Intro
Unlock the secrets of a CBC blood test, understanding complete blood count, hematocrit, hemoglobin, and platelet count to diagnose anemia, infection, and inflammation, with our comprehensive guide explaining the procedure, results, and implications.
A complete blood count (CBC) test, also known as a full blood count, is a crucial diagnostic tool used to evaluate the overall health of an individual. It is one of the most commonly ordered blood tests, providing valuable information about the different components of blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. The results of a CBC test can help healthcare professionals diagnose and monitor a wide range of medical conditions, from anemia and infection to leukemia and lymphoma.
The importance of a CBC test lies in its ability to provide a comprehensive overview of the blood's cellular composition. By analyzing the various components of blood, healthcare professionals can identify potential health issues, track the progression of diseases, and monitor the effectiveness of treatments. For instance, a CBC test can help diagnose anemia, a condition characterized by a lack of red blood cells or hemoglobin, which can lead to fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath. Similarly, an elevated white blood cell count can indicate the presence of an infection or inflammation, while an abnormal platelet count can suggest a bleeding disorder.
In addition to its diagnostic capabilities, a CBC test is also a useful tool for monitoring patients with chronic medical conditions, such as diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease. Regular CBC tests can help healthcare professionals track changes in blood cell counts, detect potential complications, and adjust treatment plans accordingly. Furthermore, a CBC test is often used as a screening tool for asymptomatic individuals, allowing healthcare professionals to identify potential health issues before symptoms arise. This proactive approach to healthcare can help prevent serious medical conditions, improve patient outcomes, and reduce healthcare costs.
What is a CBC Test?

A CBC test is a laboratory test that measures the levels of different blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. The test is typically performed on a sample of blood drawn from a vein in the arm, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. The laboratory uses specialized equipment to count the number of each type of blood cell and measure their size, shape, and other characteristics. The results of the test are usually reported as a series of numerical values, which can be used to diagnose and monitor a wide range of medical conditions.
Components of a CBC Test
A CBC test typically includes the following components: * Red blood cell count (RBC): measures the number of red blood cells in the blood * Hemoglobin (Hb): measures the amount of hemoglobin in the blood * Hematocrit (Hct): measures the proportion of red blood cells in the blood * Mean corpuscular volume (MCV): measures the average size of red blood cells * Mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH): measures the average amount of hemoglobin in red blood cells * Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC): measures the average concentration of hemoglobin in red blood cells * White blood cell count (WBC): measures the number of white blood cells in the blood * Platelet count: measures the number of platelets in the blood * Differential count: measures the proportion of different types of white blood cells in the bloodHow is a CBC Test Performed?
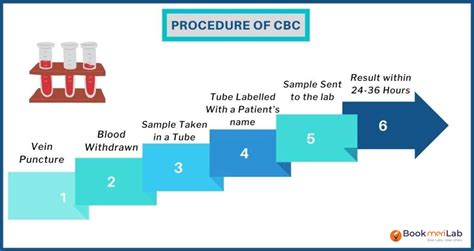
A CBC test is typically performed in a healthcare setting, such as a hospital or clinic. The test involves the following steps:
- A healthcare professional will clean and disinfect the skin where the blood sample will be drawn.
- A tourniquet will be applied to the upper arm to help locate a vein.
- A needle will be inserted into the vein, and a blood sample will be collected in a tube.
- The tourniquet will be removed, and the needle will be withdrawn.
- The blood sample will be sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Preparation for a CBC Test
To prepare for a CBC test, individuals should: * Avoid eating or drinking for at least 8 hours before the test * Avoid taking certain medications, such as anticoagulants, before the test * Inform their healthcare professional about any medical conditions or allergies they have * Wear comfortable clothing and avoid tight clothing that may interfere with the blood drawInterpreting CBC Test Results
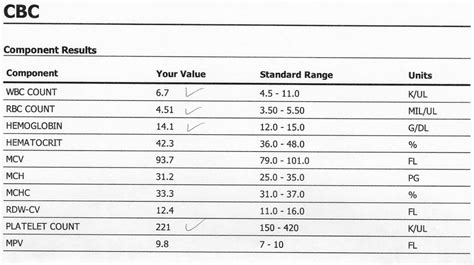
The results of a CBC test are typically reported as a series of numerical values, which can be used to diagnose and monitor a wide range of medical conditions. The following are some common abnormal results and their possible causes:
- Low red blood cell count: anemia, blood loss, or bone marrow disorders
- High red blood cell count: dehydration, polycythemia vera, or other blood disorders
- Low white blood cell count: infection, bone marrow disorders, or immunodeficiency
- High white blood cell count: infection, inflammation, or leukemia
- Low platelet count: bleeding disorders, bone marrow disorders, or certain medications
- High platelet count: thrombocytosis, infection, or inflammation
Common Conditions Diagnosed with a CBC Test
A CBC test can be used to diagnose and monitor a wide range of medical conditions, including: * Anemia * Infection * Inflammation * Leukemia * Lymphoma * Bleeding disorders * Blood clotting disorders * Bone marrow disordersLimitations and Risks of a CBC Test
While a CBC test is a valuable diagnostic tool, it has some limitations and risks. The following are some potential limitations and risks to consider:
- A CBC test may not detect all medical conditions, such as certain types of anemia or blood disorders.
- A CBC test may produce false-positive or false-negative results, which can lead to misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis.
- A CBC test may cause discomfort or pain during the blood draw.
- A CBC test may cause bruising or bleeding at the site of the blood draw.
Alternatives to a CBC Test
In some cases, alternative tests may be used to diagnose and monitor medical conditions. The following are some alternative tests that may be used: * Blood smear: a test that involves examining a sample of blood under a microscope to detect abnormal blood cells. * Bone marrow biopsy: a test that involves removing a sample of bone marrow tissue to examine for abnormal cells. * Imaging tests: such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans, which can be used to detect abnormalities in the blood or bones.What is the purpose of a CBC test?
+A CBC test is used to evaluate the overall health of an individual, diagnose and monitor medical conditions, and track the progression of diseases.
What are the components of a CBC test?
+A CBC test typically includes measurements of red blood cell count, hemoglobin, hematocrit, mean corpuscular volume, mean corpuscular hemoglobin, mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration, white blood cell count, platelet count, and differential count.
How is a CBC test performed?
+A CBC test involves drawing a blood sample from a vein in the arm, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis.
What are the limitations and risks of a CBC test?
+A CBC test may not detect all medical conditions, produce false-positive or false-negative results, cause discomfort or pain during the blood draw, or cause bruising or bleeding at the site of the blood draw.
What are the alternatives to a CBC test?
+Alternative tests may include blood smear, bone marrow biopsy, or imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans.
In conclusion, a CBC test is a valuable diagnostic tool that provides a comprehensive overview of the blood's cellular composition. By understanding the components, preparation, and interpretation of a CBC test, individuals can better appreciate the importance of this test in evaluating their overall health and diagnosing medical conditions. If you have any questions or concerns about a CBC test, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional who can provide personalized guidance and care. We encourage readers to share their experiences and ask questions in the comments section below. Additionally, we invite you to share this article with others who may benefit from this information.
