Intro
Discover what high bun means in medical terms, including elevated BUN levels, causes, and symptoms, and learn how to lower blood urea nitrogen for optimal kidney health and function.
Elevated bun levels in blood tests can be a cause for concern for many individuals. Understanding what high bun means and its implications on our health is essential for taking proactive steps towards managing and mitigating potential risks. The bun, or blood urea nitrogen, test is a crucial diagnostic tool that measures the amount of urea in our blood. Urea is a waste product produced by our kidneys as they filter and remove toxins from our bloodstream.
High bun levels can indicate that our kidneys are not functioning optimally, which can be a sign of underlying kidney disease or other health issues. It is essential to understand the significance of bun levels and how they relate to our overall health and well-being. By exploring the topic of high bun in depth, we can better comprehend the importance of maintaining healthy kidney function and the steps we can take to prevent or manage conditions that may affect our kidneys.
The importance of understanding high bun levels cannot be overstated, as it can have significant implications for our long-term health. By educating ourselves on the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for high bun, we can take a proactive approach to managing our health and preventing potential complications. Whether you are concerned about your own bun levels or are simply looking to learn more about this critical aspect of our health, this article aims to provide a comprehensive and informative guide to help you navigate the complex world of kidney health and high bun levels.
What is Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN)
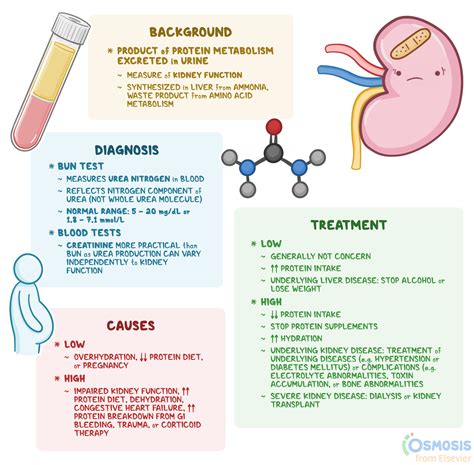
Blood urea nitrogen, or bun, is a waste product that is produced by our kidneys as they filter and remove toxins from our bloodstream. The bun test is a diagnostic tool used to measure the amount of urea in our blood, which can help healthcare professionals assess kidney function and diagnose potential kidney problems. Urea is a byproduct of protein metabolism, and our kidneys play a crucial role in removing excess urea from our body. When our kidneys are functioning properly, they filter waste products, including urea, from our blood and excrete them in our urine.
How is BUN Measured
The bun test is typically performed as part of a comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP), which is a group of tests that measure various components of our blood, including electrolytes, enzymes, and waste products. To measure bun levels, a healthcare professional will collect a blood sample from a vein in our arm, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. The results of the bun test are usually reported in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) and can be used to assess kidney function and diagnose potential kidney problems.Causes of High BUN Levels
High bun levels can be caused by a variety of factors, including kidney disease, dehydration, and certain medications. When our kidneys are not functioning properly, they may not be able to filter waste products, including urea, from our blood effectively, leading to elevated bun levels. Dehydration can also cause high bun levels, as our kidneys need adequate fluids to function properly. Certain medications, such as diuretics and certain antibiotics, can also increase bun levels by affecting kidney function or increasing urea production.
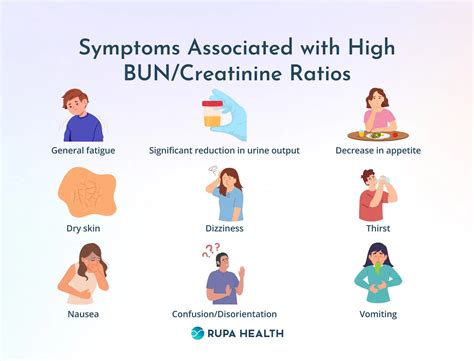
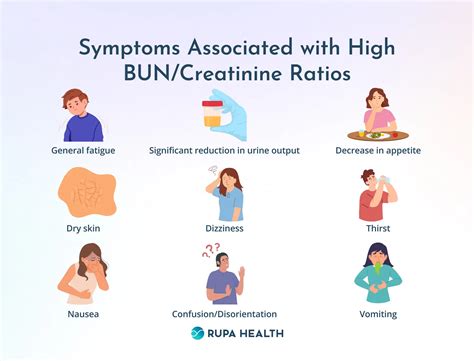
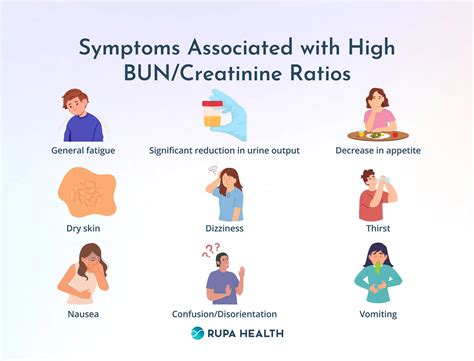
Symptoms of High BUN Levels
The symptoms of high bun levels can vary depending on the underlying cause, but may include fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath. In severe cases, high bun levels can cause more serious symptoms, such as confusion, seizures, and coma. If we are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately, as high bun levels can be a sign of a life-threatening condition.Treatment Options for High BUN Levels
The treatment for high bun levels depends on the underlying cause, but may include medications to manage symptoms, dietary changes to reduce urea production, and dialysis or kidney transplantation in severe cases. In some cases, high bun levels may be treated with medications that help to reduce urea production or improve kidney function. Dietary changes, such as reducing protein intake and increasing fluid consumption, can also help to manage high bun levels. In severe cases, dialysis or kidney transplantation may be necessary to remove waste products from our blood and restore kidney function.
