Intro
Discover what PVCs (Premature Ventricular Contractions) are, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options, including arrhythmia management and cardiac care, to understand heart health and irregular heartbeat conditions.
Premature ventricular contractions, or PVCs, are a type of abnormal heart rhythm, also known as arrhythmia. They occur when the heart's ventricles contract too early, before the heart has a chance to fill with blood. This can cause the heart to feel like it is skipping a beat or beating irregularly. PVCs are relatively common and can be caused by a variety of factors, including stress, caffeine, and certain medical conditions.
PVCs are often felt as a skipped beat or a palpitation, and they can be uncomfortable or even alarming for some people. However, in most cases, PVCs are not a cause for concern and do not require treatment. They can be a normal response to stress or fatigue, and they often resolve on their own. Nevertheless, it is essential to understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for PVCs to ensure that any underlying conditions are properly addressed.
The importance of understanding PVCs lies in their potential to be a symptom of an underlying heart condition. While PVCs are often benign, they can also be a sign of a more serious issue, such as heart disease or cardiomyopathy. By recognizing the signs and symptoms of PVCs and seeking medical attention if necessary, individuals can take steps to protect their heart health and prevent potential complications.
What Causes Pvcs
PVCs can be caused by a variety of factors, including lifestyle habits, medical conditions, and genetic predisposition. Some common causes of PVCs include:
- Stress and anxiety: High levels of stress can cause the heart to beat irregularly, leading to PVCs.
- Caffeine and nicotine: Consuming high amounts of caffeine or nicotine can stimulate the heart and lead to PVCs.
- Certain medications: Some medications, such as decongestants and asthma inhalers, can cause PVCs as a side effect.
- Heart conditions: Underlying heart conditions, such as heart disease or cardiomyopathy, can increase the risk of PVCs.
- Electrolyte imbalances: Abnormal levels of electrolytes, such as potassium or magnesium, can disrupt the heart's rhythm and lead to PVCs.
Types of Pvcs
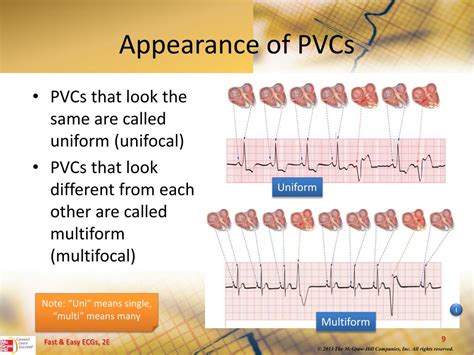
PVCs can be classified into different types based on their frequency, duration, and underlying cause. Some common types of PVCs include:- Unifocal PVCs: These occur when the premature contractions originate from a single location in the heart.
- Multifocal PVCs: These occur when the premature contractions originate from multiple locations in the heart.
- Bigeminy: This occurs when every other beat is a PVC.
- Trigeminy: This occurs when every third beat is a PVC.
Symptoms of Pvcs

The symptoms of PVCs can vary from person to person, but common symptoms include:
- Palpitations: Feeling like the heart is skipping a beat or beating irregularly.
- Chest discomfort: Feeling pressure or tightness in the chest.
- Shortness of breath: Feeling like it is difficult to catch breath.
- Dizziness: Feeling lightheaded or disoriented.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired or weak.
Diagnosing Pvcs
Diagnosing PVCs typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests. Some common diagnostic tests for PVCs include:- Electrocardiogram (ECG): This test measures the heart's electrical activity and can help identify abnormal rhythms.
- Holter monitor: This test records the heart's activity over a 24-hour period and can help identify patterns of PVCs.
- Echocardiogram: This test uses sound waves to create images of the heart and can help identify underlying heart conditions.
Treatment Options for Pvcs

Treatment for PVCs depends on the underlying cause and severity of symptoms. Some common treatment options include:
- Lifestyle modifications: Reducing stress, avoiding caffeine and nicotine, and getting regular exercise can help alleviate symptoms.
- Medications: Beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, and anti-arrhythmic medications can help regulate the heart's rhythm.
- Catheter ablation: This minimally invasive procedure involves using a catheter to destroy the abnormal electrical pathways in the heart.
Preventing Pvcs
Preventing PVCs involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle and managing underlying medical conditions. Some tips for preventing PVCs include:- Eating a healthy diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Exercising regularly: Regular exercise can help reduce stress and improve overall heart health.
- Managing stress: Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing, can help alleviate symptoms.
- Avoiding triggers: Avoiding caffeine, nicotine, and other triggers can help reduce the frequency and severity of PVCs.
Living with Pvcs

Living with PVCs requires a combination of lifestyle modifications, medical treatment, and stress management. Some tips for living with PVCs include:
- Keeping a symptom journal: Tracking symptoms and triggers can help identify patterns and improve treatment.
- Practicing relaxation techniques: Stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can help alleviate symptoms.
- Staying hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help reduce the risk of electrolyte imbalances.
- Getting enough sleep: Getting adequate rest can help reduce stress and improve overall heart health.
Coping with Pvcs
Coping with PVCs requires a combination of emotional support, lifestyle modifications, and medical treatment. Some tips for coping with PVCs include:- Seeking support: Talking to friends, family, or a support group can help alleviate feelings of anxiety and isolation.
- Practicing self-care: Engaging in activities that bring joy and relaxation can help reduce stress and improve overall well-being.
- Staying informed: Educating oneself about PVCs and underlying medical conditions can help improve treatment outcomes and reduce anxiety.
What are the symptoms of PVCs?
+The symptoms of PVCs can include palpitations, chest discomfort, shortness of breath, dizziness, and fatigue.
How are PVCs diagnosed?
+PVCs are typically diagnosed using a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests, such as ECG, Holter monitor, and echocardiogram.
Can PVCs be treated?
+Yes, PVCs can be treated using a combination of lifestyle modifications, medications, and catheter ablation.
How can I prevent PVCs?
+Preventing PVCs involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing underlying medical conditions, and avoiding triggers, such as caffeine and nicotine.
What is the prognosis for PVCs?
+The prognosis for PVCs is generally good, and most people can manage their symptoms and prevent complications with proper treatment and lifestyle modifications.
In conclusion, PVCs are a common type of abnormal heart rhythm that can be caused by a variety of factors. While they can be uncomfortable and alarming, PVCs are often benign and do not require treatment. However, it is essential to understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for PVCs to ensure that any underlying conditions are properly addressed. By maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, and seeking medical attention if necessary, individuals can reduce their risk of developing PVCs and improve their overall heart health. We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about PVCs in the comments section below, and we encourage you to share this article with anyone who may be experiencing symptoms of PVCs.
