Intro
Discover 5 ways to manage hydrocele, a swelling condition affecting testicles, including causes, symptoms, and treatments like surgery, aspiration, and natural remedies, to alleviate discomfort and prevent complications.
Hydrocele, a condition characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the scrotum, can be a source of discomfort and anxiety for those affected. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for managing this condition effectively. In this article, we will delve into the world of hydrocele, exploring its various aspects and providing valuable insights for readers.
The importance of discussing hydrocele lies in its prevalence and potential impact on quality of life. Hydrocele can affect men of all ages, although it is more common in older adults. The condition can lead to swelling, pain, and discomfort, which may interfere with daily activities and overall well-being. By shedding light on hydrocele, we aim to empower readers with knowledge, helping them navigate the complexities of this condition and seek appropriate medical attention when needed.
As we embark on this journey to explore hydrocele, it is essential to recognize the significance of timely medical intervention. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes, reducing the risk of complications and promoting a swift recovery. In the following sections, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies for hydrocele, providing readers with a comprehensive understanding of this condition.
What is Hydrocele?
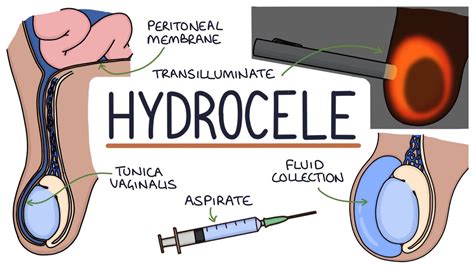
Causes of Hydrocele
The causes of hydrocele can be diverse, ranging from congenital conditions to acquired factors. Some of the common causes of hydrocele include: * Congenital conditions, such as patent processus vaginalis * Injury or trauma to the scrotum * Infection, such as epididymitis or orchitis * Tumors, including testicular cancer * Inflammation or inflammation-related conditionsSymptoms of Hydrocele

Diagnosis of Hydrocele
Diagnosing hydrocele typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests. The diagnostic process may include: * Physical examination of the scrotum and testicles * Medical history to identify underlying conditions or risk factors * Ultrasound or other imaging tests to confirm the presence of fluid * Blood tests to rule out infection or other underlying conditionsTreatment Options for Hydrocele

Prevention Strategies for Hydrocele
While hydrocele cannot always be prevented, certain strategies can reduce the risk of developing this condition. These include: * Practicing good genital hygiene and cleanliness * Avoiding injury or trauma to the scrotum * Managing underlying medical conditions, such as infection or inflammation * Wearing protective gear during sports or activities that may involve scrotal traumaComplications of Hydrocele

Living with Hydrocele
Living with hydrocele requires a comprehensive approach, incorporating medical treatment, lifestyle modifications, and emotional support. Individuals with hydrocele can benefit from: * Following a treatment plan and attending follow-up appointments * Practicing good genital hygiene and cleanliness * Managing stress and anxiety through relaxation techniques or counseling * Joining support groups or online forums to connect with others who have experienced similar conditionsConclusion and Next Steps
What are the symptoms of hydrocele?
+The symptoms of hydrocele include swelling or enlargement of the scrotum, pain or discomfort in the scrotum or testicles, feeling of heaviness or pressure in the scrotum, redness or inflammation of the scrotum, and discharge or bleeding from the scrotum.
How is hydrocele diagnosed?
+Hydrocele is typically diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests, including ultrasound or other imaging tests to confirm the presence of fluid.
What are the treatment options for hydrocele?
+The treatment options for hydrocele depend on the underlying cause, severity, and individual factors, and may include watchful waiting, antibiotics or anti-inflammatory medications, pain management medications, or surgical intervention.
