Intro
Discover Isosorbide uses, a medication treating angina, heart failure, and esophageal spasms, with benefits including vasodilation, improved blood flow, and reduced chest pain, exploring its applications and effects.
Isosorbide is a medication that has been widely used for several decades, primarily in the treatment of angina pectoris, a condition characterized by chest pain due to reduced blood flow to the heart. The importance of understanding isosorbide uses cannot be overstated, as it plays a crucial role in managing symptoms and improving the quality of life for individuals suffering from cardiovascular diseases. In this article, we will delve into the various uses of isosorbide, its mechanisms of action, benefits, and potential side effects, providing readers with a comprehensive overview of this vital medication.
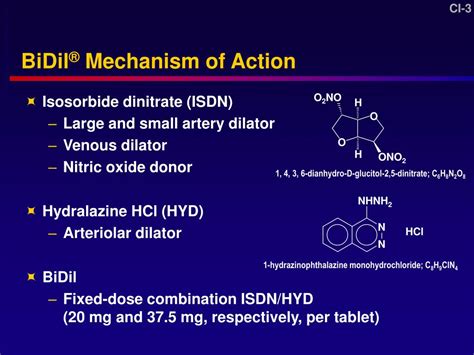
Isosorbide works by relaxing and widening blood vessels, which improves blood flow to the heart, reducing the amount of oxygen the heart needs. This action helps to alleviate chest pain and discomfort associated with angina, allowing individuals to perform daily activities with greater ease. The medication comes in various forms, including immediate-release and extended-release tablets, as well as chewable tablets, each designed to meet specific patient needs. Understanding the different formulations and their respective uses is essential for effective treatment and management of cardiovascular conditions.
The role of isosorbide in managing angina is multifaceted. Not only does it provide quick relief from symptoms, but it also helps prevent future episodes of chest pain. By reducing the frequency and severity of angina attacks, isosorbide enables individuals to lead more active lives, reducing the risk of complications and improving overall well-being. Moreover, isosorbide has been shown to be effective in combination with other medications, such as beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers, further enhancing its therapeutic benefits. As research continues to uncover the full potential of isosorbide, its importance in cardiovascular medicine is likely to grow, underscoring the need for patients and healthcare providers to be well-informed about its uses and applications.
Isosorbide Mechanism of Action
Benefits of Isosorbide

These benefits underscore the importance of isosorbide in the management of cardiovascular diseases, particularly for individuals who experience frequent or severe angina episodes. By providing effective symptom relief and improving overall cardiovascular health, isosorbide plays a vital role in reducing the risk of complications and improving long-term outcomes.
Side Effects of Isosorbide

In rare cases, isosorbide may cause more serious side effects, such as:
- Allergic reactions
- Low blood pressure
- Increased heart rate
It is essential for patients to be aware of these potential side effects and to discuss any concerns with their healthcare provider. By closely monitoring side effects and adjusting treatment as needed, individuals can minimize the risks associated with isosorbide and maximize its therapeutic benefits.
Isosorbide Interactions

By understanding these potential interactions, healthcare providers can optimize treatment regimens and minimize the risk of adverse effects. Patients should always inform their healthcare provider about all medications they are taking, including over-the-counter products and supplements, to ensure safe and effective use of isosorbide.
Isosorbide Dosage
Isosorbide Contraindications

In addition, isosorbide should be used with caution in patients with:
- Renal or hepatic impairment
- Glaucoma
- Hyperthyroidism
- Recent head injury or cerebral hemorrhage
By understanding these contraindications and precautions, healthcare providers can ensure safe and effective use of isosorbide, minimizing the risk of adverse effects and optimizing treatment outcomes.
Special Considerations

By taking these factors into account, healthcare providers can tailor treatment regimens to meet the unique needs of each patient, ensuring optimal efficacy and safety.
Isosorbide and Other Medications
By understanding the potential benefits and risks of these combinations, healthcare providers can develop effective treatment strategies that address multiple aspects of cardiovascular disease.
Isosorbide and Lifestyle Changes

By incorporating these lifestyle changes into their daily routine, individuals can enhance the therapeutic effects of isosorbide and reduce the risk of cardiovascular events.
What is isosorbide used for?
+Isosorbide is primarily used to treat angina pectoris, a condition characterized by chest pain due to reduced blood flow to the heart.
How does isosorbide work?
+Isosorbide works by relaxing and widening blood vessels, which improves blood flow to the heart and reduces the amount of oxygen the heart needs.
What are the common side effects of isosorbide?
+Common side effects of isosorbide include headache, dizziness, lightheadedness, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
In conclusion, isosorbide is a vital medication in the treatment of angina pectoris and other cardiovascular conditions. By understanding its uses, mechanisms of action, benefits, and potential side effects, individuals can make informed decisions about their treatment and work closely with their healthcare provider to optimize their care. We invite readers to share their experiences with isosorbide, ask questions, and engage in discussions about this important topic, promoting a deeper understanding of cardiovascular health and the role of isosorbide in managing these conditions.
