Intro
Discover key facts about Cyanocobalamin, a vital vitamin B12 form, exploring its benefits, deficiency symptoms, and importance in nutrition, health, and energy production.
Cyanocobalamin, also known as vitamin B12, is a crucial nutrient that plays a significant role in various bodily functions. From the production of red blood cells to the maintenance of the nervous system, cyanocobalamin is essential for overall health and well-being. Despite its importance, many people are unaware of the significance of this vitamin and the benefits it provides. In this article, we will delve into the world of cyanocobalamin, exploring its importance, benefits, and everything in between.
The human body relies heavily on cyanocobalamin to function properly. It is involved in the production of red blood cells, which are responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body. Without sufficient amounts of cyanocobalamin, the body may not be able to produce enough red blood cells, leading to a range of health problems. Furthermore, cyanocobalamin plays a critical role in the maintenance of the nervous system, helping to regulate the transmission of nerve impulses and maintain the health of nerve cells.
In addition to its role in the production of red blood cells and the maintenance of the nervous system, cyanocobalamin is also involved in the metabolism of fatty acids and amino acids. It helps to convert these compounds into energy, which is then used to power the body's various functions. With so many important roles, it is no wonder that cyanocobalamin is considered an essential nutrient. However, many people are unaware of the benefits and importance of this vitamin, and it is often overlooked in favor of other, more well-known nutrients.
What is Cyanocobalamin?

Benefits of Cyanocobalamin
The benefits of cyanocobalamin are numerous and well-documented. Some of the most significant advantages of this vitamin include: * Improved red blood cell production: Cyanocobalamin is essential for the production of red blood cells, which are responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body. * Maintenance of the nervous system: Cyanocobalamin helps to regulate the transmission of nerve impulses and maintain the health of nerve cells. * Boosted energy levels: Cyanocobalamin is involved in the metabolism of fatty acids and amino acids, helping to convert these compounds into energy. * Improved heart health: Cyanocobalamin has been shown to help lower homocysteine levels, which is a risk factor for heart disease. * Enhanced cognitive function: Cyanocobalamin has been linked to improved cognitive function, including better memory and concentration.Food Sources of Cyanocobalamin

Cyanocobalamin Deficiency
A deficiency in cyanocobalamin can have serious health consequences. Some of the most common symptoms of cyanocobalamin deficiency include: * Fatigue and weakness * Shortness of breath * Dizziness and lightheadedness * Pale skin * Diarrhea or constipation * Numbness or tingling in the hands and feetCauses of Cyanocobalamin Deficiency
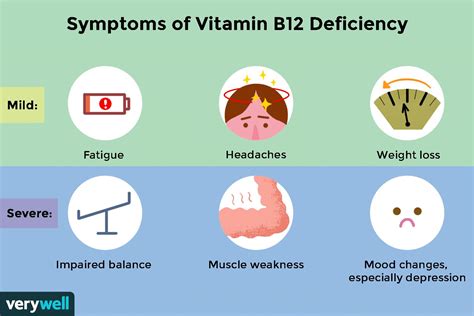
Treatment of Cyanocobalamin Deficiency
Treatment of cyanocobalamin deficiency typically involves supplementation with cyanocobalamin. This can be in the form of oral supplements or injections, depending on the severity of the deficiency. In some cases, dietary changes may also be necessary to ensure adequate intake of cyanocobalamin.Interactions and Side Effects
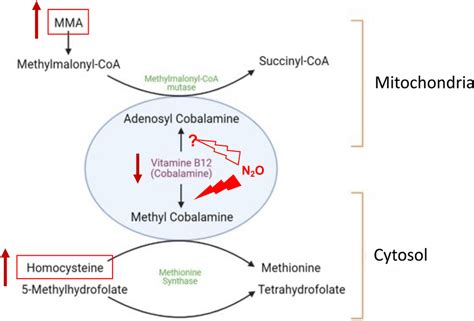
Precautions and Warnings
While cyanocobalamin is generally considered safe, there are certain precautions and warnings to be aware of: * Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Cyanocobalamin is essential for fetal development, and pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult with their healthcare provider before taking supplements. * Allergies: Some people may be allergic to cyanocobalamin, and may experience symptoms such as hives, itching, or difficulty breathing. * Kidney or liver disease: People with kidney or liver disease should consult with their healthcare provider before taking cyanocobalamin supplements.Conclusion and Future Directions
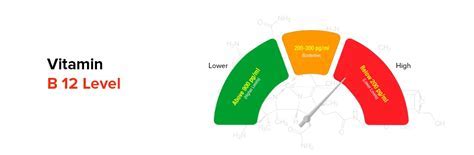
What is the recommended daily intake of cyanocobalamin?
+The recommended daily intake of cyanocobalamin varies by age and other factors, but is generally around 2.4-2.6 micrograms per day for adults.
Can I get enough cyanocobalamin from plant-based sources?
+While plant-based sources can provide some cyanocobalamin, it is often not enough to meet daily needs. Vegetarians and vegans may need to consider supplementation or fortified foods to ensure adequate intake.
What are the symptoms of cyanocobalamin deficiency?
+Symptoms of cyanocobalamin deficiency can include fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, and numbness or tingling in the hands and feet.
Can I take too much cyanocobalamin?
+While cyanocobalamin is generally considered safe, taking too much can cause side effects such as diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. It is essential to follow recommended dosages and consult with a healthcare provider before taking supplements.
How can I ensure I am getting enough cyanocobalamin?
+To ensure you are getting enough cyanocobalamin, eat a balanced diet that includes animal products, consider supplementation, and consult with a healthcare provider if you have concerns about your intake.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of cyanocobalamin and its importance for overall health and well-being. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences with cyanocobalamin, please don't hesitate to comment below. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this information.
