Intro
Discover hyperventilation symptoms, causes, and effects. Learn about breathing disorders, panic attacks, and anxiety triggers, and find relief from respiratory issues.
Hyperventilation is a common respiratory condition characterized by rapid and deep breathing, often leading to an imbalance in the body's carbon dioxide and oxygen levels. This condition can be triggered by various factors, including stress, anxiety, and underlying medical conditions. Understanding the symptoms and causes of hyperventilation is essential to manage and treat this condition effectively. In this article, we will delve into the world of hyperventilation, exploring its symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
Hyperventilation can affect anyone, regardless of age or health status. It is often associated with panic attacks, anxiety disorders, and stress. When we hyperventilate, we breathe out more carbon dioxide than usual, leading to a decrease in blood carbon dioxide levels. This decrease can cause respiratory alkalosis, a condition characterized by an increase in blood pH. Respiratory alkalosis can lead to various symptoms, including dizziness, lightheadedness, and tingling sensations in the hands and feet.
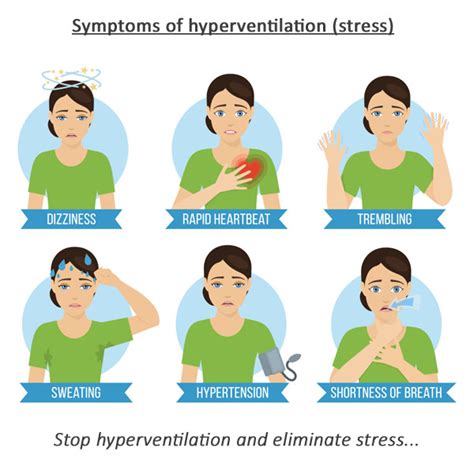
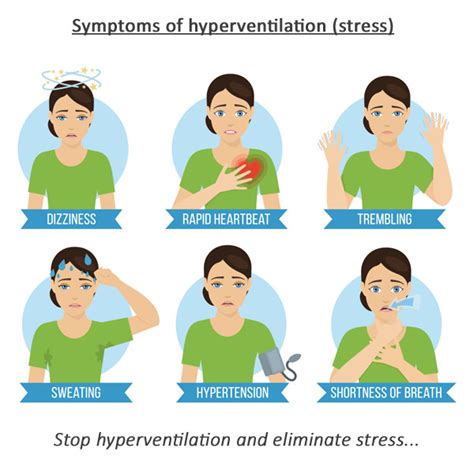
The symptoms of hyperventilation can be uncomfortable and may interfere with daily activities. Some common symptoms include rapid breathing, deep breathing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. In severe cases, hyperventilation can lead to fainting, seizures, and even respiratory failure. It is essential to recognize the symptoms of hyperventilation and seek medical attention if they persist or worsen over time. A proper diagnosis and treatment plan can help alleviate symptoms and prevent complications.
Hyperventilation Symptoms
Hyperventilation Causes
Hyperventilation can be caused by various factors, including: * Stress and anxiety: Stress and anxiety can trigger hyperventilation * Panic attacks: Panic attacks can lead to hyperventilation * Respiratory conditions: Conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and pneumonia can cause hyperventilation * Cardiovascular conditions: Conditions such as heart failure, coronary artery disease, and cardiac arrhythmias can cause hyperventilation * Neurological conditions: Conditions such as seizures, stroke, and multiple sclerosis can cause hyperventilation * Hormonal changes: Hormonal changes during pregnancy, menstruation, or menopause can cause hyperventilationHyperventilation Causes And Risk Factors

Hyperventilation Diagnosis
Diagnosing hyperventilation involves a physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests. A healthcare provider may perform the following tests: * Blood tests: To check for underlying medical conditions, such as anemia or electrolyte imbalances * Pulmonary function tests: To assess lung function and detect respiratory conditions * Electrocardiogram (ECG): To evaluate heart function and detect cardiovascular conditions * Imaging tests: Such as chest X-rays or computed tomography (CT) scans to rule out underlying conditionsHyperventilation Treatment Options
Hyperventilation Prevention
Preventing hyperventilation involves managing stress and anxiety, avoiding triggers, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Some tips for preventing hyperventilation include: * Practicing relaxation techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing * Engaging in regular exercise, such as walking or yoga * Eating a healthy, balanced diet * Getting enough sleep and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule * Avoiding triggers, such as stressful situations or certain substancesHyperventilation Complications

Hyperventilation Prognosis
The prognosis for hyperventilation depends on the underlying cause and severity of symptoms. With proper treatment and management, most people can recover from hyperventilation and prevent future episodes. However, if left untreated, hyperventilation can lead to complications and a decreased quality of life.Hyperventilation And Anxiety
Hyperventilation And Stress
Stress is a common trigger for hyperventilation. Chronic stress can lead to anxiety and hyperventilation, while acute stress can trigger panic attacks and hyperventilation episodes. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing, can help prevent hyperventilation.Hyperventilation And Panic Attacks

Hyperventilation And Respiratory Conditions
Respiratory conditions, such as asthma and COPD, can cause hyperventilation. Treating underlying respiratory conditions is essential to managing hyperventilation symptoms.Hyperventilation And Cardiovascular Conditions

What is hyperventilation?
+Hyperventilation is a respiratory condition characterized by rapid and deep breathing, often leading to an imbalance in the body's carbon dioxide and oxygen levels.
What are the symptoms of hyperventilation?
+The symptoms of hyperventilation include rapid breathing, deep breathing, chest tightness, shortness of breath, dizziness, lightheadedness, tingling sensations, muscle cramps, and nausea and vomiting.
How is hyperventilation diagnosed?
+Hyperventilation is diagnosed through a physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests, such as blood tests, pulmonary function tests, electrocardiogram (ECG), and imaging tests.
What are the treatment options for hyperventilation?
+Treatment options for hyperventilation include breathing exercises, medications, therapy, and lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise, healthy eating, and stress management.
Can hyperventilation be prevented?
+Yes, hyperventilation can be prevented by managing stress and anxiety, avoiding triggers, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, healthy eating, and adequate sleep.
In conclusion, hyperventilation is a common respiratory condition that can be triggered by various factors, including stress, anxiety, and underlying medical conditions. Understanding the symptoms and causes of hyperventilation is essential to manage and treat this condition effectively. By recognizing the symptoms and seeking medical attention, individuals can prevent complications and improve their quality of life. We encourage readers to share their experiences and ask questions in the comments section below. Additionally, we invite readers to share this article with others who may be affected by hyperventilation, and to explore other resources and support groups for further information and guidance.
