Intro
Discover how Lisinopril works, an ACE inhibitor, to lower blood pressure, reduce heart failure risk, and manage hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and diabetic nephropathy through its pharmacological effects.
Lisinopril is a medication that has been widely used for decades to treat various cardiovascular conditions, including high blood pressure and heart failure. Its effectiveness and relatively low cost have made it a staple in the treatment of these conditions. But have you ever wondered how lisinopril works? Understanding the mechanisms behind this medication can help you appreciate its benefits and potential side effects. In this article, we will delve into the world of lisinopril and explore the five ways it works to improve cardiovascular health.
The importance of lisinopril cannot be overstated. High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a major risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease. If left untreated, it can lead to serious complications, including heart failure, vision loss, and even death. Lisinopril, an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor, plays a crucial role in managing hypertension and reducing the risk of these complications. By understanding how lisinopril works, you can better appreciate its value in maintaining cardiovascular health.
Lisinopril has been extensively studied, and its mechanisms of action are well understood. It works by blocking the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor that increases blood pressure. This blockade leads to a decrease in blood pressure, which in turn reduces the workload on the heart. But lisinopril's effects don't stop there. It also has anti-inflammatory properties, improves endothelial function, and reduces oxidative stress. These effects contribute to its overall benefits in reducing cardiovascular risk.
How Lisinopril Lowers Blood Pressure
Benefits of ACE Inhibition
The benefits of ACE inhibition are numerous. By reducing the levels of angiotensin II, lisinopril decreases the workload on the heart, reducing the risk of heart failure. Additionally, ACE inhibition improves endothelial function, which helps to maintain healthy blood vessels. This effect is particularly important, as endothelial dysfunction is a key factor in the development of atherosclerosis.The Role of Lisinopril in Heart Failure
Improving Survival Rates
The benefits of lisinopril in heart failure are well established. Studies have shown that ACE inhibitors, such as lisinopril, improve survival rates in individuals with heart failure. This effect is thought to be due to the reduction in workload on the heart, as well as the improvement in endothelial function. By reducing the risk of further complications, lisinopril helps to improve the quality of life for individuals with heart failure.Lisinopril's Anti-Inflammatory Effects

Reducing Oxidative Stress
Lisinopril's anti-inflammatory effects are also thought to reduce oxidative stress, which is a key factor in the development of cardiovascular disease. By reducing the levels of reactive oxygen species, lisinopril helps to maintain healthy blood vessels and reduce the risk of atherosclerosis. This effect is particularly beneficial for individuals with hypertension, as it reduces the risk of cardiovascular complications.The Importance of Endothelial Function
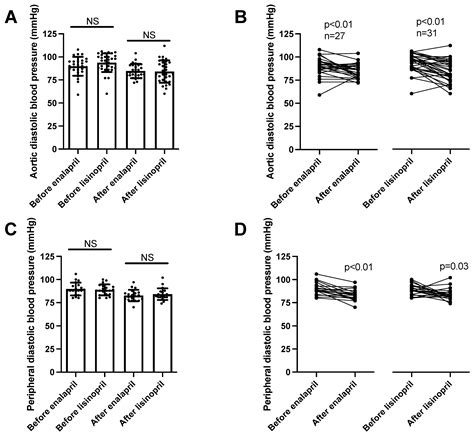
Improving Blood Flow
The improvement in endothelial function is thought to be due to the reduction in levels of angiotensin II, which is a potent vasoconstrictor. By reducing the levels of angiotensin II, lisinopril helps to improve blood flow and reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications. This effect is particularly beneficial for individuals with hypertension, as it reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease.Lisinopril's Effects on Kidney Function

Reducing Proteinuria
Lisinopril's effects on kidney function are also thought to reduce proteinuria, which is a key marker of kidney disease. By reducing the levels of protein in the urine, lisinopril helps to improve kidney function and reduce the risk of kidney disease. This effect is particularly beneficial for individuals with diabetes, as it reduces the risk of kidney disease.What is lisinopril used for?
+Lisinopril is used to treat high blood pressure and heart failure. It works by blocking the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor that increases blood pressure.
How does lisinopril work?
+Lisinopril works by blocking the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, reducing the levels of angiotensin II, and decreasing blood pressure. It also has anti-inflammatory effects, improves endothelial function, and reduces oxidative stress.
What are the benefits of taking lisinopril?
+The benefits of taking lisinopril include reducing blood pressure, improving heart failure symptoms, and reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease. It also has anti-inflammatory effects, improves endothelial function, and reduces oxidative stress.
In conclusion, lisinopril is a vital medication for managing hypertension and heart failure. Its mechanisms of action, including ACE inhibition, anti-inflammatory effects, and improvement in endothelial function, contribute to its overall benefits in reducing cardiovascular risk. By understanding how lisinopril works, you can better appreciate its value in maintaining cardiovascular health. We encourage you to share this article with others who may benefit from this information and to comment below with any questions or concerns you may have. Together, we can work towards improving cardiovascular health and reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
