Intro
Discover 5 key facts about Metronidazole, an antibiotic and antiprotozoal medication, including its uses, side effects, and interactions, to understand its role in treating infections, bacterial vaginosis, and giardiasis.
Metronidazole is a medication that has been widely used for decades to treat various infections caused by bacteria and protozoa. Its effectiveness and relatively low cost have made it a staple in many healthcare systems around the world. However, like all medications, metronidazole has its own set of benefits and drawbacks, and understanding these is crucial for both healthcare professionals and patients.
The importance of metronidazole lies in its ability to target and eliminate pathogens that can cause severe and sometimes life-threatening diseases. From gastrointestinal infections to infections of the skin, tissues, and nervous system, metronidazole's broad spectrum of activity makes it a versatile tool in the fight against microbial infections. Moreover, its use extends beyond human medicine, as it is also applied in veterinary care for similar purposes.
Despite its widespread use, there is a need for a balanced view of metronidazole, considering both its therapeutic benefits and potential side effects. This includes understanding the mechanisms by which it works, the types of infections it is most effective against, potential side effects, and how it interacts with other medications. With the rise of antibiotic resistance, the prudent use of metronidazole and other antimicrobials is more critical than ever to ensure their continued effectiveness.
Introduction to Metronidazole
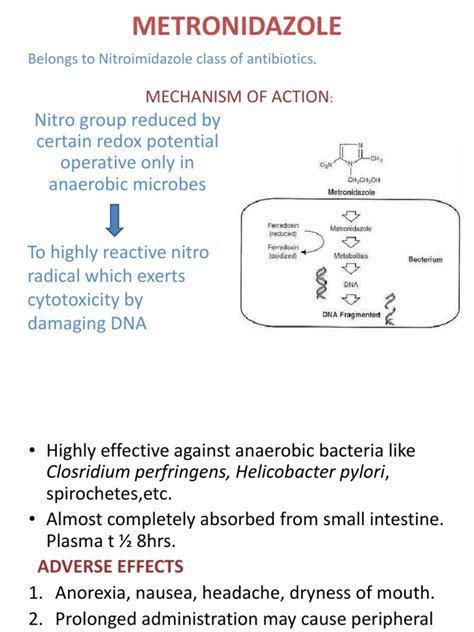
Benefits of Metronidazole

Common Uses of Metronidazole
Metronidazole's common uses include the treatment of: - Bacterial vaginosis - Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) - Infections of the abdomen, skin, tissue, and nervous system - Amoebiasis - Giardiasis - TrichomoniasisHow Metronidazole Works
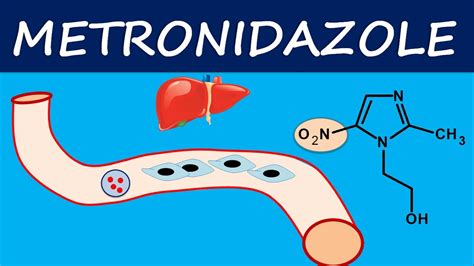
Potential Side Effects and Interactions

Precautions and Contraindications
- Patients with a history of seizure disorders or neurological conditions should use metronidazole with caution. - Metronidazole should be avoided during the first trimester of pregnancy and used with caution during breastfeeding. - It is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to the drug or other nitroimidazoles.Resistance and the Future of Metronidazole

Conclusion and Future Directions

Final Thoughts

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with metronidazole in the comments below. Have you or someone you know used metronidazole to treat an infection? What were your experiences? Your insights can help others better understand the benefits and potential drawbacks of this medication.
What is metronidazole used for?
+Metronidazole is used to treat various infections caused by bacteria and protozoa, including bacterial vaginosis, pelvic inflammatory disease, amoebiasis, giardiasis, and trichomoniasis, among others.
How does metronidazole work?
+Metronidazole works by entering the cells of microorganisms and damaging their DNA, thereby inhibiting their ability to reproduce and leading to their death. This process is particularly effective under anaerobic conditions.
What are the potential side effects of metronidazole?
+Potential side effects of metronidazole include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and a metallic taste. More severe but less common side effects may involve neurological symptoms and pseudomembranous colitis.
