Intro
Learn about 5 fever temperatures, understanding normal, low-grade, and high-grade fevers, including symptoms, treatments, and when to seek medical help for infants, children, and adults with high body temperatures and related health conditions.
Fever is a common symptom that can affect anyone, regardless of age or health status. It is characterized by an elevated body temperature, usually above 98.6°F (37°C), and can be caused by a variety of factors, including infections, inflammation, and environmental factors. Understanding fever temperatures is crucial for determining the severity of the condition and providing appropriate treatment. In this article, we will delve into the world of fever temperatures, exploring their importance, types, and implications for our health.
The human body has a complex thermoregulatory system that helps maintain a stable internal temperature. When this system is disrupted, the body's temperature can rise, leading to a fever. Fever is not a disease in itself but rather a symptom of an underlying condition. It can be a sign of the body's immune response to an infection, such as a bacterial or viral infection, or a reaction to a vaccine or medication. In some cases, fever can be a sign of a more serious condition, such as a life-threatening infection or a chronic disease.
Fever temperatures can vary greatly, ranging from mild to severe. Mild fevers are typically characterized by a temperature of 100°F (37.8°C) to 102°F (39°C), while moderate fevers range from 102°F (39°C) to 104°F (40°C). Severe fevers, on the other hand, can reach temperatures above 104°F (40°C) and can be life-threatening if left untreated. Understanding the different types of fever temperatures is essential for providing proper care and treatment.
Types of Fever Temperatures
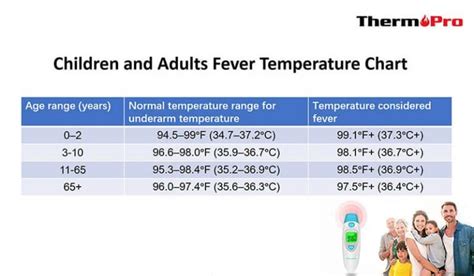
There are several types of fever temperatures, each with its unique characteristics and implications. Continuous fever, for example, is characterized by a persistent elevation in body temperature, usually above 103°F (39.4°C). This type of fever is often seen in patients with bacterial infections, such as pneumonia or meningitis. Remittent fever, on the other hand, is marked by a fluctuating body temperature, with periods of normal temperature interspersed with episodes of fever. Intermittent fever, as the name suggests, is characterized by periods of fever followed by periods of normal temperature.
Continuous Fever
Continuous fever is a type of fever that persists for an extended period, usually 24 hours or more. This type of fever is often seen in patients with severe infections, such as sepsis or meningitis. Continuous fever can be caused by a variety of factors, including bacterial or viral infections, and can be treated with antibiotics or antiviral medications.Remittent Fever
Remittent fever is a type of fever that is characterized by a fluctuating body temperature. This type of fever is often seen in patients with chronic infections, such as tuberculosis or brucellosis. Remittent fever can be caused by a variety of factors, including bacterial or viral infections, and can be treated with antibiotics or antiviral medications.Causes of Fever Temperatures
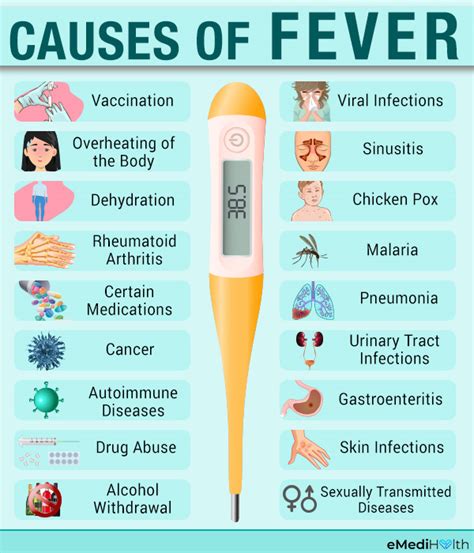
Fever temperatures can be caused by a variety of factors, including infections, inflammation, and environmental factors. Infections, such as bacterial or viral infections, are the most common cause of fever temperatures. These infections can be caused by a variety of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Inflammation, on the other hand, can be caused by a variety of factors, including injury, surgery, or chronic diseases such as arthritis.
Some common causes of fever temperatures include:
- Infections, such as pneumonia, meningitis, or sepsis
- Inflammation, such as arthritis or injury
- Environmental factors, such as heatstroke or hypothermia
- Medications, such as antibiotics or vaccines
- Chronic diseases, such as cancer or HIV/AIDS
Infections
Infections are the most common cause of fever temperatures. These infections can be caused by a variety of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Bacterial infections, such as pneumonia or meningitis, can cause severe fever temperatures and can be life-threatening if left untreated. Viral infections, such as influenza or HIV, can also cause fever temperatures and can be treated with antiviral medications.Inflammation
Inflammation is another common cause of fever temperatures. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including injury, surgery, or chronic diseases such as arthritis. Inflammation can cause the body's temperature to rise, leading to a fever. This type of fever is often treated with anti-inflammatory medications, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen.Treatment of Fever Temperatures

