Intro
Discover the Molar Pregnancy Definition, a rare gestational trophoblastic disease, also known as hydatidiform mole, characterized by abnormal cell growth, affecting fetal development and maternal health, requiring prompt medical attention and treatment.
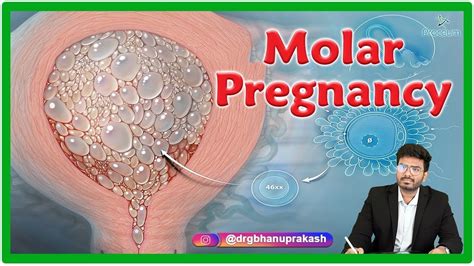
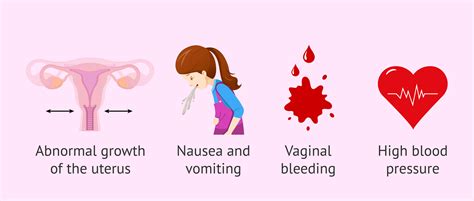
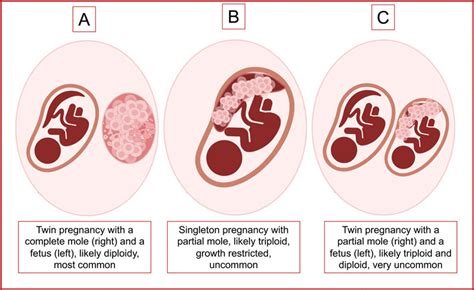
A molar pregnancy is a rare and complex condition that affects women during early pregnancy. It is characterized by the abnormal growth of trophoblast cells, which are the cells that normally develop into the placenta. In a molar pregnancy, these cells grow and multiply abnormally, leading to the formation of a mass of tissue that resembles a cluster of grapes. This mass can cause a range of symptoms, including vaginal bleeding, abdominal pain, and nausea. Molar pregnancies are also known as hydatidiform moles, and they can be either complete or partial.
Molar pregnancies are often detected during routine ultrasound scans, and they can be a cause of concern for women who are expecting a healthy baby. The condition is relatively rare, affecting about 1 in every 1,000 pregnancies in the United States. However, it is essential to understand the risks and complications associated with molar pregnancies, as well as the treatment options available. Women who have had a molar pregnancy in the past are at a higher risk of developing the condition again in future pregnancies. Therefore, it is crucial to seek medical attention if any symptoms or concerns arise during pregnancy.
The importance of understanding molar pregnancies cannot be overstated. The condition can have significant physical and emotional implications for women, and it is essential to provide them with accurate and comprehensive information. By learning more about molar pregnancies, women can better understand their risks, symptoms, and treatment options. This knowledge can help alleviate anxiety and uncertainty, allowing women to make informed decisions about their health and well-being. Furthermore, understanding molar pregnancies can also help healthcare providers to diagnose and manage the condition more effectively, reducing the risk of complications and improving patient outcomes.
Molar Pregnancy Causes and Risk Factors
Genetic Factors
Genetic factors are thought to play a role in the development of molar pregnancies. In most cases, a molar pregnancy occurs when there is an abnormal fertilization of the egg, resulting in an imbalance of genetic material. This can happen when a single sperm fertilizes an empty egg or when two sperm fertilize a single egg. The resulting genetic material is then unable to develop into a healthy fetus, leading to the growth of abnormal trophoblast cells.Hormonal Factors
Hormonal factors may also contribute to the development of molar pregnancies. The hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) plays a crucial role in the growth and development of the placenta. In women with molar pregnancies, hCG levels are often higher than normal, which can cause a range of symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.Molar Pregnancy Symptoms and Diagnosis
Ultrasound Scan
An ultrasound scan is usually the first test performed to diagnose a molar pregnancy. The scan uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the uterus and the developing fetus. In women with molar pregnancies, the ultrasound scan may show a characteristic "snowstorm" appearance, which is caused by the abnormal growth of trophoblast cells.Blood Tests
Blood tests may also be performed to diagnose a molar pregnancy. These tests measure the levels of hCG in the blood, which can be higher than normal in women with molar pregnancies. Additionally, blood tests can help to rule out other conditions that may be causing symptoms, such as ectopic pregnancy or miscarriage.Molar Pregnancy Treatment Options
Dilation and Curettage (D&C)
A D&C is a common procedure used to treat molar pregnancies. The procedure involves dilating the cervix and removing the abnormal tissue from the uterus using a suction device. The tissue is then sent to a laboratory for examination, where it can be confirmed that the tissue is a molar pregnancy.Hysterectomy
In some cases, a hysterectomy may be necessary to treat a molar pregnancy. This involves the removal of the entire uterus, which can help to prevent future complications. A hysterectomy is usually only performed in women who have completed their family and do not wish to become pregnant again.Molar Pregnancy Complications and Risks

Gestational Trophoblastic Disease (GTD)
GTD is a rare but potentially life-threatening condition that can develop after a molar pregnancy. The condition is caused by the continued growth and multiplication of abnormal trophoblast cells, which can invade the uterus and other organs. GTD can be treated using chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or surgery, depending on the severity of the condition.Bleeding and Infection
Molar pregnancies can also be associated with bleeding and infection. The abnormal tissue can cause significant bleeding, which can lead to anemia and other complications. Additionally, the tissue can become infected, leading to symptoms such as fever, chills, and abdominal pain.Follow-up Care and Support

Regular Blood Tests
Regular blood tests are essential after a molar pregnancy to monitor hCG levels. These tests can help to detect any remaining abnormal tissue or the development of GTD. Women who have had a molar pregnancy should have regular blood tests for at least 12 months after the condition has been treated.Ultrasound Scans
Ultrasound scans can also be used to monitor for any remaining abnormal tissue after a molar pregnancy. These scans can help to detect any abnormalities in the uterus, as well as any signs of GTD.Living with a Molar Pregnancy
Emotional Support
Emotional support is crucial for women who have had a molar pregnancy. This can include counseling, support groups, and online forums. Women who have had a molar pregnancy may benefit from talking to others who have experienced the condition, as well as receiving support from family and friends.Medical Care
Medical care is also essential for women who have had a molar pregnancy. This can include regular blood tests, ultrasound scans, and follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider. Women who have had a molar pregnancy should receive regular medical care for at least 12 months after the condition has been treated.What is a molar pregnancy?
+A molar pregnancy is a rare condition that affects women during early pregnancy, characterized by the abnormal growth of trophoblast cells.
What are the symptoms of a molar pregnancy?
+The symptoms of a molar pregnancy can include vaginal bleeding, abdominal pain, and nausea, although some women may experience no symptoms at all.
How is a molar pregnancy treated?
+A molar pregnancy is typically treated using a procedure called a dilation and curettage (D&C), which involves removing the abnormal tissue from the uterus.
What are the complications of a molar pregnancy?
+Molar pregnancies can be associated with several complications, including bleeding, infection, and gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD).
How can I prevent a molar pregnancy?
+While it is not possible to prevent a molar pregnancy, women can reduce their risk by maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding smoking and alcohol, and seeking regular medical care during pregnancy.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of molar pregnancies, including their causes, symptoms, treatment options, and complications. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider. Additionally, we invite you to share this article with others who may be affected by molar pregnancies, and to leave a comment below with your thoughts and experiences. By working together, we can raise awareness and support for women who have had a molar pregnancy, and help to improve their physical and emotional well-being.
