Intro
Discover what statins are, how they work, and their role in lowering cholesterol levels, reducing heart disease risk, and managing cardiovascular health with statin medications.
Statin medications have become a cornerstone in the management of cholesterol levels and the prevention of cardiovascular diseases. With their widespread use, it's essential to understand what statins are, how they work, and their benefits and risks. Statins are a group of medicines that are prescribed to lower the level of cholesterol in the blood. They work by inhibiting an enzyme in the liver, known as HMG-CoA reductase, which is necessary for the production of cholesterol. By reducing the amount of cholesterol produced in the liver, statins help decrease the overall level of cholesterol in the blood.
The importance of managing cholesterol levels cannot be overstated. High levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, often referred to as "bad" cholesterol, can lead to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, known as atherosclerosis. This condition increases the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events. Statins, by effectively lowering LDL cholesterol, play a critical role in preventing these outcomes. Furthermore, statins have anti-inflammatory properties and can help stabilize plaques in the arteries, making them less likely to rupture and cause a blockage.
Understanding how statins work and their impact on cardiovascular health is crucial for individuals at risk of heart disease. Statins are not just limited to lowering cholesterol; they have been shown to reduce the risk of major vascular events even in individuals without a history of cardiovascular disease but who are at high risk due to factors such as diabetes, high blood pressure, or smoking. The mechanism by which statins exert their effects involves not only the reduction of cholesterol production but also modulation of the immune system and improvement of endothelial function, which is the lining of blood vessels.
Benefits of Statins
The benefits of statins are multifaceted and well-documented. They include the reduction of LDL cholesterol levels, which in turn decreases the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Statins have also been shown to be effective in preventing cardiovascular events in individuals with existing heart disease, a condition known as secondary prevention. Moreover, statins can help reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease in individuals without a history of heart disease but who have risk factors, a concept known as primary prevention. The ability of statins to stabilize plaques and reduce inflammation within the arterial walls adds to their protective effects against cardiovascular events.
Primary and Secondary Prevention
Statins are used for both primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease. Primary prevention involves the use of statins in individuals who do not have a history of cardiovascular disease but are at high risk due to various factors such as high cholesterol levels, diabetes, hypertension, or a family history of early heart disease. Secondary prevention, on the other hand, involves the use of statins in individuals who have already experienced a cardiovascular event, such as a heart attack or stroke, to prevent further events.How Statins Work
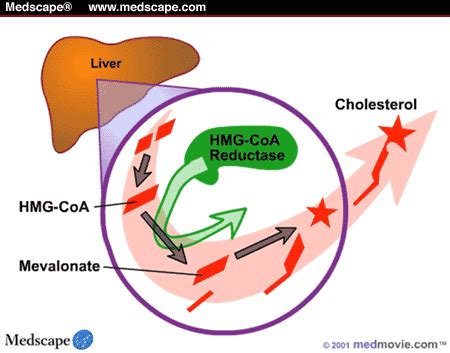
The mechanism of action of statins involves the inhibition of the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase. This enzyme is crucial for the production of cholesterol in the liver. By inhibiting this enzyme, statins reduce the amount of cholesterol produced by the liver, which in turn lowers the level of LDL cholesterol in the blood. Statins also increase the uptake of LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream by the liver, further contributing to the reduction of LDL cholesterol levels. Additionally, statins have been found to have pleiotropic effects, including anti-inflammatory properties, improvement of endothelial function, and stabilization of atherosclerotic plaques, all of which contribute to their cardiovascular protective effects.
