Intro
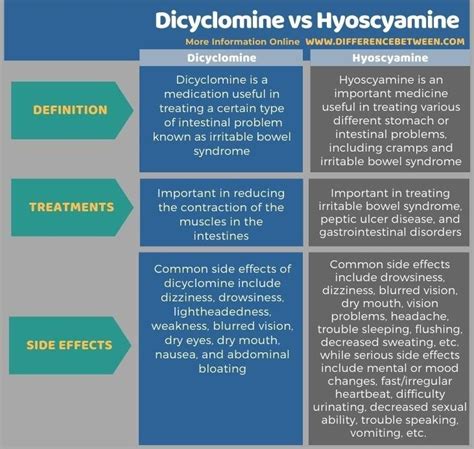
Dicyclomine uses include treating irritable bowel syndrome, relieving muscle spasms, and reducing gastrointestinal cramps, with effects including smooth muscle relaxation and anti-cholinergic benefits.
Dicyclomine is a medication that has been widely used for several decades to treat various gastrointestinal disorders. Its effectiveness in relieving symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), functional bowel disorders, and other conditions has made it a popular choice among healthcare providers. However, like any medication, dicyclomine has its own set of uses, effects, and potential side effects that need to be understood to ensure safe and effective use.
The importance of understanding dicyclomine's uses and effects cannot be overstated. With the rising incidence of gastrointestinal disorders, it is essential to have a comprehensive knowledge of the available treatment options. Dicyclomine, in particular, has been shown to be effective in managing symptoms of IBS, which affects millions of people worldwide. By exploring the uses and effects of dicyclomine, individuals can make informed decisions about their treatment and work closely with their healthcare providers to achieve optimal results.
As a medication, dicyclomine has a unique mechanism of action that sets it apart from other treatments. Its ability to relax the muscles in the gastrointestinal tract and reduce spasms makes it an effective option for relieving symptoms of IBS, functional bowel disorders, and other conditions. Moreover, dicyclomine has been shown to have a positive impact on the quality of life of individuals with these conditions, allowing them to manage their symptoms and engage in daily activities with greater ease. With its proven track record and relatively low risk of side effects, dicyclomine has become a valuable tool in the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders.
Dicyclomine Mechanism of Action

Dicyclomine Uses

Dicyclomine Benefits
The benefits of using dicyclomine are numerous. Some of the most significant advantages include: * Rapid relief from symptoms: Dicyclomine can provide quick relief from symptoms of IBS and other gastrointestinal disorders, making it an effective option for individuals who need fast and reliable relief. * Improved quality of life: By reducing symptoms of gastrointestinal disorders, dicyclomine can improve the quality of life of individuals with these conditions, allowing them to engage in daily activities with greater ease. * Low risk of side effects: Dicyclomine has a relatively low risk of side effects, making it a safe and effective option for individuals who are sensitive to medications.Dicyclomine Side Effects

Dicyclomine Interactions
Dicyclomine can interact with other medications, including: * Antihistamines * Sedatives * Tranquilizers * Muscle relaxants * Anticholinergic medications It is essential to inform a healthcare provider about all medications being taken, including prescription and over-the-counter medications, to minimize the risk of interactions.Dicyclomine Dosage

Dicyclomine Administration
Dicyclomine can be administered orally, usually in the form of tablets or capsules. It is essential to take the medication as directed and not to crush or chew the tablets, as this can affect the release of the medication.Dicyclomine Contraindications
Dicyclomine Warnings
Dicyclomine can cause drowsiness and dizziness, and individuals taking the medication should avoid operating heavy machinery or engaging in activities that require alertness. Additionally, dicyclomine can cause dry mouth, and individuals should drink plenty of water to stay hydrated.Dicyclomine Overdose

Dicyclomine Toxicity
Dicyclomine toxicity can occur if the medication is taken in excess or for an extended period. Symptoms of toxicity may include: * Severe dry mouth * Blurred vision * Urinary retention * Constipation * Abdominal painDicyclomine Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Dicyclomine Pediatric Use
Dicyclomine is not recommended for use in children under the age of 6 months. In children over 6 months, the medication should be used with caution and under close supervision of a healthcare provider.Dicyclomine Geriatric Use

Dicyclomine Special Populations
Dicyclomine can be used in individuals with renal or hepatic impairment, but with caution. The dosage may need to be adjusted accordingly, and individuals should be closely monitored for signs of toxicity.What is dicyclomine used for?
+Dicyclomine is used to treat various gastrointestinal disorders, including irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), functional bowel disorders, and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
What are the common side effects of dicyclomine?
+The common side effects of dicyclomine include dry mouth, dizziness, drowsiness, blurred vision, constipation, and urinary retention.
Can dicyclomine be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding?
+Dicyclomine is classified as a Category B medication, which means that it is generally considered safe for use during pregnancy. However, individuals should consult a healthcare provider before taking the medication, especially during the first trimester. Dicyclomine is also excreted in breast milk, and individuals should consult a healthcare provider before breastfeeding while taking the medication.
What is the recommended dosage of dicyclomine?
+The typical dosage range of dicyclomine is 10-20 mg orally, three to four times a day, or as needed.
Can dicyclomine interact with other medications?
+Yes, dicyclomine can interact with other medications, including antihistamines, sedatives, tranquilizers, muscle relaxants, and anticholinergic medications. Individuals should inform their healthcare provider about all medications being taken, including prescription and over-the-counter medications, to minimize the risk of interactions.
In conclusion, dicyclomine is a valuable medication for the treatment of various gastrointestinal disorders. Its unique mechanism of action, benefits, and relatively low risk of side effects make it a popular choice among healthcare providers. By understanding the uses and effects of dicyclomine, individuals can make informed decisions about their treatment and work closely with their healthcare providers to achieve optimal results. We invite readers to share their experiences with dicyclomine and provide feedback on this article. Additionally, we encourage readers to explore other resources and consult with healthcare professionals to learn more about dicyclomine and its uses.
