Intro
Discover gabapentin uses and benefits for nerve pain, epilepsy, and anxiety, highlighting its efficacy as an anticonvulsant and neuropathic pain reliever, with related treatments like fibromyalgia and restless leg syndrome management.
The world of medicine is vast and complex, with numerous medications available to treat a wide range of conditions. Among these, gabapentin has emerged as a versatile and widely used drug, with a variety of applications that have significantly improved the lives of many patients. Initially developed as an anticonvulsant, gabapentin's uses have expanded over the years, making it a crucial component in the treatment of several neurological and psychiatric disorders. Its benefits are multifaceted, offering relief from symptoms that can significantly impact an individual's quality of life.
Gabapentin's mechanism of action, although not fully understood, is believed to involve the modulation of calcium channels in the nervous system, which in turn affects the release of various neurotransmitters. This unique action allows gabapentin to have a broad spectrum of therapeutic effects, making it useful in managing conditions such as epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and even certain psychiatric disorders. The drug's ability to cross the blood-brain barrier efficiently contributes to its efficacy in treating neurological conditions, providing patients with much-needed relief from debilitating symptoms.
The versatility of gabapentin lies in its application across various medical disciplines, from neurology to psychiatry. Its use in treating epilepsy, for instance, has been well-documented, with gabapentin often prescribed as an adjunct therapy to help control seizures. Additionally, its efficacy in managing neuropathic pain, a condition often characterized by shooting, burning, or stabbing pain due to nerve damage, has made it a valuable option for patients suffering from this debilitating condition. Furthermore, gabapentin's role in psychiatric care, particularly in the treatment of mood disorders and anxiety, underscores its potential as a therapeutic agent beyond its original anticonvulsant purpose.
Gabapentin Mechanism of Action
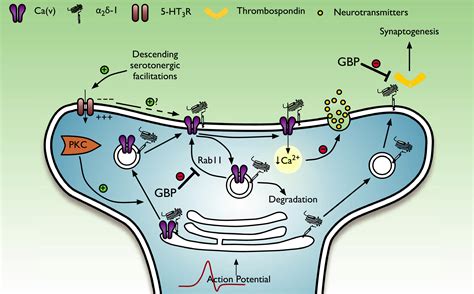
Understanding gabapentin's mechanism of action is crucial to appreciating its therapeutic benefits. While the exact mechanisms are complex and not fully elucidated, research suggests that gabapentin binds to voltage-gated calcium channels, specifically the alpha2-delta subunit, which is widely distributed in the central nervous system. This binding modulates the release of excitatory neurotransmitters, such as glutamate, and inhibitory neurotransmitters, like gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), thereby exerting its anticonvulsant and analgesic effects. This unique mechanism of action distinguishes gabapentin from other anticonvulsants and contributes to its efficacy in treating a range of neurological conditions.
Benefits for Neuropathic Pain
Gabapentin's benefits in managing neuropathic pain are well-documented. Neuropathic pain, resulting from damage to the nervous system, can be challenging to treat, with many patients experiencing inadequate relief from traditional pain medications. Gabapentin, however, has been shown to be effective in reducing the intensity of neuropathic pain, improving sleep quality, and enhancing overall quality of life for these patients. Its ability to modulate neurotransmitter release and reduce excitatory neurotransmission is thought to contribute to its analgesic effects.Gabapentin in Epilepsy Treatment

In the context of epilepsy, gabapentin is often used as an adjunctive therapy, meaning it is prescribed in addition to other antiepileptic drugs to help control seizures. Its efficacy in reducing the frequency of seizures, particularly partial seizures and generalized seizures, has made it a valuable component of epilepsy management. Gabapentin's role in epilepsy treatment underscores its neuroprotective properties and its ability to stabilize neuronal membranes, thereby reducing the propensity for seizure activity.
Psychiatric Applications
Beyond its neurological applications, gabapentin has shown promise in the treatment of certain psychiatric disorders. Its anxiolytic (anxiety-reducing) effects have been observed in both clinical and preclinical studies, suggesting that gabapentin may be useful in managing anxiety disorders, including social anxiety disorder and generalized anxiety disorder. Additionally, gabapentin's mood-stabilizing properties make it a potential therapeutic option for patients with bipolar disorder, particularly for the treatment of manic episodes. While more research is needed to fully understand gabapentin's psychiatric applications, its potential as a therapeutic agent in this field is undeniable.Gabapentin Side Effects and Precautions

