Intro
Discover key facts about Lisinopril, a common ACE inhibitor for blood pressure and heart failure, including its benefits, side effects, and interactions, to better manage hypertension and cardiovascular health effectively.
Lisinopril is a medication that has been widely used for decades to treat various cardiovascular conditions, including high blood pressure and heart failure. Despite its popularity, many people are not fully aware of the benefits, side effects, and proper usage of this medication. In this article, we will delve into the world of lisinopril, exploring its history, mechanisms, and practical applications. Whether you are a patient taking lisinopril or simply interested in learning more about this medication, this article aims to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of its importance and relevance in modern medicine.
The development of lisinopril marked a significant milestone in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. By inhibiting the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, lisinopril helps to relax blood vessels, reducing blood pressure and decreasing the workload on the heart. This mechanism of action has made lisinopril an essential component of treatment plans for patients with hypertension, heart failure, and other related conditions. As research continues to uncover the full potential of lisinopril, its role in maintaining cardiovascular health is becoming increasingly evident.
The widespread use of lisinopril can be attributed to its effectiveness in managing symptoms and slowing disease progression. Patients taking lisinopril often experience significant improvements in their quality of life, with reduced blood pressure, decreased fatigue, and enhanced overall well-being. Moreover, lisinopril has been shown to reduce the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events, making it a vital medication for individuals at high risk of these complications. As the medical community continues to explore the benefits and limitations of lisinopril, its importance in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases remains unparalleled.
Introduction to Lisinopril

Benefits of Lisinopril
The benefits of lisinopril are numerous and well-documented. Some of the most significant advantages of taking lisinopril include: * Reduced blood pressure: Lisinopril has been shown to effectively lower blood pressure in patients with hypertension, reducing the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events. * Improved heart function: Lisinopril has been shown to improve heart function in patients with heart failure, reducing symptoms such as fatigue, shortness of breath, and swelling. * Reduced risk of cardiovascular events: Lisinopril has been shown to reduce the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events in patients with high blood pressure or heart failure. * Improved quality of life: Patients taking lisinopril often experience significant improvements in their quality of life, with reduced symptoms and enhanced overall well-being.How Lisinopril Works
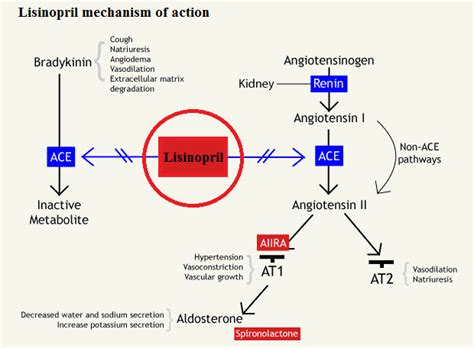
Side Effects of Lisinopril
While lisinopril is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects in some patients. Some of the most common side effects of lisinopril include: * Cough: A dry, persistent cough is a common side effect of lisinopril, affecting up to 20% of patients. * Dizziness: Lisinopril can cause dizziness or lightheadedness, particularly when standing up quickly. * Fatigue: Lisinopril can cause fatigue or weakness, particularly when first starting the medication. * Headache: Lisinopril can cause headaches, particularly when first starting the medication.Practical Applications of Lisinopril

Steps to Take Lisinopril Effectively
To take lisinopril effectively, patients should follow these steps: * Take the medication as directed: Patients should take lisinopril exactly as directed by their healthcare provider, without missing doses or taking extra doses. * Monitor blood pressure: Patients should monitor their blood pressure regularly to ensure that lisinopril is working effectively. * Report side effects: Patients should report any side effects to their healthcare provider, particularly if they are severe or persistent.Statistical Data on Lisinopril

Real-World Examples of Lisinopril Use
Lisinopril has been used in numerous real-world scenarios to improve cardiovascular outcomes. Some examples include: * A 55-year-old man with high blood pressure and diabetes, who experienced a significant reduction in blood pressure and improvement in symptoms after starting lisinopril. * A 65-year-old woman with heart failure, who experienced improved heart function and reduced symptoms after starting lisinopril. * A 40-year-old man with kidney disease, who experienced a significant reduction in blood pressure and improvement in kidney function after starting lisinopril.Future Directions for Lisinopril Research

Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In conclusion, lisinopril is a vital medication that has revolutionized the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Its ability to reduce blood pressure, improve heart function, and decrease the risk of cardiovascular events has made it an essential component of treatment plans for patients with hypertension, heart failure, and other related conditions. As research continues to uncover the full potential of lisinopril, its importance in maintaining cardiovascular health is becoming increasingly evident. We hope that this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of lisinopril and its role in modern medicine.We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with lisinopril in the comments section below. Have you taken lisinopril for a cardiovascular condition? What were your experiences with the medication? Do you have any questions or concerns about lisinopril? We encourage you to ask, and we will do our best to provide you with accurate and helpful information.
What is lisinopril used for?
+Lisinopril is used to treat high blood pressure, heart failure, and other related conditions. It works by relaxing blood vessels and reducing the workload on the heart.
What are the side effects of lisinopril?
+Common side effects of lisinopril include cough, dizziness, fatigue, and headache. Less common side effects include kidney problems, allergic reactions, and increased potassium levels.
How long does it take for lisinopril to start working?
+Lisinopril can start working within a few hours of taking the first dose, but it may take several weeks to reach its full effect. Patients should monitor their blood pressure regularly and report any changes to their healthcare provider.
