Intro
Discover the 5 common causes of cough, including respiratory infections, allergies, and acid reflux, and learn how to manage symptoms with effective treatments and home remedies for a persistent cough.
Coughing is a common symptom that can be caused by a variety of factors, ranging from minor irritations to serious health conditions. It's a natural reflex that helps to clear the airways of mucus, dust, and other foreign particles. However, when coughing persists or is accompanied by other symptoms, it can be a sign of an underlying issue that needs attention. Understanding the causes of coughing is essential to providing effective treatment and relief.
A cough can be acute or chronic, with acute coughs lasting less than three weeks and chronic coughs persisting for more than eight weeks. The duration and characteristics of a cough can provide clues about its cause. For instance, a dry, hacking cough may indicate a viral infection, while a cough that produces mucus could be a sign of a bacterial infection or allergies.
The importance of identifying the cause of a cough cannot be overstated. Not only can it lead to more effective treatment, but it can also help prevent complications, especially in vulnerable populations such as the elderly, young children, and people with compromised immune systems. By understanding the underlying cause, individuals can take steps to manage their symptoms, prevent the spread of infection, and seek medical attention if necessary.
Respiratory Infections
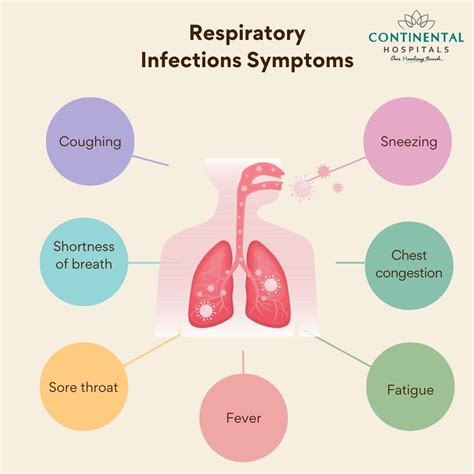
Viral vs. Bacterial Infections
It's crucial to differentiate between viral and bacterial infections, as the treatment approaches can vary significantly. Viral infections typically do not require antibiotics and may be managed with rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications to alleviate symptoms. Bacterial infections, on the other hand, may necessitate antibiotic treatment to prevent complications and promote recovery.Allergies and Asthma
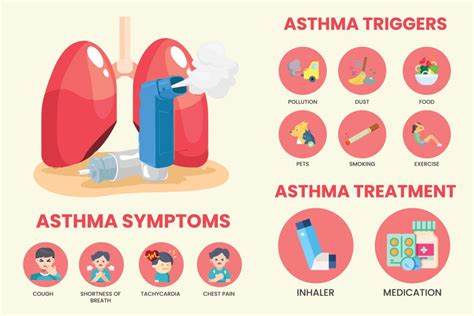
Managing Allergies and Asthma
Managing allergies and asthma involves avoiding triggers, using medications as prescribed, and monitoring symptoms. For allergies, this might include avoiding exposure to known allergens, using nasal corticosteroids, or taking antihistamines. For asthma, treatment typically involves a combination of long-term control medications (such as inhaled corticosteroids) and quick-relief medications (like bronchodilators) to manage symptoms and prevent exacerbations.Environmental Factors

Reducing Exposure
Reducing exposure to environmental irritants is key to preventing coughing caused by these factors. This can involve avoiding smoking and secondhand smoke, using air purifiers in the home, and taking measures to reduce exposure to pollutants in the workplace. In areas with high levels of air pollution, wearing masks and staying indoors when pollution levels are high can help minimize exposure.Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
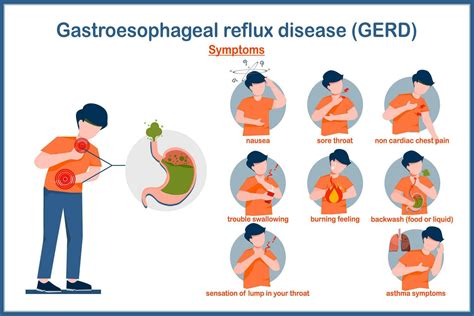
Managing GERD
Managing GERD typically involves lifestyle changes and medication. Dietary adjustments, such as avoiding trigger foods, eating smaller meals, and avoiding lying down after eating, can help reduce symptoms. Over-the-counter or prescription medications, including antacids, histamine-2 (H2) blockers, and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), can also help alleviate symptoms by reducing acid production in the stomach.Other Causes

Seeking Medical Attention
It's essential to seek medical attention if a cough persists, worsens over time, or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms such as fever, chest pain, or difficulty breathing. A healthcare provider can perform a physical examination, take a thorough medical history, and order diagnostic tests (such as chest X-rays or pulmonary function tests) to determine the underlying cause of the cough.What are the most common causes of coughing?
+The most common causes of coughing include respiratory infections, allergies, asthma, environmental factors, and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
How can I differentiate between a viral and bacterial infection?
+Viral infections typically do not require antibiotics and may be managed with rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications. Bacterial infections may necessitate antibiotic treatment. A healthcare provider can perform tests to determine the type of infection.
What are the symptoms of GERD that can lead to coughing?
+GERD can cause a dry, persistent cough, especially at night or after eating, along with other symptoms such as heartburn, difficulty swallowing, and chest pain.
In summary, coughing can be caused by a wide range of factors, from minor irritations to serious health conditions. Understanding the underlying cause is crucial for providing effective treatment and relief. By recognizing the signs and symptoms associated with different causes and seeking medical attention when necessary, individuals can manage their cough and prevent potential complications. We invite readers to share their experiences with coughing, ask questions about the causes and treatments discussed, and explore further resources for managing respiratory health. Whether you're looking for ways to alleviate symptoms or seeking a deeper understanding of the mechanisms behind coughing, we hope this article has provided valuable insights and encouragement to prioritize your health.
