Intro
Discover Azithromycin, a broad-spectrum antibiotic medicine treating bacterial infections, respiratory issues, and STDs with efficacy, dosage, and side effects explained.
Azithromycin is a widely used antibiotic that belongs to the macrolide class of antibiotics. It is prescribed to treat various bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, skin infections, and sexually transmitted diseases. The importance of azithromycin lies in its ability to effectively combat bacterial infections while minimizing the risk of adverse effects. As a result, it has become a popular choice among healthcare professionals and patients alike. In this article, we will delve into the world of azithromycin, exploring its benefits, working mechanisms, and key information related to its use.
Azithromycin has revolutionized the treatment of bacterial infections, offering a convenient and effective solution for patients. Its broad-spectrum activity allows it to target a wide range of bacteria, making it a versatile antibiotic. Moreover, azithromycin has a relatively long half-life, which enables it to remain in the body for an extended period, providing prolonged antibacterial activity. This characteristic makes it an ideal choice for treating infections that require prolonged treatment, such as pneumonia and sinusitis. With the rise of antibiotic resistance, azithromycin has become an essential tool in the fight against bacterial infections, and its importance cannot be overstated.
The discovery of azithromycin has been a significant milestone in the development of antibiotic therapy. First introduced in the 1990s, azithromycin has undergone extensive research and testing, demonstrating its efficacy and safety in various clinical trials. Today, it is widely used to treat a range of infections, including community-acquired pneumonia, acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis, and uncomplicated skin and soft tissue infections. Azithromycin's effectiveness in treating these conditions has made it a staple in many healthcare settings, and its use continues to grow as new applications are discovered.
Azithromycin Mechanism of Action
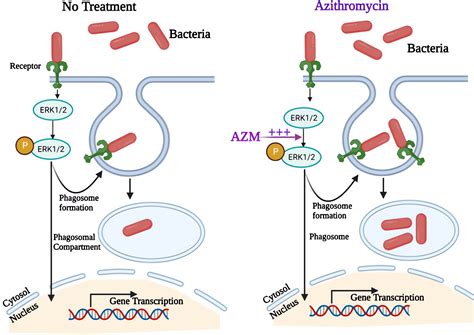
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
The pharmacokinetics of azithromycin involve its absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. After oral administration, azithromycin is rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream, with peak plasma concentrations reached within 2-3 hours. It is widely distributed throughout the body, with high concentrations found in tissues such as the lungs, liver, and kidneys. Azithromycin is metabolized by the liver and excreted primarily in the bile, with a small amount excreted in the urine.Azithromycin Benefits and Advantages

Common Uses of Azithromycin
Azithromycin is commonly used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, including: * Community-acquired pneumonia * Acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis * Uncomplicated skin and soft tissue infections * Genital ulcers and chlamydia * Sinusitis and otitis mediaAzithromycin Side Effects and Interactions

Precautions and Contraindications
Azithromycin is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to macrolide antibiotics. It should be used with caution in patients with liver or kidney disease, as well as in pregnant and breastfeeding women. Patients with a history of QT interval prolongation or those taking medications that prolong the QT interval should also use azithromycin with caution.Azithromycin Dosage and Administration
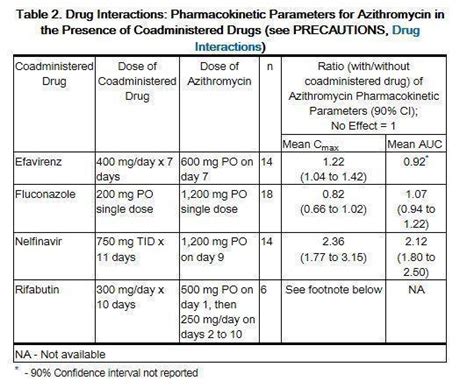
Special Considerations
Azithromycin should be used with caution in patients with a history of cardiovascular disease, as it may increase the risk of QT interval prolongation. Patients with a history of seizure disorders should also use azithromycin with caution, as it may increase the risk of seizures.Azithromycin Resistance and Future Directions
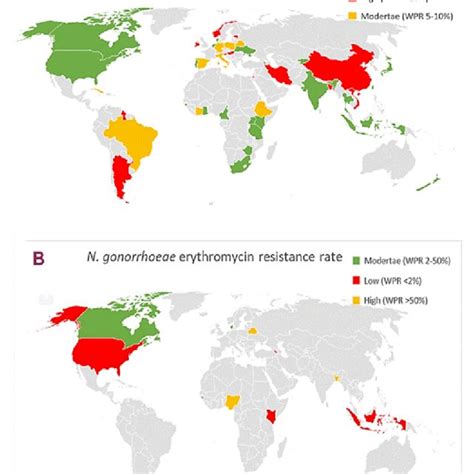
Current Research and Developments
Current research is focused on developing new macrolide antibiotics with improved activity against resistant bacteria. Additionally, studies are being conducted to investigate the use of azithromycin in combination with other antibiotics to enhance its effectiveness and reduce the risk of resistance.Azithromycin in Pediatric and Geriatric Populations
Pediatric Dosage and Administration
The pediatric dosage of azithromycin varies depending on the age and weight of the child. The typical dosage is 10-20 mg/kg/day, given once daily for 3-5 days.Azithromycin and Pregnancy

Lactation and Breastfeeding
Azithromycin is excreted in breast milk, and its use during breastfeeding should be cautious. The benefits of azithromycin should be weighed against the potential risks to the infant, and alternative antibiotics should be considered if possible.What is azithromycin used for?
+Azithromycin is used to treat various bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, skin infections, and sexually transmitted diseases.
How does azithromycin work?
+Azithromycin works by inhibiting protein synthesis in bacteria, ultimately leading to the death of the bacterial cells.
What are the common side effects of azithromycin?
+The common side effects of azithromycin include gastrointestinal disturbances, allergic reactions, headache, and dizziness.
Can azithromycin be used during pregnancy?
+Azithromycin is classified as a category B medication during pregnancy, meaning that it is generally considered safe to use during pregnancy. However, it should be used with caution.
How long does azithromycin take to work?
+Azithromycin typically starts working within 2-3 days of treatment, although it may take longer to fully clear the infection.
In summary, azithromycin is a versatile and effective antibiotic that has revolutionized the treatment of bacterial infections. Its broad-spectrum activity, convenient dosing regimen, and relatively low risk of adverse effects make it a popular choice among healthcare professionals. As antibiotic resistance continues to rise, the importance of azithromycin will only continue to grow. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with azithromycin in the comments section below. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this information.
