Intro
Eosinophilic esophagitis, a chronic immune system disease, has been increasingly recognized as a significant cause of esophageal dysfunction. The condition is characterized by the presence of eosinophils, a type of white blood cell, in the esophagus, leading to inflammation and damage. This disease often presents with symptoms similar to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), making diagnosis and treatment challenging. Understanding eosinophilic esophagitis is crucial for both healthcare providers and patients to manage the condition effectively and improve quality of life.
The importance of recognizing eosinophilic esophagitis lies in its potential to cause severe complications if left untreated. These complications can include esophageal narrowing (stricture), which may lead to difficulty swallowing, and esophageal rupture, a medical emergency. Furthermore, eosinophilic esophagitis is often associated with other allergic conditions, such as asthma and atopic dermatitis, suggesting a complex interplay between allergic responses and gastrointestinal health. As research into this condition continues to evolve, it is essential for patients and healthcare providers to stay informed about the latest in diagnosis, treatment, and management strategies.
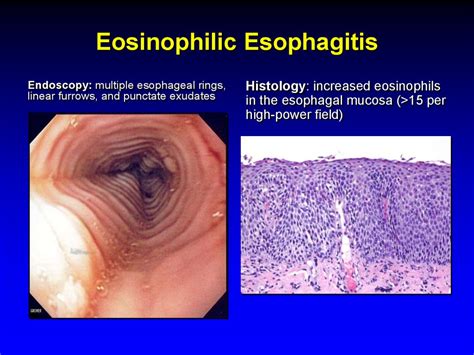
Eosinophilic esophagitis affects individuals of all ages, although it is more commonly diagnosed in children and young adults. The symptoms can vary widely, from mild discomfort to severe pain and difficulty swallowing. The variability in presentation, combined with the fact that symptoms can mimic those of other conditions, underscores the need for a comprehensive diagnostic approach. This includes endoscopy with biopsy, where a tissue sample from the esophagus is examined for the presence of eosinophils, as well as other tests to rule out alternative causes of symptoms. By understanding the complexities of eosinophilic esophagitis, individuals can better navigate the healthcare system and advocate for their needs.
Introduction to Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact causes of eosinophilic esophagitis are not fully understood, but several factors are known to contribute to its development. These include: - Genetic predisposition: Individuals with a family history of eosinophilic esophagitis or other atopic diseases are at increased risk. - Allergens: Food and aeroallergens can trigger the immune response leading to eosinophilic inflammation. - Immune system dysregulation: An imbalance in the immune response, with an overactive Th2 response, is thought to play a critical role.Diagnosis of Eosinophilic Esophagitis

Treatment Options
Treatment for eosinophilic esophagitis is aimed at reducing inflammation, preventing future flares, and managing symptoms. The main treatment options include: - Dietary therapy: Avoidance of known food triggers, elemental diets, or empiric diets. - Medications: Corticosteroids, either topical (swallowed) or systemic, to reduce inflammation. - Esophageal dilation: For patients with significant esophageal narrowing.Living with Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Nutrition and Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Nutritional management is a critical component of treating eosinophilic esophagitis. Patients may need to follow specific diets to avoid trigger foods, which can vary widely among individuals. Some common trigger foods include dairy, eggs, wheat, soy, fish, and nuts. Elemental diets, which involve consuming only amino acid-based formulas, may be recommended in severe cases or when the trigger foods are not identified.Future Directions in Eosinophilic Esophagitis Research

Conclusion and Next Steps
Eosinophilic esophagitis is a complex and multifaceted condition that requires a comprehensive approach to management. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals affected by this condition can better navigate their care and improve their quality of life. As research continues to uncover the intricacies of eosinophilic esophagitis, it is essential for patients, families, and healthcare providers to stay informed and engaged in the pursuit of better treatments and, ultimately, a cure.What are the common symptoms of eosinophilic esophagitis?
+Common symptoms include difficulty swallowing, food impaction, chest pain, and abdominal pain. In children, symptoms can also include refusal to eat and failure to thrive.
How is eosinophilic esophagitis diagnosed?
+Diagnosis involves a combination of clinical evaluation, endoscopy with biopsy, and sometimes other tests to rule out alternative causes of symptoms.
What are the treatment options for eosinophilic esophagitis?
+Treatment options include dietary therapy (avoiding trigger foods), medications (such as corticosteroids), and esophageal dilation for severe narrowing.
We invite you to share your experiences and questions about eosinophilic esophagitis in the comments below. Your insights can help others understand this complex condition better and foster a supportive community for those affected. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from this information. Together, we can work towards raising awareness and improving the lives of individuals with eosinophilic esophagitis.
