Intro
Improve blood sugar control with 5 ways to achieve good A1c levels, including diet, exercise, and monitoring, to manage diabetes and prevent complications, promoting healthy glucose levels and overall well-being.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is crucial for individuals, especially those dealing with diabetes or prediabetes. One of the key indicators of blood sugar control is the A1c level, which reflects average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months. A good A1c level is essential for preventing diabetes-related complications and ensuring overall well-being. In this article, we will delve into the importance of A1c levels, the benefits of maintaining a good A1c, and provide practical tips on how to achieve and sustain a healthy A1c level.
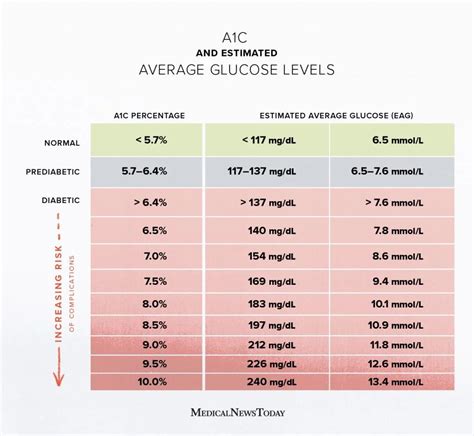
The A1c test is a blood test that measures the percentage of glucose attached to hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen. This test provides a snapshot of average blood glucose levels over the preceding months, offering valuable insights into how well diabetes is being managed. For individuals without diabetes, a normal A1c level is typically below 5.7%, while for those with diabetes, the American Diabetes Association recommends an A1c goal of less than 7% for most adults. Achieving and maintaining a good A1c level is vital for reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications, such as heart disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage.
Understanding the significance of A1c levels and their impact on health can motivate individuals to adopt healthier habits. A good A1c level not only indicates good blood sugar control but also reflects a reduced risk of long-term diabetes complications. Moreover, maintaining a healthy A1c level can improve overall quality of life, enhance energy levels, and support weight management. By focusing on diet, physical activity, stress management, and adherence to medication regimens (when prescribed), individuals can effectively manage their A1c levels and foster a healthier lifestyle.
Understanding A1c Levels

Benefits of Good A1c Levels
The benefits of maintaining good A1c levels are numerous and significant. They include a reduced risk of diabetes-related complications, improved energy levels, better weight management, and enhanced overall health and well-being. By keeping A1c levels within the target range, individuals can also reduce their risk of heart disease, which is a leading cause of death among people with diabetes. Furthermore, good A1c levels can decrease the risk of kidney disease, a common complication of diabetes that can lead to kidney failure if left untreated.Strategies for Achieving Good A1c Levels

Practical Tips for Sustaining Good A1c Levels
Sustaining good A1c levels over time requires commitment, patience, and the right strategies. Here are some practical tips that can help: - **Keep a Food Diary**: Tracking what you eat and when can help identify patterns and make informed decisions about dietary changes. - **Find Enjoyable Physical Activities**: Engaging in physical activities that bring joy can make it easier to stick to an exercise routine. - **Set Realistic Goals**: Setting achievable goals, both in the short and long term, can help stay motivated and focused on diabetes management. - **Seek Support**: Connecting with others who are managing diabetes can provide emotional support, practical advice, and a sense of community.Overcoming Challenges in A1c Management

The Role of Technology in A1c Management
Technology has revolutionized the way individuals manage their diabetes, offering tools that can track blood glucose levels, monitor medication adherence, and provide personalized advice based on real-time data. Mobile apps, continuous glucose monitoring systems, and insulin pumps are examples of technological innovations that can make diabetes management more efficient and effective. These tools can help individuals identify patterns in their glucose levels, receive alerts when levels are too high or too low, and share data with healthcare providers to inform treatment decisions.Nutrition and A1c Levels
Physical Activity and A1c Management
Regular physical activity is another cornerstone of A1c management. Exercise not only improves insulin sensitivity but also enhances cardiovascular health, supports weight management, and boosts mood. The American Diabetes Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week. Additionally, incorporating strength-training exercises, high-intensity interval training, and flexibility exercises can provide a well-rounded fitness regimen.Stress Management and A1c Levels

Medication Adherence and A1c Management
For individuals with diabetes, taking medications as prescribed is crucial for maintaining good A1c levels. Medications can help control blood glucose levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and prevent complications. However, adherence to medication regimens can be challenging due to factors like cost, side effects, and complexity of the regimen. Strategies to improve adherence include using pill boxes, setting reminders, and discussing any concerns or side effects with healthcare providers.Conclusion and Future Directions

We invite you to share your experiences, tips, and questions about managing A1c levels in the comments below. Your insights can help others on their journey to better health. Additionally, consider sharing this article with friends and family who may benefit from the information provided. Together, we can support each other in achieving and maintaining good health.
What is a good A1c level for someone with diabetes?
+A good A1c level for someone with diabetes is generally considered to be less than 7%. However, this target may vary depending on individual factors, such as age, other health conditions, and the risk of hypoglycemia.
How often should I check my A1c levels?
+The frequency of A1c checks depends on the individual's diabetes management plan and their healthcare provider's recommendations. Generally, A1c levels are checked every 3 to 6 months.
Can diet and exercise alone control A1c levels?
+For some individuals, especially those with prediabetes or type 2 diabetes, diet and exercise can be enough to control A1c levels. However, for many people with diabetes, medication is also necessary to achieve and maintain good A1c levels.
