Intro
Magnesium oxide, a compound made up of magnesium and oxygen, is a crucial element in various industries and aspects of our daily lives. The importance of magnesium oxide cannot be overstated, as it plays a significant role in human health, industrial applications, and environmental sustainability. With its unique properties and diverse uses, magnesium oxide has become an essential component in many products and processes. In this article, we will delve into the world of magnesium oxide, exploring its benefits, working mechanisms, and key information related to this vital compound.
As we navigate through the complexities of magnesium oxide, it becomes clear that its significance extends beyond its industrial applications. Magnesium oxide is also a crucial nutrient for human health, involved in numerous bodily functions, including muscle and nerve function, bone health, and energy production. The human body relies on magnesium to maintain proper physiological functions, and magnesium oxide is one of the most common forms of magnesium used in dietary supplements. With the increasing awareness of the importance of magnesium in human health, the demand for magnesium oxide has grown significantly, driving research and development in this field.
The versatility of magnesium oxide is another factor contributing to its widespread use. In addition to its role in human health, magnesium oxide is used in various industrial applications, such as refractories, ceramics, and construction materials. Its high melting point, thermal stability, and resistance to corrosion make it an ideal material for high-temperature applications. Furthermore, magnesium oxide is used as a filler in plastics, rubber, and paper, as well as a pigment in paints and coatings. The unique properties of magnesium oxide have led to its adoption in a wide range of industries, from pharmaceuticals to aerospace.
What is Magnesium Oxide?

Properties of Magnesium Oxide
The properties of magnesium oxide make it a highly versatile compound. Some of its key properties include: * High melting point: Magnesium oxide has a melting point of approximately 2800°C, making it suitable for high-temperature applications. * Thermal stability: Magnesium oxide is highly stable at high temperatures, resisting decomposition and maintaining its structure. * Resistance to corrosion: Magnesium oxide is highly resistant to corrosion, making it an ideal material for applications where exposure to harsh environments is a concern. * High solubility: Magnesium oxide is highly soluble in water, allowing it to be easily dissolved and absorbed by the body.Benefits of Magnesium Oxide

Industrial Applications of Magnesium Oxide
The industrial applications of magnesium oxide are diverse and widespread. Some of the key applications include: * Refractories: Magnesium oxide is used in the production of refractory materials, which are used to line furnaces and other high-temperature equipment. * Ceramics: Magnesium oxide is used in the production of ceramic materials, including pottery and other decorative items. * Construction materials: Magnesium oxide is used in the production of construction materials, including cement and concrete.Working Mechanisms of Magnesium Oxide
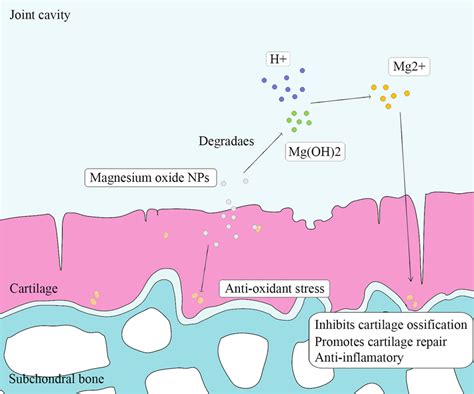
Steps for Using Magnesium Oxide
The steps for using magnesium oxide vary depending on the specific application. Some general steps include: * Measurement: Accurately measure the amount of magnesium oxide required for the specific application. * Mixing: Mix the magnesium oxide with other materials, such as water or other compounds, to form the desired consistency. * Application: Apply the magnesium oxide mixture to the desired surface or material.Practical Examples of Magnesium Oxide

Statistical Data on Magnesium Oxide
Statistical data on magnesium oxide highlights its growing importance in various industries. Some key statistics include: * Global demand: The global demand for magnesium oxide is expected to grow by 5% annually over the next five years. * Market size: The global market size for magnesium oxide is estimated to be approximately $1.5 billion. * Industrial applications: Magnesium oxide is used in over 50% of all industrial applications, including refractories, ceramics, and construction materials.Conclusion and Future Outlook

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with magnesium oxide in the comments section below. Have you used magnesium oxide in any of its various forms? What benefits or challenges have you encountered? Your input will help us better understand the complexities of magnesium oxide and its role in our daily lives.
What is magnesium oxide used for?
+Magnesium oxide is used in various applications, including dietary supplements, refractory materials, ceramics, and construction materials.
What are the benefits of magnesium oxide?
+The benefits of magnesium oxide include improved bone health, enhanced muscle function, energy production, and industrial applications.
How is magnesium oxide produced?
+Magnesium oxide is produced through the reaction of magnesium with oxygen, resulting in a highly stable and inert compound.
