Intro
Learn about Hemoglobin A1c, a blood test measuring average glucose levels, diagnosing diabetes, and monitoring blood sugar control, with related terms like glycated hemoglobin, HbA1c levels, and diabetes management.
Hemoglobin A1c, also known as HbA1c, is a protein in red blood cells that is bound to glucose. It is a crucial measure of average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months. The HbA1c test is widely used to diagnose and monitor diabetes, as well as to assess the risk of developing cardiovascular disease. In this article, we will delve into the importance of HbA1c, its working mechanisms, and the steps to maintain healthy HbA1c levels.
The importance of HbA1c lies in its ability to provide a comprehensive picture of blood glucose control. Unlike regular blood glucose tests, which only measure glucose levels at a specific point in time, HbA1c reflects average glucose levels over an extended period. This makes it an essential tool for healthcare providers to evaluate the effectiveness of diabetes treatment plans and make informed decisions about patient care. Moreover, research has shown that high HbA1c levels are associated with an increased risk of complications, such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage.
The HbA1c test is relatively simple and non-invasive. It involves a blood draw, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. The results are typically reported as a percentage, with higher percentages indicating higher average blood glucose levels. For people without diabetes, a normal HbA1c level is typically below 5.7%. For those with diabetes, the American Diabetes Association recommends an HbA1c target of less than 7%. However, individual targets may vary depending on factors such as age, health status, and the presence of other medical conditions.
Understanding HbA1c
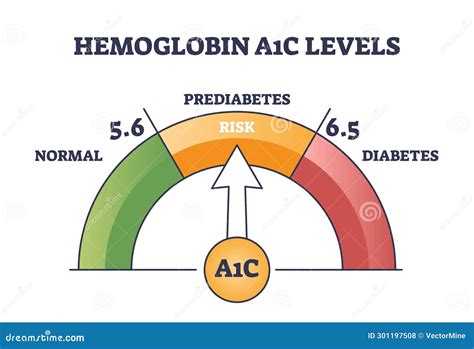
To understand HbA1c, it is essential to know how it is formed. Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen to different parts of the body. When glucose is present in the blood, it binds to hemoglobin, forming a molecule called glycated hemoglobin. The more glucose in the blood, the more hemoglobin is glycated. Since red blood cells have a lifespan of approximately 120 days, the HbA1c test can provide a snapshot of average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months.
Factors That Affect HbA1c Levels
Several factors can influence HbA1c levels, including: * Red blood cell lifespan: Variations in red blood cell lifespan can affect HbA1c levels. For example, people with conditions that shorten red blood cell lifespan, such as anemia, may have lower HbA1c levels. * Hemoglobin variants: Certain hemoglobin variants, such as sickle cell disease, can affect HbA1c measurements. * Kidney function: Impaired kidney function can lead to increased HbA1c levels, as the kidneys play a crucial role in glucose regulation. * Liver function: Liver disease can also impact HbA1c levels, as the liver is involved in glucose metabolism.Benefits of Maintaining Healthy HbA1c Levels
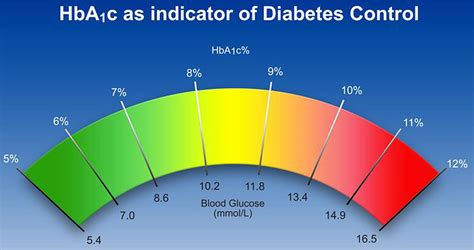
Maintaining healthy HbA1c levels is crucial for people with diabetes, as it can help prevent or delay the onset of complications. Some benefits of healthy HbA1c levels include:
- Reduced risk of cardiovascular disease: High HbA1c levels are associated with an increased risk of heart disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease.
- Improved kidney function: Healthy HbA1c levels can help prevent kidney damage and reduce the risk of kidney failure.
- Enhanced nerve function: High blood glucose levels can damage nerves, leading to conditions such as neuropathy. Maintaining healthy HbA1c levels can help prevent or slow the progression of nerve damage.
