Intro
Discover the causes of goiter, including iodine deficiency, thyroid disorders, and autoimmune diseases, to understand this swollen thyroid gland condition and its related symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
The thyroid gland plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, including metabolism, growth, and development. However, when the thyroid gland becomes enlarged, it can lead to a condition known as goiter. Goiter is a common health issue that affects millions of people worldwide, and it is essential to understand its causes to develop effective prevention and treatment strategies. In this article, we will delve into the various causes of goiter, exploring the underlying factors that contribute to the development of this condition.
Goiter can be caused by a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. One of the primary causes of goiter is iodine deficiency, which is a significant public health concern in many parts of the world. Iodine is an essential nutrient that plays a critical role in the production of thyroid hormones, and its deficiency can lead to an increase in the size of the thyroid gland. Other causes of goiter include thyroid nodules, thyroiditis, and certain medications. Additionally, goiter can be caused by genetic disorders, such as Pendred syndrome, which affects the thyroid gland's ability to produce hormones.
The importance of understanding the causes of goiter cannot be overstated. By identifying the underlying factors that contribute to the development of this condition, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent goiter and reduce their risk of developing related health issues. Furthermore, understanding the causes of goiter can help healthcare professionals develop effective treatment strategies, which can improve patient outcomes and quality of life. In the following sections, we will explore the causes of goiter in more detail, examining the various factors that contribute to the development of this condition.
Introduction to Goiter

Types of Goiter
There are several types of goiter, each with distinct causes and characteristics. The most common types of goiter include: * Simple goiter: This type of goiter is caused by iodine deficiency and is characterized by an enlarged thyroid gland. * Toxic goiter: This type of goiter is caused by an overproduction of thyroid hormones and can lead to symptoms such as weight loss, anxiety, and palpitations. * Nontoxic goiter: This type of goiter is caused by a variety of factors, including thyroid nodules, thyroiditis, and certain medications.Causes of Goiter

Iodine Deficiency
Iodine deficiency is a significant public health concern in many parts of the world and is a primary cause of goiter. Iodine is an essential nutrient that plays a critical role in the production of thyroid hormones, and its deficiency can lead to an increase in the size of the thyroid gland. Iodine deficiency can be caused by a variety of factors, including a diet that is low in iodine, lack of access to iodized salt, and certain environmental factors.Symptoms of Goiter
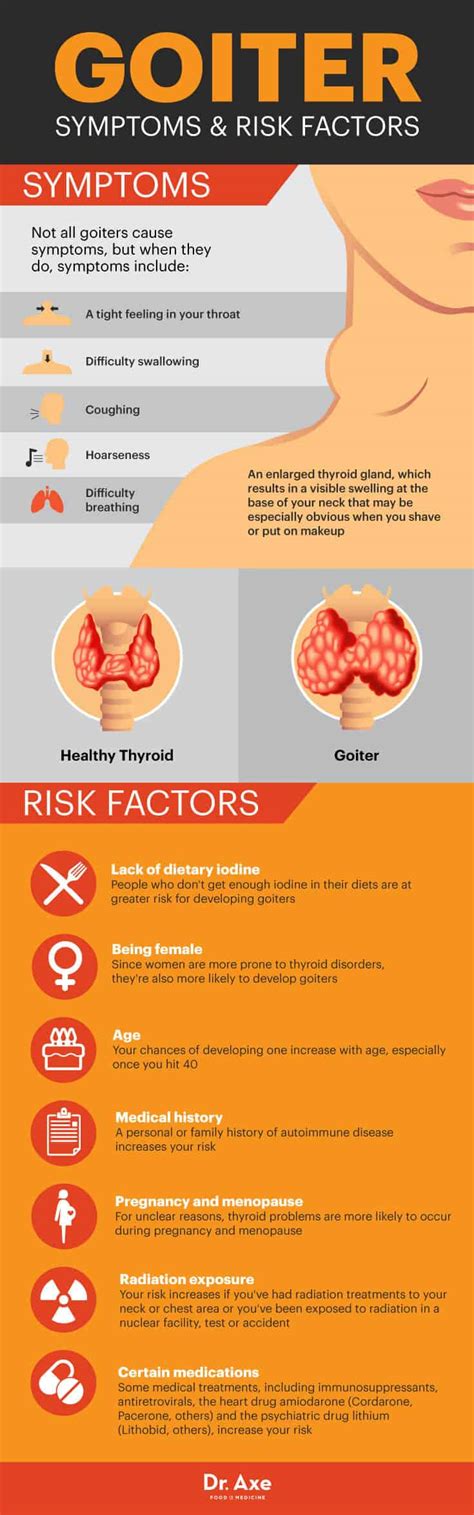
Diagnosis of Goiter
The diagnosis of goiter typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and a range of diagnostic tests. The diagnostic tests used to diagnose goiter include: * Thyroid function tests: These tests measure the levels of thyroid hormones in the blood. * Thyroid ultrasound: This test uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of the thyroid gland. * Thyroid scan: This test uses a small amount of radioactive material to produce images of the thyroid gland.Treatment of Goiter

Prevention of Goiter
Preventing goiter requires a combination of dietary and lifestyle changes. Some ways to prevent goiter include: * Eating a diet that is rich in iodine: Iodine is an essential nutrient that plays a critical role in the production of thyroid hormones. * Using iodized salt: Iodized salt is a good source of iodine and can help to prevent iodine deficiency. * Avoiding certain environmental toxins: Certain environmental toxins, such as perchlorates, can interfere with the production of thyroid hormones.Complications of Goiter
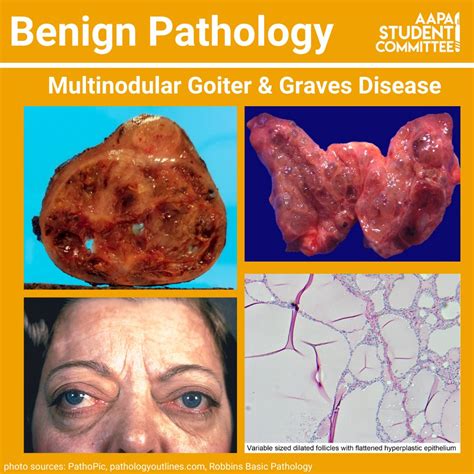
Living with Goiter
Living with goiter requires a combination of dietary and lifestyle changes. Some ways to manage goiter include: * Eating a healthy diet: A healthy diet that is rich in iodine and other essential nutrients can help to manage goiter. * Getting regular exercise: Regular exercise can help to improve overall health and reduce the risk of complications associated with goiter. * Managing stress: Stress can exacerbate goiter, and managing stress through techniques such as meditation and yoga can help to reduce symptoms.What are the symptoms of goiter?
+The symptoms of goiter include swelling in the neck, difficulty swallowing, shortness of breath, coughing, and hoarseness.
How is goiter diagnosed?
+Goiter is typically diagnosed through a physical examination, medical history, and a range of diagnostic tests, including thyroid function tests, thyroid ultrasound, and thyroid scan.
Can goiter be prevented?
+Yes, goiter can be prevented through a combination of dietary and lifestyle changes, including eating a diet that is rich in iodine, using iodized salt, and avoiding certain environmental toxins.
In conclusion, goiter is a common health issue that affects millions of people worldwide. Understanding the causes of goiter is essential for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies. By identifying the underlying factors that contribute to the development of this condition, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent goiter and reduce their risk of developing related health issues. We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with goiter in the comments section below. Additionally, we encourage readers to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about goiter and its causes. By working together, we can raise awareness about this important health issue and promote healthy living practices that can help to prevent goiter and other related health conditions.