Prevention and Management
Preventing and managing high bun levels requires a comprehensive approach that includes maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, and managing underlying medical conditions. By eating a balanced diet that is low in protein and high in fruits and vegetables, we can help to reduce urea production and manage high bun levels. Staying hydrated is also essential, as our kidneys need adequate fluids to function properly. Managing underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes and high blood pressure, can also help to prevent and manage high bun levels.Complications of High BUN Levels
High bun levels can cause a range of complications, including kidney damage, heart disease, and neurological problems. When our kidneys are not functioning properly, they may not be able to filter waste products from our blood effectively, leading to a buildup of toxins that can damage our kidneys and other organs. High bun levels can also increase the risk of heart disease, as excess urea can damage blood vessels and increase blood pressure. In severe cases, high bun levels can cause neurological problems, such as confusion, seizures, and coma.
Long-Term Effects of High BUN Levels
The long-term effects of high bun levels can be significant, and may include chronic kidney disease, end-stage renal disease, and increased mortality. When our kidneys are not functioning properly, they may not be able to filter waste products from our blood effectively, leading to a buildup of toxins that can damage our kidneys and other organs. Chronic kidney disease can cause a range of symptoms, including fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath, and can increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other complications. In severe cases, high bun levels can cause end-stage renal disease, which requires dialysis or kidney transplantation to manage.Dietary Changes for Managing High BUN Levels
Dietary changes can play a crucial role in managing high bun levels, and may include reducing protein intake, increasing fluid consumption, and eating a balanced diet that is low in sodium and phosphorus. By reducing protein intake, we can help to reduce urea production and manage high bun levels. Increasing fluid consumption can also help to manage high bun levels, as our kidneys need adequate fluids to function properly. Eating a balanced diet that is low in sodium and phosphorus can also help to manage high bun levels, as excess sodium and phosphorus can increase blood pressure and damage our kidneys.
Medications for Managing High BUN Levels
Medications can also play a crucial role in managing high bun levels, and may include diuretics, phosphate binders, and erythropoiesis-stimulating agents. Diuretics can help to increase urine production and reduce fluid buildup in our body, which can help to manage high bun levels. Phosphate binders can help to reduce phosphorus levels in our blood, which can help to manage high bun levels and prevent kidney damage. Erythropoiesis-stimulating agents can help to increase red blood cell production, which can help to manage anemia and fatigue caused by high bun levels.Lifestyle Changes for Managing High BUN Levels
Lifestyle changes can also play a crucial role in managing high bun levels, and may include quitting smoking, reducing stress, and getting regular exercise. Quitting smoking can help to reduce the risk of kidney disease and manage high bun levels, as smoking can damage our kidneys and increase blood pressure. Reducing stress can also help to manage high bun levels, as stress can increase blood pressure and damage our kidneys. Getting regular exercise can also help to manage high bun levels, as exercise can help to improve kidney function and reduce blood pressure.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Monitoring and follow-up are essential for managing high bun levels, and may include regular blood tests, urine tests, and medical check-ups. Regular blood tests can help to monitor bun levels and assess kidney function, while urine tests can help to detect proteinuria and hematuria. Medical check-ups can also help to monitor blood pressure, fluid status, and overall health, and can help to identify any potential complications or side effects of treatment.What is the normal range for BUN levels?
+The normal range for BUN levels is typically between 6 and 24 mg/dL, but this can vary depending on the laboratory and the individual's age, sex, and medical history.
What are the symptoms of high BUN levels?
+The symptoms of high BUN levels can vary depending on the underlying cause, but may include fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, and confusion.
How are high BUN levels treated?
+The treatment for high BUN levels depends on the underlying cause, but may include medications to manage symptoms, dietary changes to reduce urea production, and dialysis or kidney transplantation in severe cases.
In summary, high bun levels can be a sign of underlying kidney disease or other health issues, and it is essential to understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for managing high bun levels. By taking a proactive approach to our health and seeking medical attention if we are experiencing any symptoms of high bun levels, we can help to prevent and manage potential complications and improve our overall health and well-being. We encourage you to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about high bun levels and kidney health, and to comment below with any questions or concerns you may have. By working together, we can help to promote kidney health and reduce the risk of kidney disease and other related complications.
