Intro
Learn about Shin Splints, a common running injury causing medial tibial stress syndrome, calf pain, and inflammation, with expert treatment and prevention tips for athletes and runners.
Shin splints are a common issue that affects many individuals, particularly those who engage in athletic activities or have jobs that require standing or walking for extended periods. The condition is characterized by pain and inflammation in the lower leg, specifically in the area between the knee and ankle. Shin splints can be debilitating and may hinder an individual's ability to perform daily tasks or participate in their favorite sports. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for shin splints is essential for effective management and prevention.
Shin splints are often associated with overuse or repetitive stress on the muscles, tendons, and bone tissue in the lower leg. This can occur due to sudden changes in exercise intensity or frequency, inadequate footwear, or poor running or walking techniques. Additionally, individuals with flat feet or other foot abnormalities may be more prone to developing shin splints. The condition can also be caused by inadequate warm-up or cool-down routines, insufficient stretching, or failing to incorporate rest days into a training schedule.
The symptoms of shin splints can vary in severity and may include pain, swelling, and inflammation in the affected area. In some cases, the pain may be severe enough to limit an individual's ability to walk or engage in physical activities. Shin splints can also cause redness and warmth in the affected area, as well as numbness or tingling sensations in the feet. If left untreated, shin splints can lead to more severe complications, such as stress fractures or chronic pain.
Understanding Shin Splints
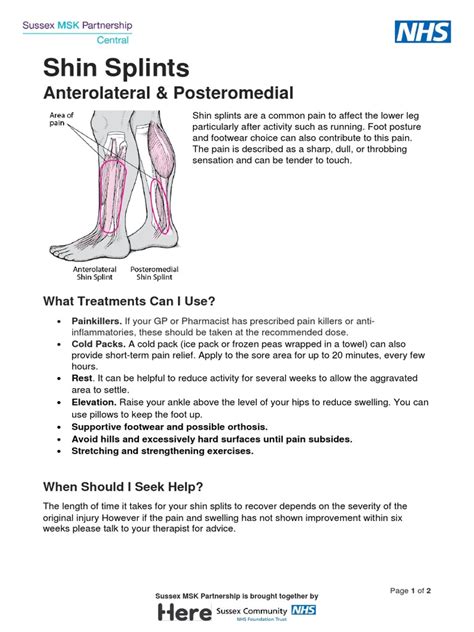
To understand shin splints, it's essential to know the anatomy of the lower leg and how it functions. The tibia and fibula bones in the lower leg are surrounded by muscles, tendons, and ligaments that work together to facilitate movement. When these tissues become inflamed or irritated, it can lead to pain and discomfort. Shin splints can be classified into two main categories: medial shin splints and anterior shin splints. Medial shin splints occur on the inner aspect of the lower leg, while anterior shin splints occur on the front of the lower leg.
Causes of Shin Splints
The causes of shin splints are diverse and can include: * Overuse or repetitive stress on the muscles, tendons, and bone tissue in the lower leg * Sudden changes in exercise intensity or frequency * Inadequate footwear or poor running or walking techniques * Flat feet or other foot abnormalities * Inadequate warm-up or cool-down routines * Insufficient stretching or failing to incorporate rest days into a training schedule * Poor biomechanics, such as overpronation or supinationTreatment Options for Shin Splints
Treatment for shin splints typically involves a combination of rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). This can help reduce pain and inflammation and promote healing. Additionally, individuals with shin splints may need to modify their exercise routine to avoid exacerbating the condition. This can include reducing the frequency or intensity of workouts, incorporating low-impact activities, or taking regular breaks to rest and stretch.
Exercises for Shin Splints
Certain exercises can help alleviate the symptoms of shin splints and promote healing. These include: * Calf stretches: Stand facing a wall with one hand on the wall for balance. Step one foot back about a foot and a half, keeping your heel on the ground. Slowly bend your front knee, keeping your back leg straight, until you feel a stretch in your calf. Hold for 15-30 seconds and repeat on the other side. * Toe raises: Stand on the edge of a stair or curb with your heels hanging off the edge. Slowly raise up onto your tiptoes and then lower back down. Repeat for 10-15 repetitions. * Ankle circles: Sit on the floor with your legs straight out in front of you. Lift one foot off the ground and draw circles with your ankle, starting from small circles and gradually increasing in size. Repeat on the other side.Prevention Strategies for Shin Splints
Preventing shin splints requires a combination of proper training techniques, adequate footwear, and regular stretching and strengthening exercises. Individuals can reduce their risk of developing shin splints by:
- Gradually increasing exercise intensity and frequency
- Incorporating rest days into their training schedule
- Wearing proper footwear with adequate support and cushioning
- Stretching and strengthening the muscles in the lower leg
- Avoiding overtraining and listening to their body
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When trying to prevent or treat shin splints, there are several common mistakes to avoid. These include: * Ignoring pain or discomfort in the lower leg * Failing to warm up or cool down properly * Not incorporating rest days into a training schedule * Wearing inadequate footwear or failing to replace shoes regularly * Not stretching or strengthening the muscles in the lower legRehabilitation and Recovery

Rehabilitation and recovery from shin splints require patience and a gradual approach. Individuals should avoid activities that exacerbate the condition and focus on low-impact exercises, such as cycling or swimming. As the condition improves, individuals can gradually introduce higher-impact activities, such as running or jumping. It's essential to listen to your body and not push yourself too hard, as this can lead to further injury or prolonged recovery.
Returning to Activity
When returning to activity after a shin splint injury, it's essential to do so gradually. This can involve: * Starting with low-impact activities, such as cycling or swimming * Gradually introducing higher-impact activities, such as running or jumping * Incorporating strengthening and stretching exercises to promote healing and prevent further injury * Listening to your body and not pushing yourself too hardConclusion and Final Thoughts

In conclusion, shin splints are a common condition that can be debilitating and affect an individual's quality of life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for shin splints is essential for effective management and prevention. By incorporating proper training techniques, adequate footwear, and regular stretching and strengthening exercises, individuals can reduce their risk of developing shin splints. If you're experiencing pain or discomfort in your lower leg, don't hesitate to seek medical attention and take the necessary steps to promote healing and recovery.
We invite you to share your experiences with shin splints in the comments below. Have you ever suffered from shin splints? What treatments or prevention strategies have you found most effective? Share your thoughts and help others who may be struggling with this condition.
What are the most common causes of shin splints?
+Shin splints are often caused by overuse or repetitive stress on the muscles, tendons, and bone tissue in the lower leg. This can occur due to sudden changes in exercise intensity or frequency, inadequate footwear, or poor running or walking techniques.
How can I prevent shin splints?
+To prevent shin splints, it's essential to incorporate proper training techniques, adequate footwear, and regular stretching and strengthening exercises. Individuals should also listen to their body and avoid overtraining.
What are the best treatment options for shin splints?
+Treatment for shin splints typically involves a combination of rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). Additionally, individuals may need to modify their exercise routine to avoid exacerbating the condition and incorporate strengthening and stretching exercises to promote healing.
