Intro
Understand flu symptoms, causes, and treatments. Learn about common influenza signs, fever, cough, and body aches, to manage and prevent the flu virus effectively.
The flu, also known as influenza, is a highly contagious respiratory illness caused by the influenza virus. It can affect anyone, regardless of age or health status, and its symptoms can range from mild to severe. Understanding the flu symptoms is crucial for early detection, proper treatment, and prevention of complications. In this article, we will delve into the world of flu symptoms, exploring their causes, effects, and implications for our health.
The flu is a significant public health concern, with the World Health Organization (WHO) estimating that it affects up to 10% of the global population each year. In the United States alone, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) report that the flu results in approximately 140,000 to 720,000 hospitalizations and 12,000 to 79,000 deaths annually. The flu's impact on our health and wellbeing is substantial, making it essential to recognize its symptoms and take proactive measures to prevent its spread.
The flu virus is highly contagious, spreading through the air when an infected person talks, coughs, or sneezes, and by touching surfaces contaminated with the virus. The incubation period, which is the time between exposure to the virus and the onset of symptoms, is typically between one to four days. During this period, the virus multiplies rapidly, causing a range of symptoms that can vary in severity and duration.
Introduction to Flu Symptoms
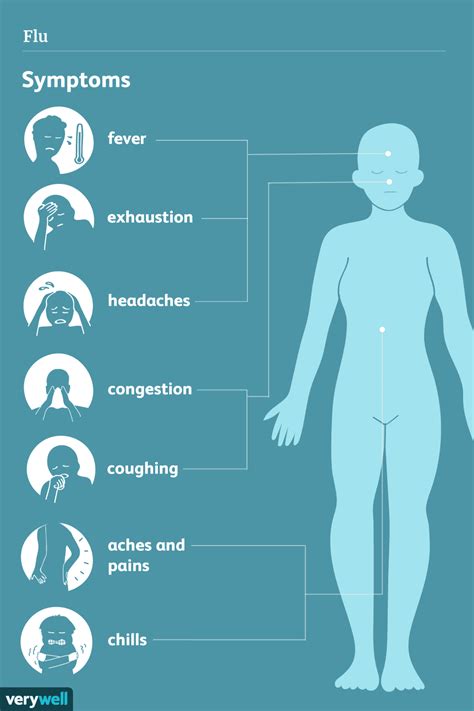
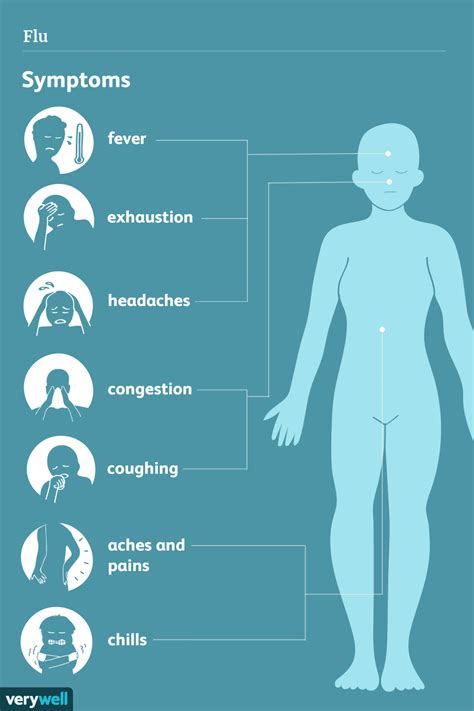
Flu symptoms can be divided into two categories: common and severe. Common symptoms include fever, chills, cough, sore throat, runny or stuffy nose, headache, fatigue, and muscle or body aches. Severe symptoms, which may indicate a more serious infection, include difficulty breathing, chest pain or pressure, severe headache, confusion, and seizures. It is essential to recognize these symptoms to seek medical attention promptly if they occur.
Common Flu Symptoms
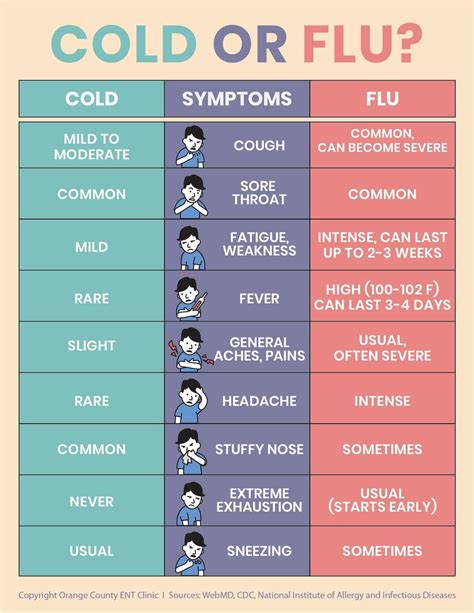
Common flu symptoms can be uncomfortable and debilitating, affecting daily activities and overall wellbeing. Fever, which is a common symptom, can range from mild to severe, with temperatures often reaching 102°F (39°C) or higher. Chills, cough, and sore throat can also be present, making it difficult to eat, sleep, or perform daily tasks. The flu can also cause fatigue, headache, and muscle or body aches, which can be severe and lingering.
Causes of Common Flu Symptoms
The causes of common flu symptoms are multifaceted, involving the immune system's response to the influenza virus. When the virus enters the body, it triggers an immune response, which leads to the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. These cytokines cause inflammation, leading to fever, chills, and other symptoms. The severity of symptoms depends on various factors, including the individual's overall health, age, and the strain of the virus.Severe Flu Symptoms
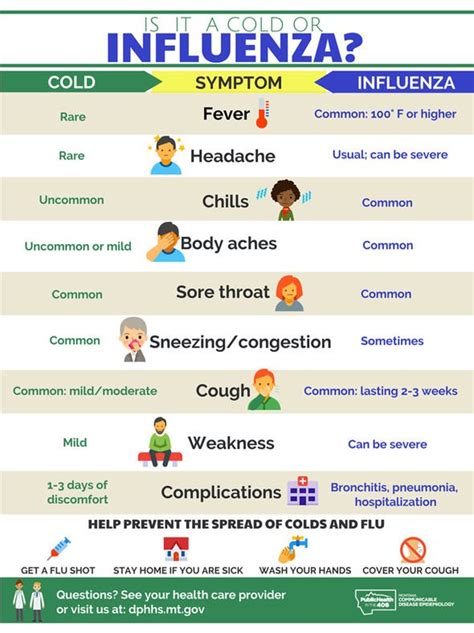
Severe flu symptoms can be life-threatening, especially for high-risk individuals, such as older adults, young children, and people with underlying health conditions. Difficulty breathing, chest pain or pressure, and severe headache can indicate pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), or other complications. Confusion, seizures, and loss of consciousness can also occur, requiring immediate medical attention.
Risk Factors for Severe Flu Symptoms
Certain risk factors increase the likelihood of developing severe flu symptoms. Age is a significant factor, with older adults and young children being more susceptible to severe illness. Underlying health conditions, such as heart disease, diabetes, and lung disease, can also increase the risk of complications. Additionally, pregnant women, people with weakened immune systems, and those taking certain medications may be more prone to severe flu symptoms.Diagnosing Flu Symptoms

