Intro
Discover 5 uses of Fluconazole, an antifungal medication, including treating yeast infections, thrush, and ringworm, with applications in veterinary medicine and prevention of fungal diseases, highlighting its efficacy and safety as a triazole antifungal agent.
The importance of antifungal medications cannot be overstated, especially in today's world where fungal infections are becoming increasingly common. One such medication that has gained significant attention in recent years is Fluconazole. This powerful antifungal agent has been widely used to treat a variety of fungal infections, ranging from mild to severe. In this article, we will delve into the 5 uses of Fluconazole, exploring its benefits, working mechanisms, and key information related to its usage.
Fluconazole is a triazole antifungal agent that works by inhibiting the growth of fungi. It is commonly used to treat fungal infections such as vaginal yeast infections, thrush, and ringworm. The medication is available in various forms, including oral tablets, suspensions, and injectable solutions. Its ease of use and effectiveness have made it a popular choice among healthcare professionals and patients alike.
The rise of fungal infections has been alarming, with many people suffering from recurring infections. This has led to an increased demand for effective treatments, and Fluconazole has emerged as a leading solution. Its ability to target a wide range of fungi, including Candida, Aspergillus, and Cryptococcus, has made it an essential medication in the fight against fungal infections. In the following sections, we will explore the 5 uses of Fluconazole in more detail, discussing its benefits, side effects, and usage guidelines.
Introduction to Fluconazole

How Fluconazole Works
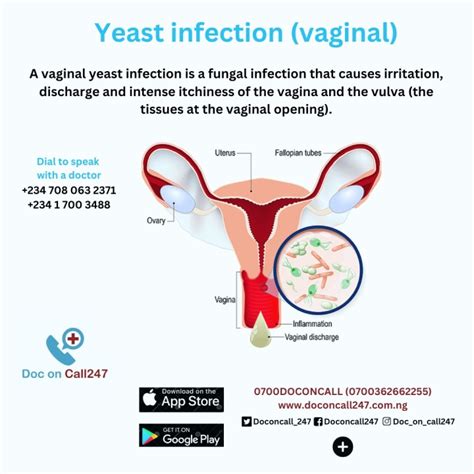
Fluconazole is available in various forms, including oral tablets, suspensions, and injectable solutions. The medication is typically taken orally, and its absorption is rapid and complete. It is then distributed throughout the body, with high concentrations found in the liver, kidneys, and lungs. Fluconazole is metabolized by the liver and excreted in the urine, with a half-life of approximately 30 hours.Treatment of Vaginal Yeast Infections
Benefits and Side Effects
The benefits of using Fluconazole to treat vaginal yeast infections include its high efficacy, ease of use, and minimal side effects. The medication is generally well-tolerated, with common side effects including nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. However, in rare cases, Fluconazole can cause more serious side effects, such as liver damage and allergic reactions.Treatment of Thrush

Usage Guidelines
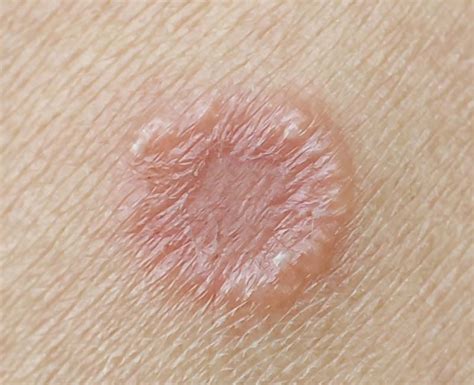
When using Fluconazole to treat thrush, it is essential to follow the recommended dosage and usage guidelines. The medication is typically taken for 7-14 days, depending on the severity of the infection. It is also important to maintain good oral hygiene, including brushing and flossing regularly, to help prevent the recurrence of thrush.Treatment of Ringworm
Practical Examples
In practical terms, Fluconazole is often used to treat ringworm in people who have weakened immune systems or who are taking immunosuppressive medications. The medication is typically taken orally, and its ability to inhibit the growth of fungi makes it an effective treatment option. For example, a person with ringworm may be prescribed Fluconazole for 4-6 weeks, depending on the severity of the infection.Treatment of Cryptococcal Meningitis

Statistical Data
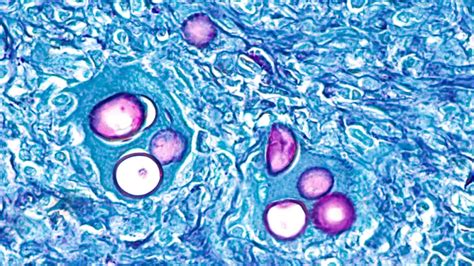
According to statistical data, Fluconazole is effective in treating cryptococcal meningitis, with a success rate of approximately 70-80%. The medication is typically taken orally, and its ability to inhibit the growth of Cryptococcus neoformans makes it an effective treatment option. For example, a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine found that Fluconazole was effective in treating cryptococcal meningitis in people with HIV/AIDS.Treatment of Coccidioidomycosis
Benefits and Side Effects
The benefits of using Fluconazole to treat coccidioidomycosis include its high efficacy, ease of use, and minimal side effects. The medication is generally well-tolerated, with common side effects including nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. However, in rare cases, Fluconazole can cause more serious side effects, such as liver damage and allergic reactions.What is Fluconazole used for?
+Fluconazole is used to treat a variety of fungal infections, including vaginal yeast infections, thrush, ringworm, cryptococcal meningitis, and coccidioidomycosis.
How does Fluconazole work?
+Fluconazole works by inhibiting the synthesis of ergosterol, a critical component of fungal cell membranes. This leads to the disruption of cell membrane function, ultimately resulting in the death of the fungal cells.
What are the side effects of Fluconazole?
+The common side effects of Fluconazole include nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. However, in rare cases, the medication can cause more serious side effects, such as liver damage and allergic reactions.
How long does it take for Fluconazole to work?
+The time it takes for Fluconazole to work varies depending on the type of infection being treated. For example, vaginal yeast infections may be cleared within 1-3 days, while more severe infections such as cryptococcal meningitis may take several weeks to treat.
Can Fluconazole be used to treat other types of infections?
+No, Fluconazole is specifically designed to treat fungal infections. It should not be used to treat bacterial or viral infections, as it will not be effective and may cause unnecessary side effects.
In conclusion, Fluconazole is a powerful antifungal agent that has been widely used to treat a variety of fungal infections. Its ability to inhibit the growth of fungi, combined with its ease of use and minimal side effects, make it an essential medication in the fight against fungal infections. Whether you are suffering from a vaginal yeast infection, thrush, ringworm, cryptococcal meningitis, or coccidioidomycosis, Fluconazole may be an effective treatment option. We encourage you to consult with your healthcare professional to determine the best course of treatment for your specific infection. Share this article with others who may be suffering from fungal infections, and let's work together to raise awareness about the importance of antifungal medications like Fluconazole.
