Intro
Discover Hirschsprungs Disease, a congenital condition affecting bowel movements, characterized by intestinal obstruction, constipation, and enterocolitis, requiring surgical treatment and management.
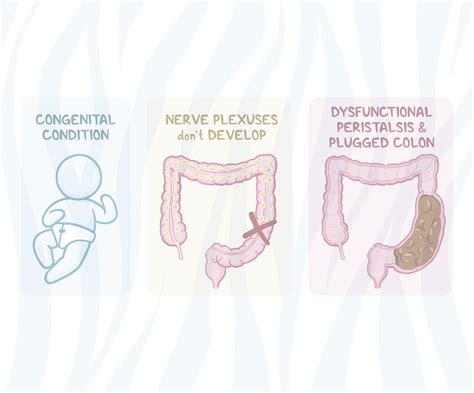
Hirschsprung's disease is a rare congenital condition that affects the large intestine, also known as the colon. It is characterized by the absence of nerve cells, known as ganglia, in the muscle layers of the colon, which can lead to severe constipation, intestinal obstruction, and other complications. The disease is usually diagnosed in newborns, but it can also be diagnosed in older children and adults. In this article, we will delve into the world of Hirschsprung's disease, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and management strategies.
The importance of understanding Hirschsprung's disease cannot be overstated. This condition can have a significant impact on a person's quality of life, causing chronic constipation, abdominal pain, and other symptoms that can be debilitating. Moreover, if left untreated, Hirschsprung's disease can lead to serious complications, such as intestinal obstruction, perforation, and peritonitis. Therefore, it is crucial to recognize the signs and symptoms of the disease and seek medical attention promptly. By doing so, individuals can receive timely and effective treatment, which can significantly improve their overall health and well-being.
Hirschsprung's disease is a complex condition that requires a comprehensive approach to management. While it is a rare condition, affecting only about 1 in 5,000 births, it is essential to raise awareness about the disease to promote early detection and treatment. In addition, advancements in medical technology and surgical techniques have improved the outcomes for individuals with Hirschsprung's disease, offering new hope for those affected by the condition. As we explore the world of Hirschsprung's disease, we will examine the latest research, treatment options, and management strategies, providing readers with a comprehensive understanding of the condition.
Causes and Risk Factors of Hirschsprung's Disease
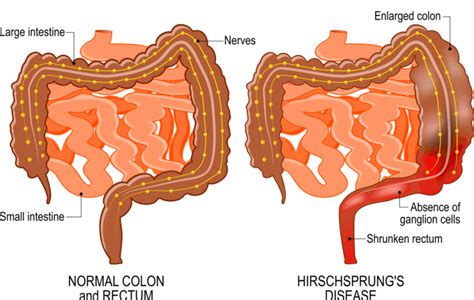
Several risk factors have been identified, including family history, genetic syndromes, and prenatal exposure to certain toxins. For example, individuals with a family history of Hirschsprung's disease are more likely to develop the condition. Additionally, certain genetic syndromes, such as Down syndrome, can increase the risk of developing Hirschsprung's disease. It is essential to note that the presence of these risk factors does not guarantee the development of the disease, and many individuals with Hirschsprung's disease do not have a family history or genetic syndrome.
Symptoms of Hirschsprung's Disease

In some cases, individuals with Hirschsprung's disease may experience enterocolitis, which is an inflammation of the intestines. This can lead to severe diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fever. If left untreated, enterocolitis can lead to serious complications, such as intestinal perforation and peritonitis. Therefore, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly if symptoms persist or worsen over time.
Diagnosis of Hirschsprung's Disease
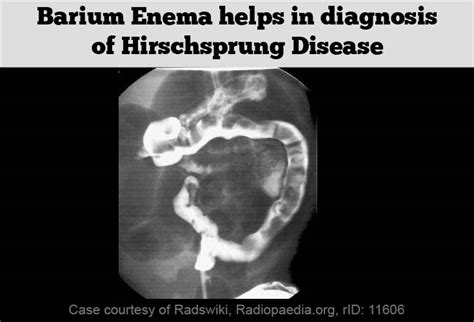
Diagnostic tests, such as a barium enema, may be used to visualize the colon and rule out other conditions. A rectal biopsy, which involves removing a tissue sample from the rectum, can confirm the diagnosis by showing the absence of nerve cells in the muscle layers of the colon. Other tests, such as anorectal manometry, may be used to assess the function of the anal sphincter and the rectum.
