Intro
Discover 5 essential uses of Amoxicillin, a broad-spectrum antibiotic, for treating bacterial infections, pneumonia, skin infections, urinary tract infections, and more, with its mechanism, benefits, and side effects, for effective health management and disease prevention.
Amoxicillin is a widely prescribed antibiotic that belongs to the penicillin class of medications. It is effective against a broad range of bacterial infections, including those affecting the respiratory tract, skin, and urinary tract. The importance of amoxicillin lies in its ability to combat bacterial infections by inhibiting the growth of bacteria, thereby helping the body's immune system to fight off the infection. Understanding the various uses of amoxicillin is crucial for patients and healthcare providers to ensure its proper and effective use.
The versatility of amoxicillin is evident in its application across different age groups and for various infections. It is often prescribed for children due to its palatability and efficacy in treating common childhood infections. In adults, amoxicillin is used for a range of conditions, from mild to severe bacterial infections. Its effectiveness, combined with its relatively low cost and availability, makes it a preferred choice among antibiotics. Moreover, amoxicillin's mechanism of action, which involves interfering with the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall, leading to the death of the bacteria, underscores its importance in the treatment of bacterial infections.
Amoxicillin's widespread use also stems from its safety profile, which is generally considered favorable, especially when compared to other antibiotics. However, like all medications, it can cause side effects, and its use must be guided by a healthcare professional to minimize the risk of adverse reactions and ensure that the benefits of treatment outweigh the risks. The proper use of amoxicillin is also critical in the context of antibiotic resistance, a growing global health concern. Misuse or overuse of antibiotics like amoxicillin can contribute to the development of resistant bacterial strains, making infections harder to treat.
Introduction to Amoxicillin

Amoxicillin works by stopping the growth of bacteria. It is a beta-lactam antibiotic, which means it works by interfering with the formation of the bacterial cell wall. This interference leads to the weakening and eventual bursting of the cell wall, resulting in the death of the bacteria. The drug is effective against a wide range of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, making it a versatile antibiotic for various infections.
Benefits of Amoxicillin

The benefits of amoxicillin include its broad-spectrum activity, which means it can treat a variety of bacterial infections. It is also relatively safe and well-tolerated, especially in children, making it a common choice for pediatric infections. Amoxicillin is available in various formulations, including capsules, tablets, and liquid suspensions, which facilitates its administration in different patient populations. Furthermore, its pharmacokinetic properties allow for twice-daily dosing in many cases, enhancing patient compliance.
Common Infections Treated by Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin is commonly used to treat:
- Respiratory tract infections such as pneumonia, bronchitis, and sinusitis.
- Skin and soft tissue infections like impetigo and cellulitis.
- Urinary tract infections, including cystitis and pyelonephritis.
- Ear, nose, and throat infections, such as otitis media and strep throat.
Working Mechanism of Amoxicillin
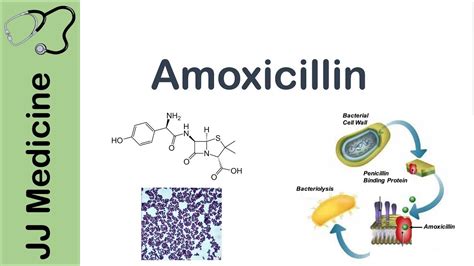
The working mechanism of amoxicillin involves the inhibition of bacterial cell wall synthesis. Bacteria have a cell wall that provides structural support and maintains the osmotic environment of the cell. Amoxicillin binds to and inhibits penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) located inside the bacterial cell wall, which are essential for the synthesis of the cell wall. This inhibition leads to a weakening of the cell wall, causing the cell to lyse and die.
Resistance to Amoxicillin
Resistance to amoxicillin and other antibiotics is a significant concern. Bacteria can develop resistance through several mechanisms, including the production of beta-lactamase enzymes that degrade the antibiotic, alterations in PBPs that reduce the binding of the antibiotic, and changes in membrane permeability that prevent the antibiotic from entering the cell. The misuse and overuse of amoxicillin contribute to the selection and spread of resistant bacterial strains, making infections harder to treat and necessitating the use of alternative, often more toxic or expensive antibiotics.
Steps for Taking Amoxicillin

To ensure the effectiveness of amoxicillin and minimize the risk of side effects, it is crucial to follow the prescribed dosage and treatment duration. Here are key steps:
- Take amoxicillin exactly as directed by your healthcare provider.
- Complete the full treatment course, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication.
- Take amoxicillin at the start of a meal to enhance absorption and reduce gastrointestinal side effects.
- Do not crush or chew extended-release tablets; swallow them whole.
- For liquid suspensions, shake the bottle well before measuring the dose, and use a dosing spoon or measuring cup to ensure accurate dosing.
Practical Examples of Amoxicillin Use
Practical examples of amoxicillin use include treating a child with otitis media (middle ear infection) or an adult with community-acquired pneumonia. In both cases, amoxicillin would be prescribed based on the severity of the infection, patient age, weight, and renal function, among other factors. The dosing regimen would be tailored to ensure that the infection is adequately treated while minimizing the risk of side effects.
Side Effects and Interactions of Amoxicillin

While amoxicillin is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects, including:
- Gastrointestinal disturbances like nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
- Allergic reactions, which can range from mild rash to severe anaphylaxis.
- Superinfections, such as yeast infections, due to the disruption of normal bacterial flora.
It is also important to consider potential interactions with other medications, such as:
- Decreased efficacy of oral contraceptives.
- Increased risk of side effects when used with certain antibiotics or medications that affect kidney function.
Statistical Data on Amoxicillin Use
Statistical data highlight the widespread use of amoxicillin. For instance, it is one of the most commonly prescribed antibiotics in both pediatric and adult populations. Studies have shown that amoxicillin is effective in treating a range of bacterial infections, with cure rates often exceeding 80% for conditions like streptococcal pharyngitis and acute otitis media.
Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, amoxicillin is a valuable antibiotic for treating various bacterial infections. Its broad-spectrum activity, safety profile, and effectiveness make it a preferred choice among healthcare providers. However, the rising concern of antibiotic resistance underscores the need for responsible use and stewardship of amoxicillin and other antibiotics. Future directions include the development of new antibiotics and strategies to combat resistance, as well as ongoing education for both healthcare providers and the public on the appropriate use of antibiotics.
We invite readers to share their experiences or ask questions about amoxicillin and its uses. Your input can help foster a community that promotes the responsible use of antibiotics and supports public health initiatives. Feel free to comment below or share this article with others who might find it informative and useful.
What is amoxicillin used for?
+Amoxicillin is used to treat a wide range of bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, urinary tract infections, and ear, nose, and throat infections.
How does amoxicillin work?
+Amoxicillin works by inhibiting the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall, leading to the death of the bacteria. It binds to penicillin-binding proteins located inside the bacterial cell wall, which are essential for cell wall synthesis.
What are the common side effects of amoxicillin?
+Common side effects of amoxicillin include gastrointestinal disturbances like nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, allergic reactions, and superinfections such as yeast infections.
