Intro
Discover what is club foot, a congenital foot deformity affecting toddlers, characterized by twisted feet, causing mobility issues, and treated with ponseti method, orthotics, and surgery to correct foot alignment and promote normal growth.
Club foot, also known as talipes equinovarus, is a common birth defect that affects the foot and ankle. It is characterized by a deformity of the foot, where the foot is twisted inward or outward, and the ankle is stiff. This condition can make it difficult for a person to walk or stand properly, and if left untreated, can lead to long-term mobility problems.
The exact cause of club foot is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some research suggests that club foot may be caused by a problem with the development of the muscles, tendons, and bones in the foot and ankle during fetal development. In some cases, club foot may be associated with other birth defects or genetic conditions, such as spina bifida or cerebral palsy.
Club foot can be diagnosed at birth or shortly after, and it is typically identified by a physical examination of the foot and ankle. In some cases, imaging tests such as X-rays or ultrasound may be used to confirm the diagnosis and to assess the severity of the condition. If left untreated, club foot can lead to a range of complications, including difficulty walking, pain, and arthritis.
Causes and Risk Factors

The exact cause of club foot is not fully understood, but there are several risk factors that may increase the likelihood of a child being born with this condition. These risk factors include a family history of club foot, as well as certain genetic conditions, such as spina bifida or cerebral palsy. Additionally, club foot is more common in boys than girls, and it is also more common in certain ethnic groups, such as African Americans and Hispanics.
In some cases, club foot may be caused by a problem with the development of the muscles, tendons, and bones in the foot and ankle during fetal development. This may be due to a variety of factors, including genetic mutations, environmental factors, or problems with the mother's health during pregnancy. For example, women who smoke during pregnancy or who have diabetes may be at increased risk of having a child with club foot.
Treatment Options
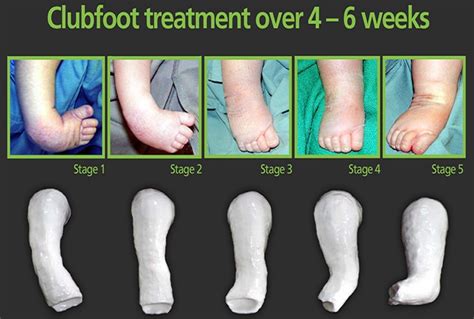
There are several treatment options available for club foot, and the most effective approach will depend on the severity of the condition and the individual needs of the child. In some cases, club foot may be treated with non-surgical methods, such as physical therapy or orthotics. These approaches can help to stretch and strengthen the muscles and tendons in the foot and ankle, and can help to improve mobility and reduce pain.In more severe cases of club foot, surgery may be necessary to correct the deformity. This may involve a range of procedures, including tendon transfers, bone grafts, or osteotomies. The goal of surgery is to improve the alignment and function of the foot and ankle, and to reduce pain and discomfort.
Symptoms and Diagnosis

The symptoms of club foot can vary depending on the severity of the condition, but common signs include a foot that is twisted inward or outward, and an ankle that is stiff. In some cases, the foot may be smaller than usual, or the toes may be curled under. Club foot can also cause pain and discomfort, especially when walking or standing.
Diagnosing club foot typically involves a physical examination of the foot and ankle, as well as imaging tests such as X-rays or ultrasound. A doctor may also assess the range of motion in the foot and ankle, and may check for any signs of muscle weakness or imbalance.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Nonsurgical treatment for club foot typically involves a range of approaches, including physical therapy, orthotics, and bracing. Physical therapy can help to stretch and strengthen the muscles and tendons in the foot and ankle, and can help to improve mobility and reduce pain.Orthotics and bracing can also be used to support the foot and ankle, and to help correct the deformity. These devices can be custom-made to fit the individual needs of the child, and can be adjusted as the child grows and develops.
Complications and Prognosis

If left untreated, club foot can lead to a range of complications, including difficulty walking, pain, and arthritis. In some cases, club foot can also cause problems with balance and coordination, and can increase the risk of falls and injuries.
The prognosis for club foot is generally good, especially if treatment is started early. With prompt and effective treatment, most children with club foot can expect to have normal or near-normal mobility and function. However, in some cases, club foot can be a recurring condition, and may require ongoing treatment and management.
Surgical Treatment
Surgical treatment for club foot typically involves a range of procedures, including tendon transfers, bone grafts, or osteotomies. The goal of surgery is to improve the alignment and function of the foot and ankle, and to reduce pain and discomfort.Surgery for club foot is typically performed under general anesthesia, and may involve a range of incisions and procedures. The type and extent of surgery will depend on the individual needs of the child, and may involve a combination of procedures to achieve the best possible outcome.
Living with Club Foot

Living with club foot can be challenging, especially for children and their families. However, with the right treatment and support, most children with club foot can lead active and fulfilling lives.
It is essential to work closely with a healthcare team to develop a treatment plan that meets the individual needs of the child. This may involve a range of approaches, including physical therapy, orthotics, and bracing, as well as surgery in some cases.
Coping and Support
Coping with club foot can be emotional and challenging, especially for families who are new to the condition. However, there are many resources and support groups available to help families navigate the challenges of club foot.Support groups can provide a sense of community and connection, and can offer valuable advice and guidance from others who have experienced similar challenges. Online resources and forums can also provide a wealth of information and support, and can help families stay up-to-date on the latest treatments and research.
Prevention and Research
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent club foot, there are several steps that can be taken to reduce the risk. These include maintaining a healthy lifestyle during pregnancy, avoiding smoking and substance abuse, and getting regular prenatal care.
Research into club foot is ongoing, and scientists are working to better understand the causes and mechanisms of the condition. This research may lead to new and improved treatments, as well as a better understanding of how to prevent club foot.
Future Directions
The future of club foot treatment is promising, with new and innovative approaches being developed all the time. These include advances in surgical techniques, as well as the development of new orthotics and bracing devices.Additionally, researchers are exploring new ways to prevent club foot, such as through the use of genetic testing and counseling. This may help to identify families who are at risk of having a child with club foot, and may allow for early intervention and treatment.
What is club foot?
+Club foot, also known as talipes equinovarus, is a common birth defect that affects the foot and ankle.
What are the symptoms of club foot?
+The symptoms of club foot can vary depending on the severity of the condition, but common signs include a foot that is twisted inward or outward, and an ankle that is stiff.
How is club foot treated?
+Club foot can be treated with a range of approaches, including physical therapy, orthotics, and bracing, as well as surgery in some cases.
Can club foot be prevented?
+While there is no guaranteed way to prevent club foot, there are several steps that can be taken to reduce the risk, including maintaining a healthy lifestyle during pregnancy and avoiding smoking and substance abuse.
What is the prognosis for club foot?
+The prognosis for club foot is generally good, especially if treatment is started early. With prompt and effective treatment, most children with club foot can expect to have normal or near-normal mobility and function.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of club foot, its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prognosis. If you have any further questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional. Additionally, we invite you to share your experiences and thoughts on club foot in the comments section below. Your input can help others who may be going through similar challenges, and can contribute to a greater understanding of this condition.
