Intro
Discover Metoprolol uses, effects, and benefits for heart health, including blood pressure control, angina relief, and heart failure management, with insights into dosage, interactions, and side effects.
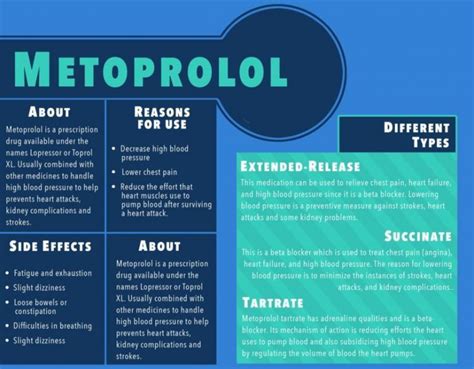
Metoprolol is a medication that has been widely used for decades to treat various cardiovascular conditions. Its importance cannot be overstated, as it has improved the quality of life for millions of people worldwide. The medication belongs to a class of drugs known as beta blockers, which work by slowing the heart rate and reducing blood pressure. This, in turn, decreases the heart's workload and its demand for oxygen, making it an essential treatment for conditions such as angina, heart failure, and high blood pressure.
The significance of metoprolol lies in its ability to manage symptoms, prevent complications, and improve survival rates in patients with cardiovascular disease. By reducing the heart rate and blood pressure, metoprolol helps to alleviate chest pain, shortness of breath, and other symptoms associated with these conditions. Moreover, its effectiveness in preventing heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events has made it a cornerstone in the treatment of patients with a history of heart disease. As a result, understanding the uses and effects of metoprolol is crucial for patients, healthcare providers, and anyone interested in cardiovascular health.
The widespread use of metoprolol has also led to extensive research on its effects, benefits, and potential side effects. Studies have consistently shown that metoprolol is well-tolerated and effective in managing various cardiovascular conditions. However, like any medication, it can cause side effects, some of which may be mild, while others can be more severe. Therefore, it is essential to discuss the uses and effects of metoprolol in detail, including its benefits, working mechanisms, potential side effects, and practical examples of its use in clinical practice.
What is Metoprolol?
How Does Metoprolol Work?
Metoprolol's working mechanism involves the inhibition of beta-1 adrenergic receptors in the heart, which reduces the heart's response to sympathetic stimulation. This leads to a decrease in heart rate, contractility, and blood pressure, resulting in a reduction in the heart's workload and oxygen demand. Additionally, metoprolol has been shown to increase the threshold for ventricular fibrillation, making it an effective treatment for patients with a history of heart attacks.Benefits of Metoprolol

Common Uses of Metoprolol
Metoprolol is commonly used to treat various cardiovascular conditions, including: * Hypertension (high blood pressure) * Angina (chest pain) * Heart failure * Arrhythmias (irregular heart rhythms) * Myocardial infarction (heart attack) * Cardiac surgeryPotential Side Effects of Metoprolol
Severe Side Effects of Metoprolol
In rare cases, metoprolol can cause severe side effects, including: * Allergic reactions and anaphylaxis * Bradycardia (slow heart rate) and hypotension (low blood pressure) * Heart block and cardiac arrest * Worsening of heart failure and angina * Increased risk of stroke and heart attackPractical Examples of Metoprolol Use
Case Studies of Metoprolol Use
Several case studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of metoprolol in managing cardiovascular conditions. For example: * A study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology found that metoprolol reduced the risk of heart attacks and strokes in patients with hypertension. * A study published in the European Heart Journal found that metoprolol improved survival rates and reduced symptoms of heart failure in patients with reduced ejection fraction.FAQs
What is metoprolol used for?
+Metoprolol is used to treat various cardiovascular conditions, including hypertension, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
How does metoprolol work?
+Metoprolol works by blocking the action of epinephrine and norepinephrine on the heart, reducing the heart rate, contractility, and blood pressure.
What are the potential side effects of metoprolol?
+Common side effects of metoprolol include fatigue, dizziness, shortness of breath, and nausea. Severe side effects can include allergic reactions, bradycardia, and heart block.
In conclusion, metoprolol is a widely used and effective medication for managing various cardiovascular conditions. Its benefits, working mechanisms, and potential side effects make it an essential treatment for patients with hypertension, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias. By understanding the uses and effects of metoprolol, patients and healthcare providers can work together to improve cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of complications. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with metoprolol in the comments below and to share this article with anyone who may benefit from this information.
