Intro
Metoprolol is a medication that belongs to a class of drugs known as beta blockers. It is primarily used to treat high blood pressure, chest pain (angina), and certain heart-related conditions. Metoprolol works by slowing the heart rate and reducing the force of the heart's contractions, which helps to lower blood pressure and increase oxygen supply to the heart. This medication is available in various forms, including immediate-release and extended-release tablets, as well as injectable solutions.
The importance of metoprolol lies in its ability to manage and prevent complications associated with high blood pressure and heart disease. High blood pressure is a major risk factor for heart attacks, strokes, and kidney disease, and metoprolol helps to mitigate these risks by reducing blood pressure and alleviating the workload on the heart. Additionally, metoprolol has been shown to improve survival rates in patients with heart failure and reduce the risk of recurrent heart attacks.
Metoprolol has been extensively studied and has a well-established safety profile. It is generally well-tolerated, and side effects are usually mild and temporary. However, like all medications, metoprolol can cause adverse effects, such as dizziness, fatigue, and shortness of breath. It is essential to follow the prescribed dosage and consult with a healthcare provider if any concerns or side effects arise.
How Metoprolol Works
Metoprolol works by blocking the effects of epinephrine (adrenaline) on the heart and blood vessels. Epinephrine is a hormone that stimulates the heart to beat faster and stronger, which increases blood pressure. By blocking the effects of epinephrine, metoprolol reduces the heart rate and the force of the heart's contractions, which leads to a decrease in blood pressure. This mechanism of action also helps to reduce the oxygen demand of the heart, which can help to alleviate chest pain (angina) and improve exercise tolerance.
Benefits of Metoprolol
The benefits of metoprolol include: * Lowering blood pressure and reducing the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and kidney disease * Relieving chest pain (angina) and improving exercise tolerance * Reducing the risk of recurrent heart attacks and improving survival rates in patients with heart failure * Slowing the heart rate and reducing the force of the heart's contractions, which can help to alleviate symptoms of anxiety and stressTypes of Metoprolol
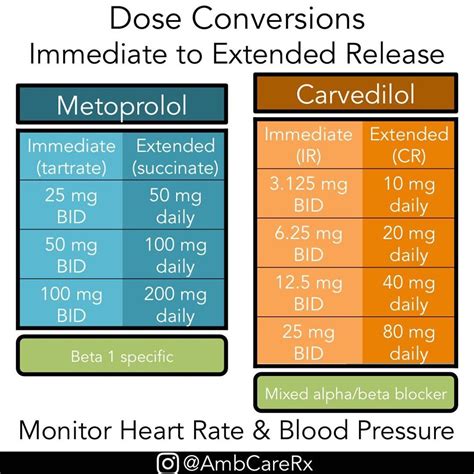
There are several types of metoprolol, including:
- Immediate-release tablets: These tablets release the medication quickly and are usually taken 2-3 times a day.
- Extended-release tablets: These tablets release the medication slowly over a longer period and are usually taken once a day.
- Injectable solutions: These solutions are used in emergency situations, such as during a heart attack, and are administered intravenously.
Side Effects of Metoprolol
While metoprolol is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects, including: * Dizziness and lightheadedness * Fatigue and weakness * Shortness of breath * Nausea and vomiting * Diarrhea and constipation * Headaches and dizzinessInteractions with Other Medications
Metoprolol can interact with other medications, including:
- Other beta blockers: Taking metoprolol with other beta blockers can increase the risk of side effects, such as dizziness and shortness of breath.
- Calcium channel blockers: Taking metoprolol with calcium channel blockers can increase the risk of low blood pressure and fainting.
- Anti-arrhythmic medications: Taking metoprolol with anti-arrhythmic medications can increase the risk of abnormal heart rhythms.
Precautions and Warnings
Before taking metoprolol, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider, especially if you have: * A history of heart failure or low blood pressure * A history of asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) * A history of diabetes or hypoglycemia * A history of thyroid disease or hyperthyroidism * A history of peripheral vascular disease or Raynaud's diseaseDosage and Administration
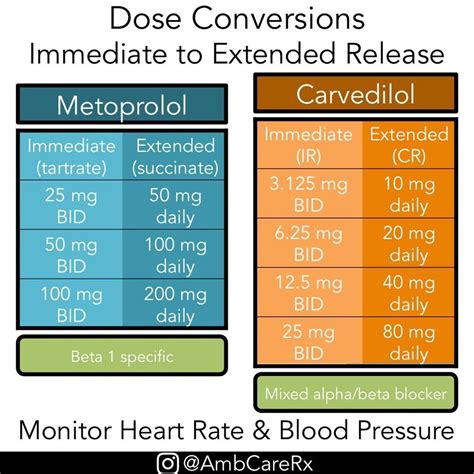
The dosage and administration of metoprolol vary depending on the condition being treated and the individual patient's response. The typical dosage range is 50-200 mg per day, taken orally in divided doses. It is essential to follow the prescribed dosage and consult with a healthcare provider if any concerns or side effects arise.
Special Considerations
Metoprolol can be used in pregnant and breastfeeding women, but it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider before taking the medication. Additionally, metoprolol can be used in children, but the dosage and administration may vary depending on the child's age and weight.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

In conclusion, metoprolol is a medication that belongs to a class of drugs known as beta blockers. It is primarily used to treat high blood pressure, chest pain (angina), and certain heart-related conditions. Metoprolol works by slowing the heart rate and reducing the force of the heart's contractions, which helps to lower blood pressure and increase oxygen supply to the heart. While metoprolol is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects, and it is essential to follow the prescribed dosage and consult with a healthcare provider if any concerns or side effects arise.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with metoprolol in the comments below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to ask. Additionally, if you found this article informative and helpful, please share it with others who may benefit from the information.
What is metoprolol used for?
+Metoprolol is used to treat high blood pressure, chest pain (angina), and certain heart-related conditions.
How does metoprolol work?
+Metoprolol works by blocking the effects of epinephrine (adrenaline) on the heart and blood vessels, which helps to slow the heart rate and reduce the force of the heart's contractions.
What are the side effects of metoprolol?
+Common side effects of metoprolol include dizziness, fatigue, shortness of breath, nausea, and vomiting. Less common side effects include diarrhea, constipation, headaches, and dizziness.
