Intro
Discover 5 uses of Metronidazole, an antibiotic and antiprotozoal medication, treating infections, bacterial vaginosis, pelvic inflammatory disease, giardiasis, and amoebiasis, with its antimicrobial properties.
Metronidazole is a versatile antibiotic and antiprotozoal medication that has been widely used for decades to treat various infections. Its effectiveness against a range of microorganisms, including bacteria and protozoa, makes it a crucial component in the treatment of several conditions. The importance of understanding the uses of metronidazole lies in its potential to improve patient outcomes by targeting specific infections that are resistant to other treatments. Moreover, its application in both human and veterinary medicine underscores its broad utility. As we delve into the uses of metronidazole, it becomes clear that this medication plays a vital role in modern healthcare, offering a reliable option for managing infections that might otherwise be challenging to treat.
The versatility of metronidazole is evident in its application across different medical specialties, from gastroenterology to gynecology. Its ability to target anaerobic bacteria, which thrive in environments with low oxygen levels, makes it particularly useful in treating infections in areas of the body where such conditions are common. Furthermore, metronidazole's efficacy against protozoa, such as those causing amoebiasis and giardiasis, highlights its role in treating infections that are often acquired through contaminated water or food, or through contact with infected individuals. By understanding the various uses of metronidazole, healthcare professionals can better appreciate its value in combating a wide range of infectious diseases.
Metronidazole's impact on public health is also significant, given its use in treating infections that can have serious consequences if left untreated. For instance, its application in treating pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) and bacterial vaginosis (BV) underscores its importance in women's health, as these conditions can lead to complications such as infertility and increased risk of HIV transmission. Similarly, its use in managing infections related to dental procedures and in treating infections in immunocompromised patients highlights its critical role in preventing the spread of infection and promoting recovery. As research continues to uncover the full potential of metronidazole, its position as a key medication in the fight against infectious diseases is likely to be reinforced.
Introduction to Metronidazole

Pharmacology of Metronidazole
The pharmacology of metronidazole is characterized by its ability to accumulate within the cells of target microorganisms. Once inside, it is reduced to form reactive intermediates that bind to DNA, disrupting the helical structure of the DNA molecule and inhibiting the synthesis of vital proteins and nucleic acids. This process is crucial for the bactericidal activity of metronidazole, as it ensures the elimination of the infecting organisms. Understanding the pharmacological aspects of metronidazole is essential for appreciating its therapeutic effects and for optimizing its use in clinical practice.Common Uses of Metronidazole

Treatment of Trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the protozoan Trichomonas vaginalis. Metronidazole is the drug of choice for treating this condition, with a high cure rate when used appropriately. The standard treatment involves a single dose or a short course of metronidazole, which effectively clears the infection in most cases. The importance of treating trichomoniasis lies in preventing its complications, such as increased risk of HIV transmission and pregnancy-related issues.Metronidazole in Gastrointestinal Infections
Treatment of Amoebiasis
Amoebiasis is an infection caused by the protozoan Entamoeba histolytica. Metronidazole is the primary treatment for this condition, effectively clearing the infection from the intestinal lumen and preventing the development of complications. The treatment regimen typically involves a course of metronidazole followed by a luminal agent to ensure eradication of the parasite.Metronidazole in Gynecological Infections

Treatment of Bacterial Vaginosis
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is a common gynecological infection characterized by an imbalance of the vaginal flora. Metronidazole is a first-line treatment for BV, with a high success rate in resolving symptoms and restoring the normal vaginal flora. The treatment typically involves a course of metronidazole, which can be administered orally or intravaginally, depending on the severity of the infection and patient preference.Metronidazole in Dental Infections
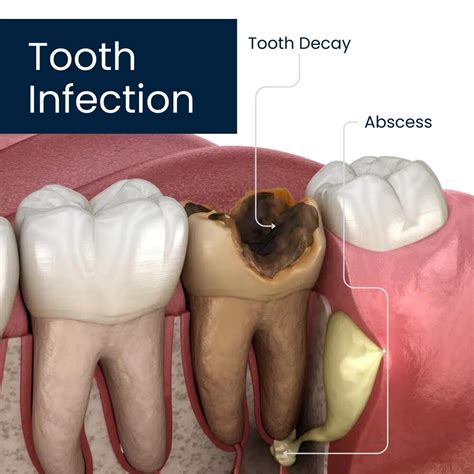
Treatment of Periodontal Infections
Periodontal infections are characterized by inflammation of the tissues surrounding the teeth, often involving anaerobic bacteria. Metronidazole, in combination with other antibiotics and mechanical debridement, is used to treat these infections. The goal of treatment is to reduce the bacterial load, control inflammation, and prevent further tissue damage.Metronidazole Resistance and Side Effects
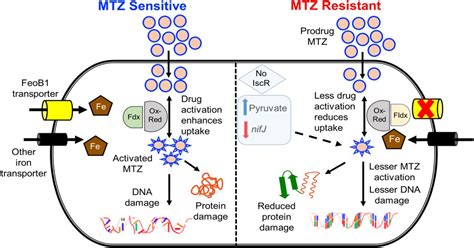
Managing Side Effects
The management of side effects associated with metronidazole involves a combination of preventive measures and symptomatic treatment. Patients should be advised to avoid alcohol during and after treatment to prevent a disulfiram-like reaction. Additionally, monitoring for signs of neurological toxicity and adjusting the dose or discontinuing the medication if necessary can help mitigate severe side effects.Conclusion and Future Perspectives

We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with metronidazole, either as a healthcare professional or as a patient who has undergone treatment with this medication. Your insights can help others better understand the uses and implications of metronidazole in clinical practice. Please feel free to comment below or share this article with others who might find it informative.
What is metronidazole used for?
+Metronidazole is used to treat various infections caused by anaerobic bacteria and protozoa, including trichomoniasis, giardiasis, amoebiasis, bacterial vaginosis, and pelvic inflammatory disease.
How does metronidazole work?
+Metronidazole works by entering the cells of microorganisms and damaging their DNA, thereby inhibiting their ability to reproduce and ultimately leading to their death.
What are the common side effects of metronidazole?
+Common side effects of metronidazole include gastrointestinal disturbances, metallic taste, and neurological effects. Severe side effects can include allergic reactions and neurological toxicity.
Can metronidazole be used in pregnancy?
+Metronidazole can be used in pregnancy but with caution. It is recommended to avoid its use during the first trimester unless the benefits outweigh the risks. Consultation with a healthcare provider is necessary before using metronidazole during pregnancy.
How long does it take for metronidazole to work?
+The time it takes for metronidazole to work can vary depending on the infection being treated. For some infections, improvement can be seen within a few days, while for others, it may take several weeks to achieve a full cure.
