Intro
Discover what beta blockers are, how they work, and their effects on heart rate, blood pressure, and cardiovascular health, including uses, types, and potential side effects of these medications.
Beta blockers are a type of medication that plays a crucial role in managing various health conditions, particularly those related to the heart and blood vessels. These medications have been widely used for decades to help control high blood pressure, reduce the risk of heart attacks, and alleviate symptoms of anxiety and tremors. The importance of beta blockers lies in their ability to slow down the heart rate and reduce the force of the heart's contractions, thereby decreasing blood pressure and the heart's oxygen demand.
The mechanism of action of beta blockers involves blocking the effects of the hormone epinephrine, also known as adrenaline, and other stress hormones that stimulate the heart. By doing so, beta blockers help to reduce the heart rate, lower blood pressure, and decrease the heart's workload. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals with conditions such as high blood pressure, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias. Moreover, beta blockers have also been shown to be effective in reducing the risk of heart attacks and strokes in people with a history of cardiovascular disease.
The benefits of beta blockers extend beyond their cardiovascular effects, as they can also be used to manage symptoms of anxiety and tremors. For example, beta blockers such as propranolol are often prescribed to help alleviate performance anxiety, stage fright, and other forms of social anxiety. Additionally, beta blockers have been used to treat essential tremors, which are involuntary movements that can affect the hands, arms, and other parts of the body. With their wide range of applications and benefits, it is essential to understand how beta blockers work, their different types, and their potential side effects.
How Beta Blockers Work
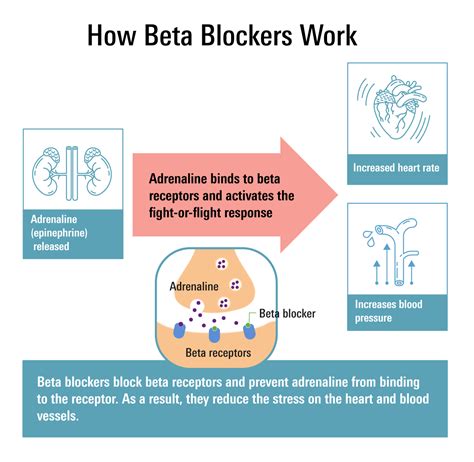
There are several types of beta blockers, each with its own unique characteristics and effects on the body. For example, non-selective beta blockers such as propranolol block both beta-1 and beta-2 receptors, while selective beta blockers such as atenolol primarily block beta-1 receptors. Beta-1 receptors are found mainly in the heart, where they stimulate the heart to beat faster and stronger. Beta-2 receptors, on the other hand, are found in the lungs, blood vessels, and other tissues, where they cause blood vessels to dilate and airways to relax.
Types of Beta Blockers
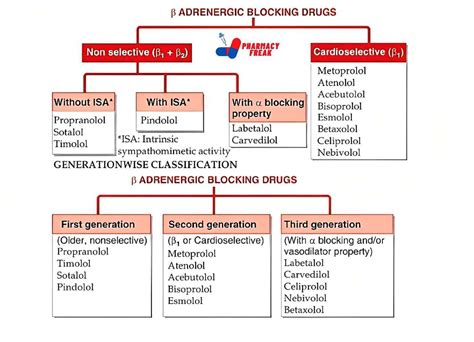
Some common types of beta blockers include:
- Non-selective beta blockers: propranolol, nadolol, and timolol
- Selective beta blockers: atenolol, metoprolol, and bisoprolol
- Beta blockers with ISA: pindolol and acebutolol
- Beta blockers with membrane-stabilizing activity: propranolol and oxprenolol
Benefits of Beta Blockers

In addition to their cardiovascular benefits, beta blockers have also been shown to have a positive effect on cognitive function and mood. For example, beta blockers such as propranolol have been used to treat performance anxiety and other forms of social anxiety, while beta blockers such as atenolol have been used to treat symptoms of depression and anxiety in people with heart disease.
Side Effects of Beta Blockers
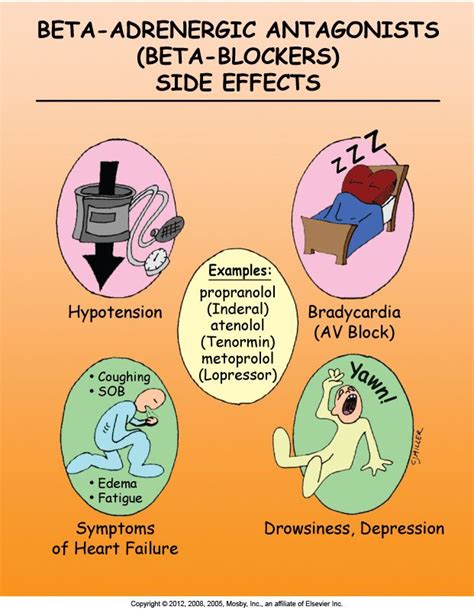
In rare cases, beta blockers can cause more serious side effects, such as:
- Allergic reactions and anaphylaxis
- Bradycardia and heart block
- Hypotension and orthostatic hypotension
- Bronchospasm and asthma exacerbation
- Masking of hypoglycemic symptoms in people with diabetes
Interactions with Other Medications
It is essential to inform your doctor or pharmacist about all the medications you are taking, including prescription and over-the-counter medications, vitamins, and supplements. This will help to minimize the risk of interactions and ensure safe and effective treatment.
Precautions and Warnings

It is essential to discuss your medical history and any concerns with your doctor before starting beta blocker therapy.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with beta blockers in the comments section below. Have you taken beta blockers for a medical condition? What were your experiences with the medication? Do you have any questions or concerns about beta blockers? Share your story and help others understand the benefits and risks of beta blocker therapy.
What are beta blockers used for?
+Beta blockers are used to manage various health conditions, including high blood pressure, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias. They can also be used to alleviate symptoms of anxiety and tremors.
How do beta blockers work?
+Beta blockers work by blocking the effects of epinephrine and other stress hormones on the heart and blood vessels, reducing the heart rate and blood pressure.
What are the different types of beta blockers?
+There are several types of beta blockers, including non-selective beta blockers, selective beta blockers, beta blockers with intrinsic sympathomimetic activity (ISA), and beta blockers with membrane-stabilizing activity.
What are the benefits of beta blockers?
+The benefits of beta blockers include reducing the risk of heart attacks and strokes, alleviating symptoms of anxiety and tremors, and improving survival rates in people with heart failure and other cardiovascular conditions.
What are the potential side effects of beta blockers?
+Beta blockers can cause a range of side effects, including fatigue, dizziness, nausea, and shortness of breath. In rare cases, they can cause more serious side effects, such as allergic reactions, bradycardia, and hypotension.