Diagnosing flu symptoms involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. Healthcare providers may use rapid influenza diagnostic tests (RIDTs) to detect the presence of the influenza virus. These tests can provide results within 15-30 minutes, allowing for prompt treatment and management of symptoms.
Types of Diagnostic Tests
There are several types of diagnostic tests used to detect the flu, including RIDTs, viral cultures, and molecular assays. RIDTs are the most commonly used tests, as they are quick and relatively accurate. However, they may not detect all cases of the flu, especially in people with mild symptoms. Viral cultures and molecular assays are more sensitive and specific but may take longer to provide results.Treating Flu Symptoms

Treating flu symptoms involves a combination of self-care, over-the-counter medications, and prescription antiviral medications. Rest, hydration, and nutrition are essential for managing symptoms and supporting the immune system. Over-the-counter medications, such as pain relievers and decongestants, can help alleviate symptoms, while prescription antiviral medications, such as oseltamivir and zanamivir, can shorten the duration and severity of the illness.
Antiviral Medications
Antiviral medications are an effective treatment for the flu, especially when started within 48 hours of symptom onset. These medications work by inhibiting the replication of the influenza virus, reducing the severity and duration of symptoms. Oseltamivir and zanamivir are the most commonly used antiviral medications, with peramivir and baloxavir also available for treatment.Preventing Flu Symptoms

Preventing flu symptoms involves a combination of vaccination, good hygiene, and lifestyle modifications. The flu vaccine is the most effective way to prevent the flu, with the CDC recommending annual vaccination for everyone six months and older. Good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing and avoiding close contact with people who are sick, can also reduce the risk of transmission. Lifestyle modifications, such as getting enough sleep, exercising regularly, and managing stress, can help support the immune system and reduce the risk of illness.
Vaccination Benefits
The flu vaccine offers several benefits, including reduced risk of illness, hospitalization, and death. The vaccine can also reduce the severity of symptoms, even if it does not prevent the illness entirely. Additionally, vaccination can help protect vulnerable populations, such as older adults and young children, who are at higher risk of complications.Complications of Flu Symptoms
Complications of flu symptoms can be severe and life-threatening, especially for high-risk individuals. Pneumonia, bronchitis, and sinus and ear infections are common complications, while more severe complications, such as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), heart attack, and stroke, can occur in rare cases.
High-Risk Groups
Certain groups are at higher risk of developing complications from the flu, including older adults, young children, and people with underlying health conditions. Pregnant women, people with weakened immune systems, and those taking certain medications may also be more prone to complications. It is essential to recognize these risk factors and take proactive measures to prevent the flu and its complications.What are the most common symptoms of the flu?
+The most common symptoms of the flu include fever, chills, cough, sore throat, runny or stuffy nose, headache, fatigue, and muscle or body aches.
How is the flu diagnosed?
+The flu is diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests, such as rapid influenza diagnostic tests (RIDTs) and viral cultures.
What are the best ways to prevent the flu?
+The best ways to prevent the flu include getting vaccinated, practicing good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing and avoiding close contact with people who are sick, and making lifestyle modifications, such as getting enough sleep, exercising regularly, and managing stress.
What are the complications of the flu?
+The complications of the flu can be severe and life-threatening, especially for high-risk individuals, and include pneumonia, bronchitis, and sinus and ear infections, as well as more severe complications, such as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), heart attack, and stroke.
How can I treat the flu?
+Treatment for the flu includes a combination of self-care, over-the-counter medications, and prescription antiviral medications, such as oseltamivir and zanamivir, which can shorten the duration and severity of the illness.
In summary, understanding flu symptoms is crucial for early detection, proper treatment, and prevention of complications. By recognizing the common and severe symptoms, diagnosing the flu, treating symptoms, and preventing the flu, we can reduce the risk of illness and protect vulnerable populations. We encourage you to share this article with your friends and family to help spread awareness about the flu and its symptoms. If you have any questions or concerns, please comment below, and we will be happy to help. Remember, staying informed and taking proactive measures is key to staying healthy and flu-free.
