Intro
Discover what Famotidine is, a histamine-2 blocker treating heartburn, acid reflux, and ulcers, with insights into its uses, side effects, and interactions, for effective gastrointestinal relief and management.
Famotidine is a medication that has been widely used for decades to treat various gastrointestinal conditions. It belongs to a class of drugs known as histamine-2 (H2) blockers, which work by reducing the amount of stomach acid produced in the body. This reduction in stomach acid helps to alleviate symptoms such as heartburn, acid reflux, and stomach ulcers. Famotidine is commonly used to treat conditions like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, and peptic ulcers. Its effectiveness and relatively mild side effect profile have made it a popular choice among both healthcare professionals and patients.
The importance of managing stomach acid cannot be overstated, as excessive acid production can lead to significant discomfort and potentially serious health issues. Conditions like GERD, for instance, can cause chronic heartburn, difficulty swallowing, and chest pain, significantly impacting a person's quality of life. By reducing stomach acid, famotidine provides relief from these symptoms, allowing individuals to manage their conditions more effectively. Furthermore, the medication's ability to heal and prevent ulcers makes it a crucial tool in the prevention of complications that can arise from untreated or poorly managed gastrointestinal diseases.
Understanding how famotidine works is essential to appreciating its benefits. The drug acts on the histamine receptors in the stomach lining, blocking the action of histamine—a chemical that stimulates the production of stomach acid. By inhibiting this process, famotidine decreases the amount of acid produced, thereby reducing the risk of acid-related damage to the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. This mechanism of action not only provides symptom relief but also promotes the healing of existing ulcers and prevents the formation of new ones. The effectiveness of famotidine in managing gastrointestinal conditions has been well-documented in clinical trials, making it a trusted medication among healthcare providers.
Benefits of Famotidine

Key Benefits
Some of the key benefits of famotidine include: - Rapid relief from heartburn and acid reflux symptoms - Healing and prevention of stomach and duodenal ulcers - Effective management of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome - Reduction in the risk of complications associated with excessive stomach acid - Generally well-tolerated with a mild side effect profileWorking Mechanism of Famotidine
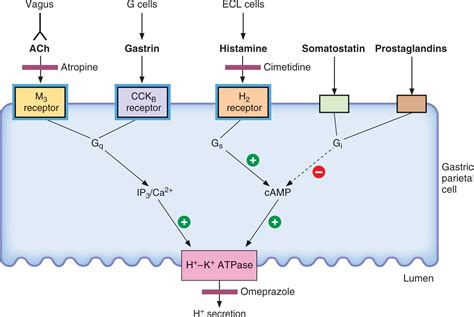
Steps Involved in the Action of Famotidine
The steps involved in the action of famotidine can be outlined as follows: 1. **Binding to H2 Receptors**: Famotidine binds to the H2 receptors on the parietal cells in the stomach, competing with histamine. 2. **Inhibition of Acid Secretion**: By blocking the H2 receptors, famotidine inhibits the secretion of gastric acid stimulated by histamine. 3. **Reduction in Acid Production**: The overall effect is a decrease in the production of stomach acid, which helps in alleviating symptoms of acid-related diseases. 4. **Healing of Ulcers**: The reduced acid environment promotes the healing of existing ulcers and prevents the formation of new ones.Steps to Take Famotidine
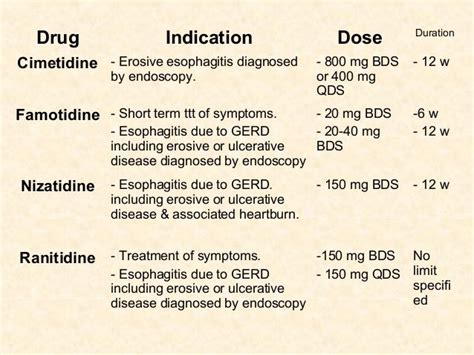
Practical Tips for Taking Famotidine
Some practical tips for taking famotidine include: - Always follow the prescribed dosage and do not exceed the recommended dose without consulting a healthcare provider. - Be consistent with the timing of doses to maintain therapeutic levels of the medication. - Monitor for side effects and report any concerns to a healthcare provider. - Do not stop taking famotidine without consulting a healthcare provider, as this can lead to rebound acid hypersecretion.Famotidine Side Effects

Managing Side Effects
To manage side effects, consider the following: - **Headache and Dizziness**: Stay hydrated and avoid standing up quickly from a sitting or lying position. - **Gastrointestinal Side Effects**: Taking famotidine with food may help alleviate these symptoms. - **Serious Side Effects**: Seek immediate medical attention if symptoms of an allergic reaction, liver dysfunction, or blood disorders occur.Famotidine Interactions
Precautions and Warnings
- **Pregnancy and Breastfeeding**: Famotidine is generally considered safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding, but it's essential to consult a healthcare provider before taking any medication. - **Allergic Reactions**: Individuals allergic to famotidine or other H2 blockers should avoid taking the medication. - **Liver and Kidney Disease**: Patients with liver or kidney disease may require dose adjustments, as famotidine is metabolized in the liver and excreted by the kidneys.Conclusion and Future Directions

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with famotidine in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from this information. Your engagement helps us create more relevant and useful content for our readers.
What is the primary use of famotidine?
+Famotidine is primarily used to treat conditions like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, and peptic ulcers by reducing stomach acid production.
How does famotidine work?
+Famotidine works by blocking histamine receptors in the stomach, which reduces the production of stomach acid. This action helps in healing and preventing ulcers and alleviating symptoms of acid reflux and heartburn.
What are the common side effects of famotidine?
+Common side effects of famotidine include headache, dizziness, constipation, and diarrhea. Less common but more serious side effects can include allergic reactions, liver dysfunction, and blood disorders.
Can I take famotidine with other medications?
+Famotidine can interact with other medications. It's essential to inform your healthcare provider about all medications you are taking before starting famotidine to avoid potential interactions.
Is famotidine safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding?
+Famotidine is generally considered safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding, but it's crucial to consult a healthcare provider before taking any medication during these periods.
