Intro
Lisinoprils uses and benefits for hypertension, heart failure, and diabetic nephropathy treatment, highlighting its therapeutic effects, dosage, and side effects management, as an ACE inhibitor medication.
Lisinopril is a medication that has been widely used for decades to treat various health conditions, particularly those related to the cardiovascular system. It belongs to a class of drugs known as angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, which work by relaxing blood vessels and reducing blood pressure. The importance of understanding lisinopril uses and benefits cannot be overstated, as it is a medication that can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals suffering from certain health issues. In this article, we will delve into the world of lisinopril, exploring its uses, benefits, and mechanisms of action, as well as providing practical examples and statistical data to support its effectiveness.
The prevalence of cardiovascular diseases, such as hypertension and heart failure, has been on the rise globally, making medications like lisinopril increasingly important. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death worldwide, accounting for more than 17.9 million deaths per year. Lisinopril has been shown to be effective in reducing the risk of cardiovascular events, such as heart attacks and strokes, making it a crucial medication for individuals at risk. Furthermore, lisinopril has been used to treat other conditions, including diabetic nephropathy and heart failure, highlighting its versatility and importance in modern medicine.
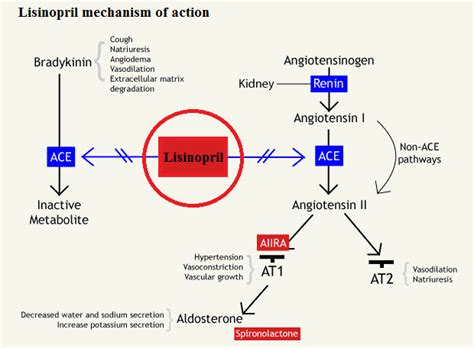
As we explore the uses and benefits of lisinopril, it is essential to understand how this medication works. Lisinopril inhibits the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor that increases blood pressure. By blocking this conversion, lisinopril causes blood vessels to relax and widen, reducing blood pressure and increasing blood flow to the heart and other vital organs. This mechanism of action has been extensively studied, and the results have consistently shown that lisinopril is effective in reducing blood pressure and improving cardiovascular outcomes.
Lisinopril Uses

Benefits of Lisinopril
The benefits of lisinopril are numerous and well-documented. Some of the most significant advantages of using lisinopril include: * Reduced blood pressure: Lisinopril has been shown to be effective in reducing blood pressure in individuals with hypertension. * Improved cardiovascular outcomes: Lisinopril has been shown to reduce the risk of cardiovascular events, such as heart attacks and strokes. * Renal protection: Lisinopril has been shown to slow the progression of kidney disease in individuals with diabetic nephropathy. * Improved survival: Lisinopril has been shown to improve survival rates in individuals with heart failure.Lisinopril Mechanism of Action
Steps to Take Lisinopril
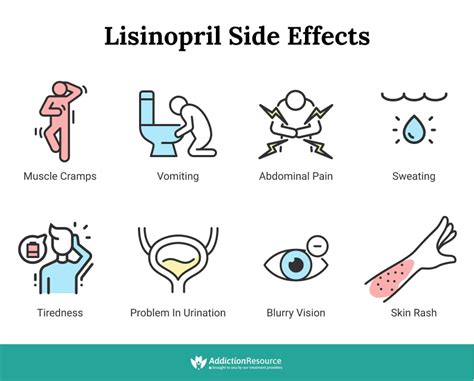
To get the most out of lisinopril, it is essential to follow the prescribed dosage and administration instructions. Here are some steps to take lisinopril: 1. Take lisinopril exactly as prescribed by your doctor. 2. Take lisinopril at the same time every day. 3. Swallow the tablet whole with water. 4. Do not crush or chew the tablet. 5. If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember.Lisinopril Side Effects
Precautions and Warnings
While lisinopril is generally well-tolerated, there are certain precautions and warnings to be aware of. These include: * Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Lisinopril should not be used during pregnancy or breastfeeding. * Kidney disease: Lisinopril should be used with caution in individuals with kidney disease. * Liver disease: Lisinopril should be used with caution in individuals with liver disease. * Allergic reactions: Lisinopril can cause allergic reactions, such as angioedema.Lisinopril Interactions

Statistical Data
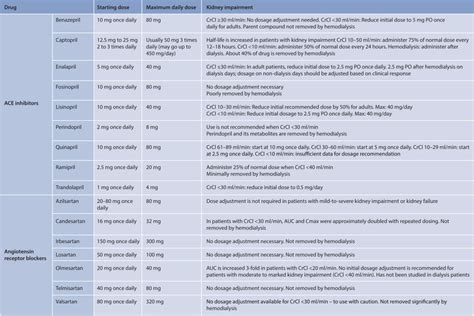
Numerous studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of lisinopril in reducing blood pressure and improving cardiovascular outcomes. For example, a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine found that lisinopril reduced the risk of cardiovascular events by 20% in individuals with hypertension. Another study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology found that lisinopril improved survival rates by 15% in individuals with heart failure.Lisinopril Dosage
Practical Examples
To illustrate the effectiveness of lisinopril, let's consider a few practical examples: * A 50-year-old man with hypertension is prescribed lisinopril 10 mg once daily. After 6 weeks, his blood pressure has decreased from 140/90 mmHg to 120/80 mmHg. * A 60-year-old woman with heart failure is prescribed lisinopril 5 mg once daily. After 3 months, her symptoms have improved, and she is able to walk further without experiencing shortness of breath.Lisinopril Conclusion and Future Directions

Final Thoughts
As we reflect on the importance of lisinopril, it is essential to remember that this medication is just one part of a comprehensive treatment plan. Lifestyle modifications, such as a healthy diet and regular exercise, are also crucial in managing cardiovascular disease. By working together with healthcare providers and following prescribed treatment plans, individuals can reduce their risk of cardiovascular events and improve their overall health and well-being.What is lisinopril used for?
+Lisinopril is used to treat hypertension, heart failure, and other cardiovascular conditions.
How does lisinopril work?
+Lisinopril works by inhibiting the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor that increases blood pressure.
What are the side effects of lisinopril?
+The most common side effects of lisinopril include cough, dizziness, headache, fatigue, nausea, and diarrhea.
Can I take lisinopril with other medications?
+Lisinopril can interact with other medications, including diuretics, potassium-sparing diuretics, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). It is essential to consult with your doctor before taking any new medications.
How long does it take for lisinopril to start working?
+Lisinopril can start working within a few hours of taking the first dose, but it may take several weeks to achieve its full effect.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of lisinopril uses and benefits. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences with lisinopril, please don't hesitate to comment below. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please share it with others who may benefit from this information. By working together, we can promote awareness and education about cardiovascular health and the importance of medications like lisinopril in managing these conditions.