Steps to Maintain Healthy HbA1c Levels
To maintain healthy HbA1c levels, follow these steps: 1. **Monitor blood glucose levels regularly**: Regular blood glucose monitoring can help identify patterns and trends, allowing for timely adjustments to treatment plans. 2. **Adhere to medication regimens**: Take medications as prescribed, and work with healthcare providers to adjust dosages or switch medications if necessary. 3. **Engage in regular physical activity**: Regular exercise can help improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood glucose levels. 4. **Eat a balanced diet**: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods, such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. 5. **Stay hydrated**: Drink plenty of water to help regulate blood glucose levels and prevent dehydration.HbA1c and Cardiovascular Disease

Research has shown that high HbA1c levels are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. The mechanisms underlying this relationship are complex and involve multiple factors, including:
- Inflammation: High blood glucose levels can lead to chronic inflammation, which can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Oxidative stress: High glucose levels can also lead to oxidative stress, which can damage blood vessels and contribute to the development of cardiovascular disease.
- Endothelial dysfunction: High HbA1c levels can impair endothelial function, leading to reduced blood flow and increased blood pressure.
Managing HbA1c Levels to Reduce Cardiovascular Risk
To reduce cardiovascular risk, it is essential to manage HbA1c levels effectively. This can be achieved through: * **Lifestyle modifications**: Engage in regular physical activity, eat a balanced diet, and maintain a healthy weight. * **Medication adherence**: Take medications as prescribed, and work with healthcare providers to adjust dosages or switch medications if necessary. * **Regular monitoring**: Regularly monitor blood glucose levels and HbA1c levels to identify patterns and trends.HbA1c and Kidney Disease
High HbA1c levels are also associated with an increased risk of kidney disease. The kidneys play a crucial role in glucose regulation, and high blood glucose levels can damage kidney function over time. To reduce the risk of kidney disease, it is essential to:
- Monitor kidney function regularly: Regularly monitor kidney function, including glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and urine albumin levels.
- Manage blood pressure: High blood pressure can damage kidney function, so it is essential to manage blood pressure through lifestyle modifications and medication.
- Maintain healthy HbA1c levels: Maintaining healthy HbA1c levels can help prevent or slow the progression of kidney disease.
Steps to Reduce Kidney Disease Risk
To reduce the risk of kidney disease, follow these steps: 1. **Stay hydrated**: Drink plenty of water to help regulate blood glucose levels and prevent dehydration. 2. **Eat a kidney-friendly diet**: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods, and limit intake of foods high in salt, sugar, and unhealthy fats. 3. **Engage in regular physical activity**: Regular exercise can help improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood glucose levels. 4. **Manage stress**: Chronic stress can damage kidney function, so it is essential to manage stress through relaxation techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing.Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, HbA1c is a crucial measure of average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months. Maintaining healthy HbA1c levels is essential for people with diabetes, as it can help prevent or delay the onset of complications. By understanding the factors that affect HbA1c levels, managing HbA1c levels effectively, and reducing cardiovascular and kidney disease risk, individuals can take control of their health and improve their overall well-being.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with HbA1c in the comments below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out. Additionally, we encourage you to share this article with friends and family who may benefit from learning more about HbA1c.
What is the normal range for HbA1c levels?
+For people without diabetes, a normal HbA1c level is typically below 5.7%. For those with diabetes, the American Diabetes Association recommends an HbA1c target of less than 7%.
How often should I get my HbA1c levels checked?
+The frequency of HbA1c testing depends on individual factors, such as the presence of diabetes, kidney disease, or cardiovascular disease. Typically, HbA1c levels are checked every 3-6 months.
Can I lower my HbA1c levels through lifestyle modifications?
+Yes, lifestyle modifications, such as regular physical activity, a balanced diet, and weight management, can help lower HbA1c levels. Additionally, stress management and getting enough sleep can also contribute to healthy HbA1c levels.
