Intro
Discover the diaphragm, a crucial muscle for breathing, separating chest and abdominal cavities, and aiding in respiration, coughing, and posture, with functions and anatomy explained in detail.
The diaphragm is a vital muscle that plays a crucial role in the human body, particularly in the respiratory system. It is a dome-shaped muscle that separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity. The diaphragm is the primary muscle used for breathing, and it works in conjunction with other muscles to facilitate the expansion and contraction of the lungs. Without the diaphragm, the human body would not be able to breathe properly, and it would lead to various health complications.
The diaphragm is a complex muscle that consists of three parts: the costal part, the posterior part, and the central part. The costal part is attached to the ribs, the posterior part is attached to the spine, and the central part is a tendinous structure that connects the two parts. When the diaphragm contracts, it flattens and moves downward, increasing the volume of the chest cavity and allowing the lungs to expand. This process is essential for inhaling air into the lungs. On the other hand, when the diaphragm relaxes, it returns to its dome shape, decreasing the volume of the chest cavity and allowing the lungs to deflate. This process is necessary for exhaling air from the lungs.
Understanding the diaphragm and its functions is essential for maintaining good health. The diaphragm is not only responsible for breathing but also plays a role in other bodily functions, such as digestion and circulation. The diaphragm helps to increase blood flow to the digestive organs, which is necessary for proper digestion and nutrient absorption. Additionally, the diaphragm helps to regulate blood pressure by increasing blood flow to the heart. Overall, the diaphragm is a vital muscle that plays a central role in maintaining the overall health and well-being of the human body.
Diaphragm Function and Importance
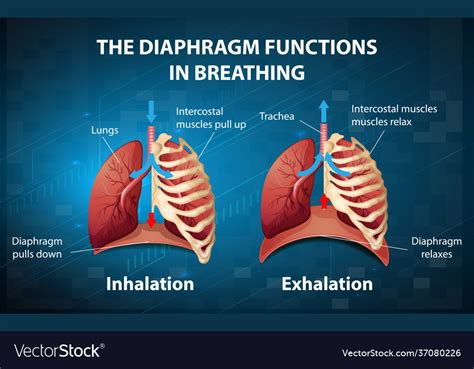
The diaphragm is also important for maintaining good posture and preventing back pain. When the diaphragm is strong and functioning properly, it helps to support the spine and maintain good posture. This can help to reduce the risk of back pain and other musculoskeletal disorders. Additionally, the diaphragm helps to regulate blood pressure and promote circulation, which is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being.
Diaphragm Anatomy and Structure
The diaphragm is a complex muscle that consists of three parts: the costal part, the posterior part, and the central part. The costal part is attached to the ribs, the posterior part is attached to the spine, and the central part is a tendinous structure that connects the two parts. The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle that separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity. It is a vital muscle that plays a central role in the respiratory system, and it is essential for maintaining good health.The diaphragm is innervated by the phrenic nerve, which arises from the cervical spine. The phrenic nerve is responsible for controlling the contraction and relaxation of the diaphragm. When the phrenic nerve is stimulated, it causes the diaphragm to contract, which increases the volume of the chest cavity and allows the lungs to expand. The diaphragm is also innervated by the intercostal nerves, which arise from the thoracic spine. The intercostal nerves help to regulate the contraction and relaxation of the intercostal muscles, which work in conjunction with the diaphragm to facilitate breathing.
Diaphragm Disorders and Diseases
Other disorders and diseases that can affect the diaphragm include diaphragmatic eventration, diaphragmatic fibrosis, and diaphragmatic tumor. Diaphragmatic eventration is a condition in which the diaphragm is weakened or thinned, allowing the abdominal organs to protrude into the chest cavity. Diaphragmatic fibrosis is a condition in which the diaphragm becomes scarred or fibrotic, which can cause breathing difficulties and other respiratory problems. Diaphragmatic tumor is a condition in which a tumor grows on the diaphragm, which can cause respiratory distress, chest pain, and other symptoms.
Treatment and Management of Diaphragm Disorders
The treatment and management of diaphragm disorders depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. In some cases, diaphragm disorders can be treated with medication, physical therapy, or other conservative measures. In other cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or replace the diaphragm. The goal of treatment is to restore normal diaphragm function, alleviate symptoms, and improve overall health and well-being.In some cases, diaphragm disorders can be managed with lifestyle modifications, such as avoiding heavy lifting, bending, or straining. It is also important to maintain good posture, engage in regular exercise, and practice stress-reducing techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation. Additionally, it is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time.
Diaphragm Exercises and Strengthening Techniques

Other exercises that can help to strengthen the diaphragm include yoga, Pilates, and tai chi. These exercises involve deep breathing, stretching, and movement, which can help to improve diaphragm function and overall respiratory health. Additionally, exercises that strengthen the core muscles, such as the transverse abdominis, can help to support the diaphragm and improve overall posture.
Benefits of Diaphragm Strengthening Exercises
The benefits of diaphragm strengthening exercises include improved lung function, increased oxygenation, and enhanced overall health and well-being. Diaphragm strengthening exercises can also help to reduce stress and anxiety, improve sleep quality, and increase energy levels. Additionally, diaphragm strengthening exercises can help to improve athletic performance, reduce the risk of injury, and enhance overall physical fitness.In conclusion, the diaphragm is a vital muscle that plays a central role in the respiratory system. Understanding the diaphragm and its functions is essential for maintaining good health and preventing various disorders and diseases. By incorporating diaphragm strengthening exercises and techniques into daily life, individuals can improve lung function, reduce stress and anxiety, and enhance overall health and well-being.
What is the diaphragm and its function?
+The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle that separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity. Its primary function is to facilitate breathing by contracting and relaxing, allowing the lungs to expand and fill with air.
What are some common disorders and diseases that affect the diaphragm?
+Some common disorders and diseases that affect the diaphragm include diaphragmatic hernia, diaphragmatic paralysis, diaphragmatic rupture, diaphragmatic eventration, diaphragmatic fibrosis, and diaphragmatic tumor.
How can I strengthen my diaphragm and improve lung function?
+You can strengthen your diaphragm and improve lung function by practicing diaphragmatic breathing exercises, yoga, Pilates, and tai chi. Additionally, exercises that strengthen the core muscles, such as the transverse abdominis, can help to support the diaphragm and improve overall posture.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the diaphragm and its importance in maintaining good health. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences, please feel free to comment below. Additionally, if you found this article informative and helpful, please share it with others who may benefit from this information.