Types of Statins
There are several types of statins available, each with its own pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties. These include atorvastatin, simvastatin, rosuvastatin, pravastatin, and lovastatin, among others. The choice of statin depends on various factors, including the patient's specific needs, potential drug interactions, and the presence of any side effects. Some statins are more potent than others in lowering LDL cholesterol, and some have a longer duration of action, allowing for once-daily dosing.Risks and Side Effects of Statins
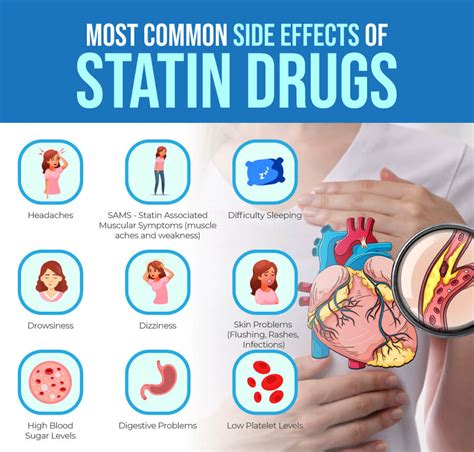
While statins are generally well-tolerated, they can cause side effects in some individuals. Common side effects include muscle pain, liver enzyme elevations, and increased risk of diabetes. Rare but serious side effects include muscle breakdown (rhabdomyolysis) and liver failure. It's essential for patients to discuss the potential benefits and risks of statin therapy with their healthcare provider to determine if statins are appropriate for them.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Patients on statin therapy require regular monitoring to assess the effectiveness of the treatment and to detect any potential side effects early. This includes regular measurements of lipid profiles, liver enzymes, and blood glucose levels. Additionally, patients should be educated on the signs and symptoms of muscle pain and liver dysfunction and instructed to report these to their healthcare provider promptly.Lifestyle Modifications and Statins

While statins are effective in lowering cholesterol levels and reducing the risk of cardiovascular events, lifestyle modifications remain a crucial component of cardiovascular disease prevention. These modifications include a healthy diet low in saturated fats and cholesterol, regular physical activity, weight management, and not smoking. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help lower cholesterol levels and improve overall cardiovascular health. Regular physical activity, such as walking or other aerobic exercises, can also contribute to the reduction of cardiovascular risk factors.
Dietary Approaches
Dietary approaches to lowering cholesterol include the use of plant sterols and stanols, which can help reduce the absorption of cholesterol from the gut. Soluble fiber, found in foods such as oats, barley, and fruits, can also bind to bile acids and lower cholesterol levels. Furthermore, adopting a Mediterranean-style diet, which is rich in monounsaturated fats, such as those found in olive oil, has been associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease.Future Directions in Statin Therapy

Research into statin therapy continues to evolve, with ongoing studies examining the use of statins in new populations, such as those with chronic kidney disease, and the development of new statins with improved safety profiles. The use of genetic testing to predict an individual's response to statin therapy and to identify those at higher risk of side effects is also an area of active investigation. Furthermore, the combination of statins with other lipid-lowering therapies, such as PCSK9 inhibitors, is being explored to achieve even greater reductions in cardiovascular risk.
Personalized Medicine
The concept of personalized medicine, where treatment is tailored to the individual's specific genetic, environmental, and clinical factors, is becoming increasingly relevant in the field of statin therapy. By identifying genetic variants that affect an individual's response to statins, healthcare providers may be able to predict which patients are more likely to benefit from statin therapy and which may be at higher risk of side effects. This personalized approach could lead to more effective and safer use of statins in the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, statins are a powerful tool in the management of cholesterol levels and the prevention of cardiovascular disease. Their benefits are well-documented, and they have become a cornerstone in the treatment of individuals at risk of heart attacks and strokes. While lifestyle modifications remain essential, statins offer an effective way to reduce cardiovascular risk when used appropriately. As research continues to uncover new aspects of statin therapy, including their pleiotropic effects and potential uses in new populations, their role in cardiovascular disease prevention is likely to expand.
We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with statin therapy in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this information. For healthcare professionals, we encourage you to continue staying updated on the latest guidelines and research regarding statin therapy to provide the best possible care for your patients.
What are statins used for?
+Statins are used to lower the level of cholesterol in the blood, particularly low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, and to prevent cardiovascular events such as heart attacks and strokes.
How do statins work?
+Statins work by inhibiting the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase, which is necessary for the production of cholesterol in the liver. This leads to a decrease in the amount of cholesterol produced and an increase in the uptake of LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream.
What are the common side effects of statins?
+Common side effects of statins include muscle pain, liver enzyme elevations, and an increased risk of diabetes. Rare but serious side effects include muscle breakdown and liver failure.
Can I stop taking statins if my cholesterol levels are normal?
+No, you should not stop taking statins without consulting your healthcare provider. Even if your cholesterol levels are normal, statins may still be providing other benefits, such as reducing inflammation and stabilizing plaques in your arteries.
How often should I have my cholesterol levels checked while taking statins?
+Your healthcare provider will recommend how often you should have your cholesterol levels checked. Typically, this is done within 4-12 weeks after starting statin therapy and then periodically thereafter to ensure that your cholesterol levels are adequately controlled.
