Intro
Discover how NSAID works to reduce inflammation and pain through 5 key mechanisms, including analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic effects, utilizing COX enzymes, prostaglandins, and immune responses to provide relief.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, commonly referred to as NSAIDs, are a class of medications widely used to reduce inflammation, alleviate pain, and lower fever. They work by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, which are chemical messengers in the body that promote pain, inflammation, and fever. Understanding how NSAIDs work is crucial for appreciating their role in managing various health conditions, from mild headaches to chronic diseases like arthritis.
The importance of NSAIDs in modern medicine cannot be overstated. They are among the most commonly used drugs worldwide, available both over-the-counter (OTC) and by prescription. Their ability to provide relief from pain and inflammation makes them a staple in many households and medical cabinets. However, like all medications, NSAIDs have their limitations and potential side effects, which must be considered when using them.
The mechanism of action of NSAIDs is complex and involves several pathways. At the core, NSAIDs inhibit the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX), which exists in two main forms: COX-1 and COX-2. COX-1 is involved in maintaining the health of the stomach lining and facilitating platelet function, while COX-2 is primarily associated with the production of prostaglandins that mediate inflammation and pain. By inhibiting these enzymes, NSAIDs reduce the production of prostaglandins, thereby reducing inflammation, pain, and fever.
How NSAIDs Reduce Inflammation
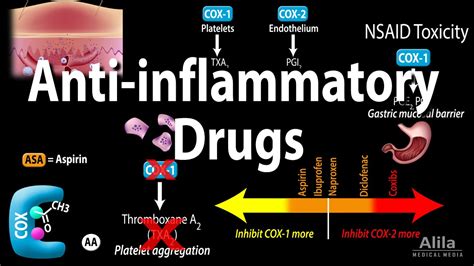
Benefits of Reduced Inflammation
The benefits of reduced inflammation due to NSAID use are multifaceted: - **Pain Relief**: By reducing inflammation, NSAIDs can significantly alleviate pain associated with inflammatory conditions. - **Improved Mobility**: In conditions like arthritis, reducing inflammation can improve joint mobility and reduce stiffness. - **Decreased Fever**: NSAIDs can lower fever by reducing the production of prostaglandins that induce fever.The Role of NSAIDs in Pain Management
Types of Pain Managed by NSAIDs
NSAIDs can manage several types of pain: - **Acute Pain**: Such as pain from injuries or surgery. - **Chronic Pain**: Long-standing pain associated with conditions like arthritis. - **Menstrual Pain**: NSAIDs are often used to alleviate menstrual cramps.NSAIDs and Fever Reduction
How NSAIDs Lower Fever
The process involves: - **Inhibition of Prostaglandin Synthesis**: Reduces the chemical signals that promote fever. - **Action on the Hypothalamus**: Helps in resetting the body's thermostat to normal.Long-term Use and Side Effects of NSAIDs

Minimizing Side Effects
To minimize side effects: - **Use the Lowest Effective Dose**: Reduces the risk of gastrointestinal and other complications. - **Short-term Use**: Limiting the duration of NSAID use can help avoid long-term side effects. - **Alternative Medications**: For chronic conditions, other types of medications or therapies might be considered to minimize NSAID use.Conclusion and Future Directions
As we look to the future, the importance of NSAIDs in clinical practice will likely endure, given their broad applicability and efficacy. Nonetheless, ongoing efforts to improve their safety profile and to discover novel therapeutic agents will be essential for enhancing patient outcomes.
What are the primary uses of NSAIDs?
+NSAIDs are primarily used to reduce inflammation, alleviate pain, and lower fever.
How do NSAIDs work?
+NSAIDs work by inhibiting the cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes, which are involved in the production of prostaglandins that mediate inflammation, pain, and fever.
What are the common side effects of long-term NSAID use?
+Common side effects include gastrointestinal issues like stomach ulcers and bleeding, kidney damage, increased blood pressure, and a slight increase in the risk of heart attack or stroke.
How can the side effects of NSAIDs be minimized?
+Side effects can be minimized by using the lowest effective dose, limiting the duration of use, and considering alternative medications or therapies for chronic conditions.
What does the future hold for NSAID research and development?
+Future research may focus on developing more selective COX-2 inhibitors with fewer side effects and exploring alternative anti-inflammatory pathways to improve patient outcomes.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with NSAIDs in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from understanding how NSAIDs work and their role in managing pain, inflammation, and fever. Your engagement and feedback are invaluable in helping us create content that meets your needs and interests.
