Intro
Discover 5 ways fiber helps boost digestive health, promoting regular bowel movements, healthy gut bacteria, and satiety, while supporting weight management and lowering cholesterol levels, with dietary fibers numerous benefits.
The importance of dietary fiber cannot be overstated. With the rise of modern diets that often prioritize convenience and taste over nutritional value, it's easy to overlook the crucial role that fiber plays in maintaining our overall health. However, incorporating sufficient amounts of fiber into our daily meals can have a profound impact on both our short-term wellbeing and long-term health outcomes. From supporting healthy digestion to aiding in weight management, the benefits of fiber are multifaceted and significant. As we delve into the ways in which fiber helps, it becomes clear that making fiber a priority is not just a good idea, but a necessity for living a healthy and balanced lifestyle.
Fiber is often misunderstood as merely a component that helps with bowel movements, but its influence extends far beyond the realm of digestive health. It plays a critical role in managing blood sugar levels, supporting healthy cholesterol levels, and even influencing our mental health. The versatility of fiber in contributing to various aspects of our health makes it an essential nutrient that should be at the forefront of our dietary considerations. Whether you're looking to improve your current health status or prevent future health issues, understanding the benefits of fiber is a crucial step in the right direction.
As we explore the ways in which fiber contributes to our health, it's essential to recognize the different types of fiber and how they can be incorporated into our diets. Soluble fiber, for example, dissolves in water and forms a gel-like substance that can help lower cholesterol levels and regulate blood sugar levels. Insoluble fiber, on the other hand, does not dissolve in water and instead helps add bulk to stool and promote regular bowel movements. Both types are vital for maintaining a healthy digestive system and overall wellbeing. By focusing on whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, we can ensure that we're getting a balanced mix of both soluble and insoluble fiber.
Introduction to Fiber Benefits

Understanding the benefits of fiber is the first step towards making informed dietary choices. One of the most significant advantages of a high-fiber diet is its ability to support healthy digestion. Fiber acts as a bulking agent, helping to prevent constipation by making stools softer and easier to pass. This can lead to a reduction in the risk of hemorrhoids and diverticulitis, conditions that are often associated with straining during bowel movements. Furthermore, a diet rich in fiber can help support the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, which play a crucial role in our immune system and overall health.
Types of Fiber
The distinction between soluble and insoluble fiber is not just a matter of classification; it has real implications for our health. Soluble fiber, found in foods like oats, barley, and fruits, can help lower cholesterol levels by binding to bile acids and removing them from the body, which in turn reduces the amount of cholesterol produced in the liver. Insoluble fiber, found in whole grains, vegetables, and legumes, adds bulk to stool and helps food move through the digestive system, reducing the risk of constipation and associated disorders.Fiber and Digestive Health

The impact of fiber on digestive health cannot be overstated. A high-fiber diet has been shown to reduce the risk of developing diverticulitis, a condition characterized by the formation of small, bulging pouches in the digestive tract. Additionally, fiber helps prevent constipation, a common issue that can lead to discomfort, pain, and more serious health complications if left untreated. The benefits of fiber on digestive health are a compelling reason to prioritize whole, unprocessed foods in our diets.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels
One of the lesser-known benefits of fiber is its ability to help manage blood sugar levels. Soluble fiber, in particular, can slow down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, which can help regulate blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. This is especially beneficial for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. By incorporating foods high in soluble fiber into their diets, individuals can better manage their blood sugar levels and reduce their risk of complications associated with diabetes.Fiber and Weight Management

Fiber also plays a significant role in weight management. High-fiber foods tend to be more filling, which can lead to a reduction in overall calorie intake. This is because fiber takes longer to digest than other nutrients, keeping us feeling fuller for longer. Additionally, many high-fiber foods are also rich in nutrients and low in calories, making them an excellent choice for those looking to lose weight or maintain a healthy weight. By prioritizing fiber-rich foods, individuals can develop healthier eating habits that support their weight management goals.
Supporting Healthy Cholesterol Levels
The ability of soluble fiber to help lower cholesterol levels is another significant benefit. By binding to bile acids and removing them from the body, soluble fiber can help reduce the amount of cholesterol produced in the liver. This can lead to a decrease in LDL (bad) cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of heart disease. Foods rich in soluble fiber, such as oats and barley, can be particularly beneficial for individuals looking to manage their cholesterol levels through dietary changes.Fiber and Mental Health
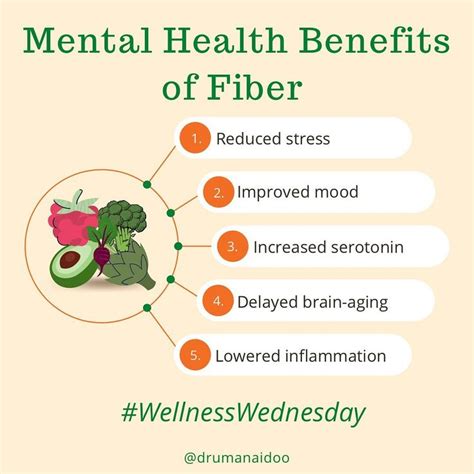
The connection between fiber and mental health is an area of growing research interest. The gut-brain axis, which refers to the bidirectional communication network between the central nervous system and the enteric nervous system of the gut, plays a crucial role in our mental wellbeing. A diet rich in fiber can support the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, which produce neurotransmitters and hormones that influence our mood and cognitive function. This suggests that a high-fiber diet may have a positive impact on mental health, potentially reducing the risk of depression and anxiety.
Practical Tips for Increasing Fiber Intake
Incorporating more fiber into our diets can seem daunting, but there are several practical steps we can take. Starting the day with a high-fiber breakfast, such as oatmeal with fruit or whole-grain toast with avocado, can set us up for success. Snacking on fruits, vegetables, and nuts throughout the day can also help meet our daily fiber needs. When cooking, choosing whole grains over refined grains and adding legumes to meals can significantly boost fiber intake. Even small changes, such as switching from white rice to brown rice, can make a difference over time.Conclusion and Next Steps
As we conclude our exploration of the ways in which fiber helps, it's clear that prioritizing fiber intake is essential for maintaining overall health and wellbeing. Whether through supporting digestive health, aiding in weight management, or influencing mental health, the benefits of fiber are undeniable. By making informed dietary choices and incorporating more whole, fiber-rich foods into our meals, we can take a proactive approach to our health. As research continues to uncover the complexities of fiber's role in our health, one thing is certain: a high-fiber diet is a key component of a healthy and balanced lifestyle.
What are the main types of fiber?
+There are two main types of fiber: soluble and insoluble. Soluble fiber dissolves in water and can help lower cholesterol levels and regulate blood sugar levels, while insoluble fiber does not dissolve in water and helps add bulk to stool and promote regular bowel movements.
How much fiber should I consume daily?
+The daily recommended intake of fiber varies by age and sex, but a general guideline is to consume at least 25-30 grams of fiber per day. However, many health professionals recommend aiming for even higher intakes, up to 35-40 grams per day, for optimal health benefits.
What are some high-fiber foods?
+High-fiber foods include fruits like apples and bananas, vegetables like broccoli and carrots, whole grains like brown rice and quinoa, and legumes like beans and lentils. Nuts and seeds, such as almonds and chia seeds, are also good sources of fiber.
We invite you to share your thoughts on the importance of fiber in your diet and any tips you might have for incorporating more fiber-rich foods into your meals. Your experiences and insights can help others on their journey to better health and wellbeing. Whether you're just starting to explore the benefits of fiber or are a long-time advocate for high-fiber diets, your voice matters. Let's work together to prioritize fiber and cultivate healthier, happier lives.