The treatment of fever temperatures depends on the underlying cause of the fever. Infections, such as bacterial or viral infections, can be treated with antibiotics or antiviral medications. Inflammation, on the other hand, can be treated with anti-inflammatory medications, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen. Environmental factors, such as heatstroke or hypothermia, can be treated by addressing the underlying cause of the condition.
Some common treatments for fever temperatures include:
- Antibiotics, such as penicillin or amoxicillin
- Antiviral medications, such as oseltamivir or zanamivir
- Anti-inflammatory medications, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen
- Rest and hydration, to help the body recover from the underlying condition
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are commonly used to treat bacterial infections, such as pneumonia or meningitis. These medications work by killing the bacteria that are causing the infection, thereby reducing the fever and other symptoms. Antibiotics can be prescribed by a doctor and should be taken as directed to ensure effective treatment.Antiviral Medications
Antiviral medications, such as oseltamivir or zanamivir, are commonly used to treat viral infections, such as influenza or HIV. These medications work by reducing the replication of the virus, thereby reducing the fever and other symptoms. Antiviral medications can be prescribed by a doctor and should be taken as directed to ensure effective treatment.Prevention of Fever Temperatures
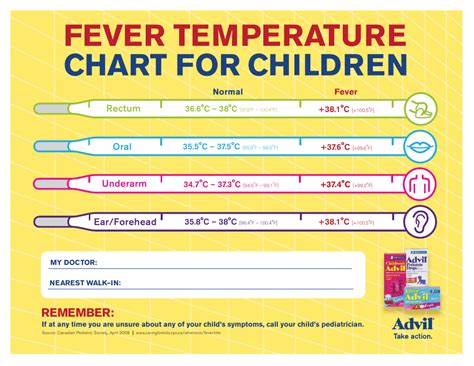
Preventing fever temperatures is crucial for maintaining good health. There are several ways to prevent fever temperatures, including practicing good hygiene, getting vaccinated, and avoiding close contact with people who are sick. Good hygiene, such as washing hands regularly and covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, can help prevent the spread of infections.
Some common ways to prevent fever temperatures include:
- Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands regularly and covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing
- Getting vaccinated, to prevent infections such as influenza or pneumococcal disease
- Avoiding close contact with people who are sick, to prevent the spread of infections
- Staying hydrated, to help the body recover from illness
Good Hygiene
Good hygiene is essential for preventing the spread of infections. This can be achieved by washing hands regularly, covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, and avoiding close contact with people who are sick. Good hygiene can help prevent the spread of infections, thereby reducing the risk of fever temperatures.Vaccination
Vaccination is another effective way to prevent fever temperatures. Vaccines work by stimulating the body's immune system to produce antibodies, which can help fight off infections. Vaccines can be administered to prevent infections such as influenza, pneumococcal disease, or meningitis.Complications of Fever Temperatures

Fever temperatures can lead to several complications, including dehydration, seizures, and organ damage. Dehydration can occur when the body loses too much fluid, either through sweating or vomiting. Seizures can occur when the body's temperature rises too high, causing damage to the brain. Organ damage can occur when the body's temperature rises too high, causing damage to organs such as the kidneys or liver.
Some common complications of fever temperatures include:
- Dehydration, which can occur when the body loses too much fluid
- Seizures, which can occur when the body's temperature rises too high
- Organ damage, which can occur when the body's temperature rises too high
- Brain damage, which can occur when the body's temperature rises too high
Dehydration
Dehydration is a common complication of fever temperatures. This can occur when the body loses too much fluid, either through sweating or vomiting. Dehydration can be treated by drinking plenty of fluids, such as water or electrolyte-rich beverages.Seizures
Seizures are a serious complication of fever temperatures. This can occur when the body's temperature rises too high, causing damage to the brain. Seizures can be treated with anticonvulsant medications, such as phenytoin or valproate.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

In conclusion, fever temperatures are a common symptom that can affect anyone, regardless of age or health status. Understanding the different types of fever temperatures, their causes, and treatment options is crucial for providing proper care and treatment. By practicing good hygiene, getting vaccinated, and avoiding close contact with people who are sick, we can reduce the risk of fever temperatures and prevent complications. If you or someone you know is experiencing fever temperatures, it is essential to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause and receive proper treatment.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with fever temperatures in the comments below. Have you or someone you know experienced fever temperatures? What were the causes and treatment options? Share your story and help others understand the importance of fever temperatures.
What is a normal body temperature?
+A normal body temperature is typically around 98.6°F (37°C), but it can vary slightly from person to person.
What are the common causes of fever temperatures?
+The common causes of fever temperatures include infections, inflammation, and environmental factors, such as heatstroke or hypothermia.
How can I prevent fever temperatures?
+You can prevent fever temperatures by practicing good hygiene, getting vaccinated, and avoiding close contact with people who are sick.
What are the complications of fever temperatures?
+The complications of fever temperatures include dehydration, seizures, and organ damage, which can occur when the body's temperature rises too high.
How can I treat fever temperatures?
+You can treat fever temperatures by using antibiotics, antiviral medications, or anti-inflammatory medications, depending on the underlying cause of the fever.
