Intro
Learn about Impetigo, a highly contagious skin infection, its symptoms, causes, and treatment options, including antibiotics and home remedies to prevent its spread and promote healing from this bacterial skin disease.
Impetigo is a highly contagious skin infection that affects millions of people worldwide, particularly children. It is characterized by red sores on the face, especially around the mouth and nose, though it can also appear on other exposed areas. The infection is usually caused by bacteria, either Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes, and can spread through direct contact with the sores or by touching items contaminated with the bacteria. Understanding impetigo, its causes, symptoms, and treatments is crucial for effective management and prevention of the infection.
Impetigo is often seen in children due to their tendency to engage in activities that increase the risk of skin-to-skin contact, such as sports and playground activities. However, adults can also contract the infection, especially if they have compromised immune systems or engage in high-risk behaviors. The infection can lead to significant discomfort, including pain, itching, and swelling, and if left untreated, it can lead to more severe complications, such as cellulitis or post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis. Therefore, recognizing the signs and symptoms of impetigo and seeking medical attention promptly is essential for preventing long-term health issues.
The importance of addressing impetigo lies not only in alleviating the discomfort and preventing complications but also in reducing the risk of transmission to others. Since the infection is highly contagious, individuals with impetigo must take precautions to avoid spreading it to family members, friends, and community. This includes practicing good hygiene, avoiding close contact with others until the infection has cleared, and ensuring that any items that may have come into contact with the sores are properly cleaned and disinfected. By understanding how impetigo spreads and taking preventive measures, individuals can play a significant role in controlling the spread of the infection within their communities.
Causes and Risk Factors of Impetigo
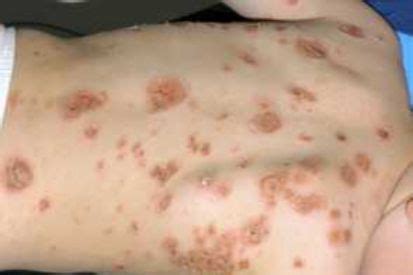
Types of Impetigo
There are two main types of impetigo: non-bullous and bullous. Non-bullous impetigo is the most common form and is characterized by red sores that eventually burst and form light brown crusts. Bullous impetigo, on the other hand, involves larger blisters that may take longer to heal. Understanding the type of impetigo an individual has is crucial for determining the most effective treatment approach.Symptoms of Impetigo
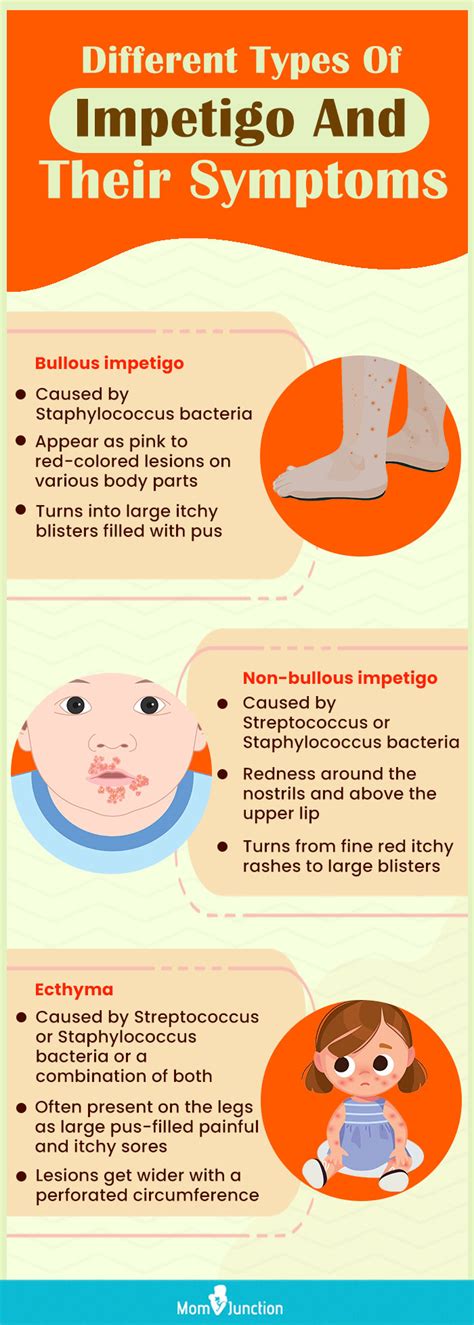
Diagnosis of Impetigo
Diagnosing impetigo typically involves a physical examination by a healthcare provider, who will look for the characteristic signs of the infection, such as red sores or blisters. In some cases, a sample of the fluid from the sores may be sent to a laboratory for testing to confirm the presence of bacteria. This is especially important for distinguishing impetigo from other skin conditions that may have similar symptoms.Treatment Options for Impetigo

Home Remedies for Impetigo
In addition to antibiotics, there are several home remedies that can help manage the symptoms of impetigo and promote healing. These include keeping the affected area clean and dry, applying cool compresses to reduce itching and discomfort, and avoiding scratching the sores to prevent further irritation and potential scarring.Prevention of Impetigo

Complications of Impetigo
If left untreated, impetigo can lead to several complications, including the spread of the infection to other parts of the body, such as the bloodstream or internal organs. In rare cases, impetigo can lead to post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis, a condition that affects the kidneys. Early treatment and proper management of the infection are essential for preventing these complications.Living with Impetigo
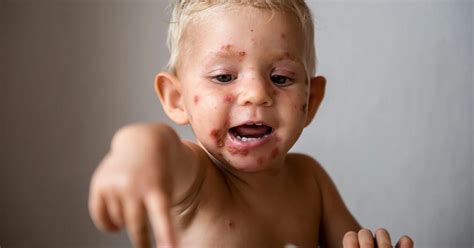
Coping with the Emotional Impact of Impetigo
Impetigo can have an emotional impact, especially for children who may feel embarrassed or self-conscious about their appearance. It is essential for parents and caregivers to provide emotional support, reassure the child that the infection is treatable and not a result of poor hygiene or behavior, and encourage them to ask questions and express their feelings.What are the symptoms of impetigo?
+The symptoms of impetigo include red sores or blisters on the skin that may burst and form crusts, itching, and swelling in the affected area.
How is impetigo treated?
+Impetigo is usually treated with antibiotics, either in the form of topical creams or oral medications, depending on the severity of the infection.
Can impetigo be prevented?
+Yes, impetigo can be prevented by practicing good hygiene, avoiding close contact with individuals who have the infection, and ensuring that any cuts or scratches are properly cleaned and covered.
What are the complications of untreated impetigo?
+Untreated impetigo can lead to several complications, including the spread of the infection to other parts of the body, such as the bloodstream or internal organs, and post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis.
How long does it take for impetigo to heal?
+The healing time for impetigo can vary depending on the severity of the infection and the effectiveness of the treatment, but it usually takes several weeks for the infection to fully clear.
In conclusion, impetigo is a common and highly contagious skin infection that requires prompt attention and proper management to prevent complications and reduce the risk of transmission. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for impetigo, individuals can take the necessary steps to protect themselves and their loved ones. If you have any questions or concerns about impetigo, we encourage you to share your thoughts, ask questions, or seek advice from a healthcare professional. Remember, early treatment and good hygiene practices are key to managing impetigo and preventing its spread.
