Intro
Discover 7 fascinating facts about Ashkenazi Jews, exploring their history, genetics, culture, and traditions, including ancestry, DNA, and heritage, revealing the unique characteristics of this Jewish diaspora group.
The history of Ashkenazi Jews is a rich and complex one, spanning over a thousand years. From their origins in the Rhineland region of Europe to their spread across the globe, Ashkenazi Jews have played a significant role in shaping the world as we know it today. With their unique culture, traditions, and contributions to various fields, it's no wonder that Ashkenazi Jews continue to fascinate people from all walks of life. In this article, we'll delve into the world of Ashkenazi Jews, exploring their history, genetics, culture, and more.
The Ashkenazi Jewish community has a long and storied past, with roots dating back to the Middle Ages. Originally from the Rhineland region of Europe, Ashkenazi Jews migrated to Eastern Europe, where they established thriving communities in present-day Poland, Russia, and Ukraine. Over time, they developed a distinct culture, language, and set of traditions that set them apart from other Jewish communities. Today, Ashkenazi Jews can be found all over the world, with significant populations in the United States, Israel, and other countries.
One of the most interesting aspects of Ashkenazi Jewish history is their genetic heritage. Studies have shown that Ashkenazi Jews have a unique genetic profile, with a high incidence of certain genetic diseases such as Tay-Sachs and Gaucher's disease. This is due in part to the fact that the Ashkenazi Jewish community has been relatively isolated for much of its history, with a limited gene pool. However, this genetic heritage has also been a source of strength, with many Ashkenazi Jews going on to make significant contributions to fields such as science, medicine, and the arts.
Introduction to Ashkenazi Jews
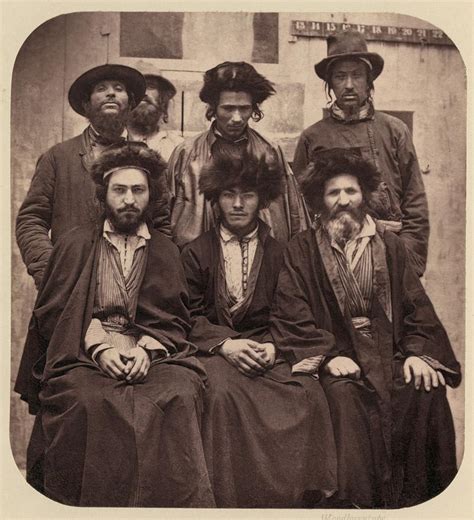

History of Ashkenazi Jews
The history of Ashkenazi Jews is a long and complex one, spanning over a thousand years. From their origins in the Rhineland region to their spread across Eastern Europe, Ashkenazi Jews have faced numerous challenges and obstacles. Despite these challenges, they have managed to maintain their cultural identity and thrive in a variety of environments. Some of the key events in Ashkenazi Jewish history include the Crusades, the Black Death, and the Holocaust, all of which had a significant impact on the community.Genetics of Ashkenazi Jews
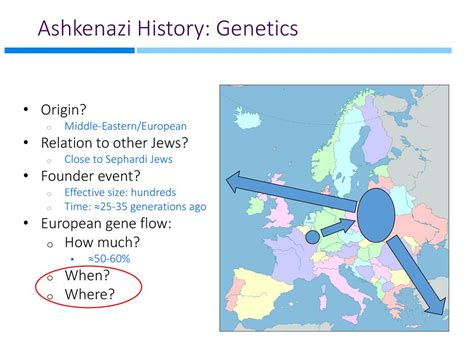
Genetic Diseases in Ashkenazi Jews
Some of the most common genetic diseases found in Ashkenazi Jews include: * Tay-Sachs disease: a rare genetic disorder that causes progressive destruction of the brain and spinal cord * Gaucher's disease: a genetic disorder that causes the buildup of a certain type of fat in the body * Cystic fibrosis: a genetic disorder that causes the production of thick, sticky mucus that can clog the lungs and digestive tract * Canavan disease: a rare genetic disorder that causes the breakdown of the myelin sheath, the protective covering of the nerve fibersCulture of Ashkenazi Jews

Traditions of Ashkenazi Jews
Some of the most important traditions of Ashkenazi Jews include: * Shabbat: the Sabbath day, which is observed from Friday evening to Saturday evening * Holidays: Ashkenazi Jews observe a variety of holidays, including Passover, Rosh Hashanah, and Yom Kippur * Life cycle events: Ashkenazi Jews have a number of important life cycle events, including birth, bar/bat mitzvah, marriage, and deathContributions of Ashkenazi Jews

Notable Ashkenazi Jews
Some other notable Ashkenazi Jews include: * Golda Meir: a politician who served as the Prime Minister of Israel * Elie Wiesel: a writer and activist who is known for his work on the Holocaust * Ruth Bader Ginsburg: a judge who serves on the US Supreme Court * Steven Spielberg: a film director and producer who is known for his work on movies such as Jaws and E.T.Challenges Faced by Ashkenazi Jews

Response to Challenges
Despite these challenges, Ashkenazi Jews have managed to maintain their cultural identity and thrive in a variety of environments. Some of the ways in which Ashkenazi Jews have responded to challenges include: * Building strong communities: Ashkenazi Jews have built strong, vibrant communities that provide support and connection * Preserving traditions: Ashkenazi Jews have worked to preserve their traditions and cultural heritage * Advocating for rights: Ashkenazi Jews have advocated for their rights and the rights of others, working to combat prejudice and discriminationConclusion and Final Thoughts

As we reflect on the history and culture of Ashkenazi Jews, we are reminded of the importance of preserving cultural heritage and promoting understanding and respect between different communities. We hope that this article has inspired readers to learn more about Ashkenazi Jews and their contributions to the world, and we look forward to hearing your thoughts and comments.
What is the origin of Ashkenazi Jews?
+Ashkenazi Jews originated in the Rhineland region of Europe, and later migrated to Eastern Europe, where they established thriving communities in present-day Poland, Russia, and Ukraine.
What are some common genetic diseases found in Ashkenazi Jews?
+Some common genetic diseases found in Ashkenazi Jews include Tay-Sachs disease, Gaucher's disease, cystic fibrosis, and Canavan disease.
What are some notable contributions of Ashkenazi Jews?
+Ashkenazi Jews have made significant contributions to a variety of fields, including science, medicine, literature, and the arts. Some notable Ashkenazi Jews include Albert Einstein, Sigmund Freud, Franz Kafka, and Leonard Bernstein.
What are some challenges faced by Ashkenazi Jews?
+Ashkenazi Jews have faced a number of challenges throughout their history, including persecution, discrimination, and genocide. Some of the most significant challenges faced by Ashkenazi Jews include the Holocaust, anti-Semitism, and assimilation.
How have Ashkenazi Jews responded to challenges?
+Ashkenazi Jews have responded to challenges by building strong communities, preserving traditions, and advocating for rights. They have also worked to promote understanding and respect between different communities, and to preserve their cultural heritage.
