are a powerful tool for understanding the properties of materials and objects, there are several challenges and limitations to consider. Some of the most significant challenges include:
- Measurement accuracy: Measuring densities accurately can be challenging, especially for small or complex objects.
- Temperature and pressure effects: Temperature and pressure can affect the density of a substance, making it challenging to measure and calculate densities accurately.
- Composition and purity: The composition and purity of a substance can affect its density, making it challenging to measure and calculate densities accurately.
- Non-uniform densities: Some substances have non-uniform densities, making it challenging to measure and calculate densities accurately.
Future Directions for Densities
There are several future directions for densities, including:- New materials and technologies: The development of new materials and technologies will require a deeper understanding of densities and their role in determining the properties of materials.
- Advanced measurement techniques: The development of advanced measurement techniques, such as digital density meters, will enable more accurate and precise measurements of densities.
- Computer simulations: The use of computer simulations will enable researchers to model and predict the behavior of materials and objects, including their densities.
- Interdisciplinary research: The study of densities will require interdisciplinary research, including collaboration between physicists, engineers, chemists, and materials scientists.
What is the difference between absolute and relative density?
+Absolute density is the density of a substance relative to the density of water at a reference temperature and pressure, while relative density is the density of a substance relative to the density of another substance, usually water.
How do temperatures and pressures affect densities?
+Temperatures and pressures can affect the density of a substance by changing its volume or molecular structure. Increasing temperature or decreasing pressure can decrease the density of a substance, while decreasing temperature or increasing pressure can increase the density.
What are some common applications of densities in everyday life?
+Densities are used in many aspects of everyday life, including the design of buildings and bridges, the development of new materials and technologies, and the optimization of transportation systems.
In summary, densities are a fundamental concept in physics and engineering that play a crucial role in understanding the behavior of materials and objects. The study of densities has a rich history, and their applications are diverse and widespread. By understanding densities and their role in determining the properties of materials, we can design and optimize systems, develop new materials and technologies, and improve our daily lives. We encourage you to share your thoughts and questions about densities in the comments section below, and to explore further resources and references for a deeper understanding of this fascinating topic.