As with any medication, gabapentin is not without its side effects. Common adverse effects include dizziness, drowsiness, fatigue, and ataxia (loss of coordination). In some patients, gabapentin can cause mood changes, such as irritability or anxiety, although these effects are less common. It is essential for patients to be aware of these potential side effects and to discuss any concerns with their healthcare provider. Furthermore, gabapentin should be used with caution in certain patient populations, including those with renal impairment, as it is primarily excreted through the kidneys. Pregnant women should also consult their healthcare provider before taking gabapentin, as its safety during pregnancy has not been fully established.
Dosage and Administration
The dosage of gabapentin varies depending on the condition being treated and the patient's response to the medication. For epilepsy, the typical starting dose is 300 mg, taken three times a day, which can be gradually increased to an effective dose. For neuropathic pain, the dosage may start at 300 mg on the first day, 600 mg on the second day, and 900 mg on the third day, with further adjustments based on patient response. It is crucial to follow the prescribed dosage and administration instructions carefully to maximize gabapentin's therapeutic benefits while minimizing its side effects.Gabapentin Interactions
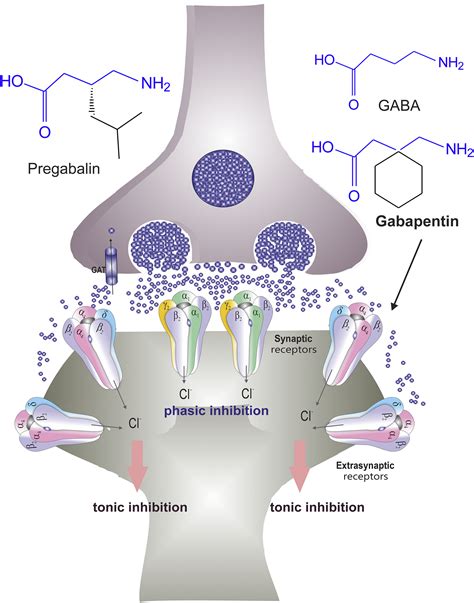
Gabapentin can interact with other medications, which may affect its efficacy or increase the risk of side effects. For instance, gabapentin can enhance the effects of other central nervous system depressants, such as opioids, benzodiazepines, and barbiturates, potentially leading to increased sedation or respiratory depression. Additionally, gabapentin may interact with certain antacids, which can reduce its absorption and efficacy. Patients should inform their healthcare provider about all medications they are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, to minimize potential interactions.
Future Directions
The future of gabapentin research holds much promise, with ongoing studies exploring its potential applications in various medical fields. Its unique mechanism of action and relatively favorable side effect profile make it an attractive candidate for treating conditions beyond its current indications. Further research into gabapentin's effects on mood disorders, anxiety disorders, and even certain types of chronic pain could lead to the development of new therapeutic strategies, offering hope to patients who have not responded adequately to current treatments.Gabapentin and Quality of Life

One of the most significant benefits of gabapentin is its potential to improve patients' quality of life. By effectively managing symptoms of epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and certain psychiatric disorders, gabapentin can significantly reduce the burden of these conditions on daily life. Improved sleep quality, reduced pain intensity, and enhanced mood stability can all contribute to increased productivity, better social interactions, and a more positive outlook on life. As such, gabapentin's impact extends beyond mere symptom management, offering patients a chance to regain control over their lives and pursue their goals with renewed vigor.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In conclusion, gabapentin's uses and benefits are multifaceted, reflecting its versatility as a therapeutic agent. From its origins as an anticonvulsant to its current applications in treating neuropathic pain and certain psychiatric disorders, gabapentin has emerged as a valuable medication in modern healthcare. Its unique mechanism of action, relatively favorable side effect profile, and potential for improving patients' quality of life make it an essential component of treatment strategies for various conditions. As research continues to uncover new aspects of gabapentin's therapeutic potential, its role in improving the lives of patients worldwide is likely to expand, offering hope and relief to those affected by debilitating neurological and psychiatric disorders.What is gabapentin primarily used for?
+Gabapentin is primarily used for the treatment of epilepsy and neuropathic pain. It is also used in the management of certain psychiatric disorders, such as anxiety and mood disorders.
How does gabapentin work?
+Gabapentin works by modulating the release of neurotransmitters in the brain, specifically by binding to voltage-gated calcium channels. This action helps to reduce excitatory neurotransmission, which can contribute to its anticonvulsant and analgesic effects.
What are the common side effects of gabapentin?
+Common side effects of gabapentin include dizziness, drowsiness, fatigue, and ataxia. Less common side effects can include mood changes, such as irritability or anxiety. It is essential to discuss any concerns with a healthcare provider.
Can gabapentin be used in pregnant women?
+The safety of gabapentin during pregnancy has not been fully established. Pregnant women should consult their healthcare provider before taking gabapentin to discuss the potential risks and benefits.
How should gabapentin be taken?
+Gabapentin should be taken as directed by a healthcare provider. The dosage and administration instructions can vary depending on the condition being treated and the patient's response to the medication.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with gabapentin in the comments below. Your insights can help others understand the benefits and challenges of this medication, contributing to a more informed and supportive community. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from this information. Together, we can promote a better understanding of gabapentin and its role in improving the lives of patients worldwide.