Treatment Options for Hirschsprung's Disease
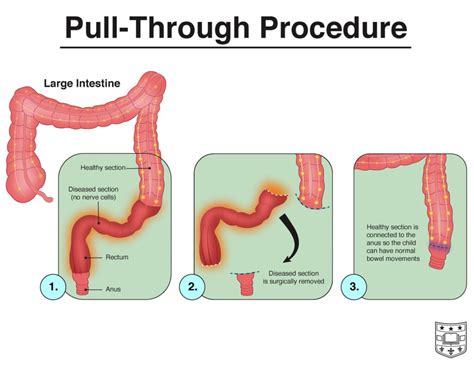
In older children and adults, a pull-through procedure may be used, which involves removing the affected portion of the colon and pulling the remaining colon down to the anus. Other treatment options, such as bowel management programs, may be used to manage symptoms and prevent complications. These programs may involve dietary changes, bowel training, and medication to manage constipation and prevent enterocolitis.
Management Strategies for Hirschsprung's Disease

Medications, such as laxatives and stool softeners, may be used to manage constipation and prevent enterocolitis. Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider are essential to monitor the condition and prevent complications. Additionally, individuals with Hirschsprung's disease may need to undergo regular bowel cleanouts to prevent the buildup of stool and reduce the risk of enterocolitis.
Complications of Hirschsprung's Disease
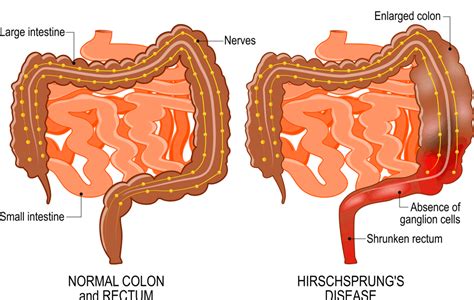
Other complications, such as rectal prolapse and fecal incontinence, can occur in individuals with Hirschsprung's disease. Rectal prolapse is a condition in which the rectum protrudes from the anus, and fecal incontinence is the inability to control bowel movements. These complications can have a significant impact on an individual's quality of life, and prompt medical attention is essential to prevent and manage them.
Current Research and Future Directions
Future directions for research on Hirschsprung's disease include the development of new diagnostic tests and treatment options. For example, researchers are working on developing non-invasive diagnostic tests that can detect Hirschsprung's disease in newborns. Additionally, new surgical techniques and bowel management programs are being developed to improve outcomes for individuals with the condition.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In conclusion, Hirschsprung's disease is a complex condition that requires a comprehensive approach to management. While it is a rare condition, it can have a significant impact on an individual's quality of life. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and management strategies for Hirschsprung's disease, individuals can take control of their condition and improve their overall health and well-being. We encourage readers to share their experiences and ask questions in the comments section below.What is Hirschsprung's disease?
+Hirschsprung's disease is a rare congenital condition that affects the large intestine, characterized by the absence of nerve cells in the muscle layers of the colon.
What are the symptoms of Hirschsprung's disease?
+The symptoms of Hirschsprung's disease include chronic constipation, abdominal pain, and intestinal obstruction. Newborns may experience delayed passage of meconium, and older children and adults may experience chronic constipation, abdominal pain, and rectal bleeding.
How is Hirschsprung's disease diagnosed?
+The diagnosis of Hirschsprung's disease typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests, such as a barium enema and rectal biopsy.
What are the treatment options for Hirschsprung's disease?
+The treatment of Hirschsprung's disease typically involves surgery, which aims to remove the affected portion of the colon and restore normal bowel function. Other treatment options, such as bowel management programs, may be used to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
Can Hirschsprung's disease be prevented?
+While Hirschsprung's disease cannot be prevented, prompt medical attention and treatment can help prevent complications and improve outcomes for individuals with the condition.
