Intro
Discover Nabumetone uses, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, for relieving osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and menstrual cramps symptoms, reducing inflammation and pain management.
Nabumetone is a type of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that has been widely used for its anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic properties. The importance of understanding nabumetone uses cannot be overstated, as it has become a crucial medication in the management of various conditions, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and other inflammatory diseases. In this article, we will delve into the world of nabumetone, exploring its benefits, working mechanisms, and practical applications, as well as providing statistical data and examples to illustrate its effectiveness.
The prevalence of inflammatory diseases has increased significantly over the years, affecting millions of people worldwide. These conditions can cause significant discomfort, pain, and disability, impacting the quality of life of those affected. Nabumetone has emerged as a valuable treatment option, offering relief from symptoms and improving functional ability. Its uses extend beyond the management of arthritis, as it has been found to be effective in treating other conditions, such as menstrual cramps, tendonitis, and bursitis. As we explore the uses of nabumetone, it becomes clear that this medication has the potential to improve the lives of many individuals suffering from inflammatory diseases.
The mechanism of action of nabumetone involves the inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis, which plays a key role in the inflammatory process. By reducing prostaglandin production, nabumetone decreases inflammation, pain, and fever, providing relief from symptoms. Its pharmacokinetic properties, including a long half-life and high bioavailability, make it an attractive option for patients requiring long-term treatment. Furthermore, nabumetone has been found to have a lower risk of gastrointestinal side effects compared to other NSAIDs, making it a safer choice for patients with a history of gastrointestinal problems.
Nabumetone Mechanism of Action
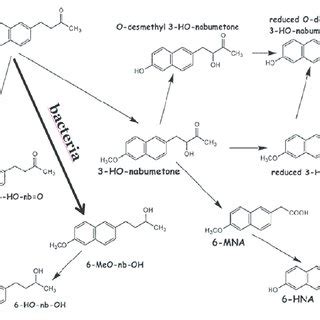
Nabumetone Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetic properties of nabumetone are characterized by a long half-life, high bioavailability, and extensive metabolism. After oral administration, nabumetone is rapidly absorbed and undergoes extensive first-pass metabolism, resulting in the formation of its active metabolite, 6-methoxy-2-naphthylacetic acid. This metabolite is responsible for the therapeutic effects of nabumetone and has a half-life of approximately 24 hours, allowing for once-daily dosing.Nabumetone Uses in Osteoarthritis
Nabumetone Efficacy in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by joint inflammation, pain, and destruction. Nabumetone has been found to be effective in reducing symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, including joint pain, swelling, and stiffness. Clinical trials have demonstrated that nabumetone improves functional ability, reduces pain, and slows disease progression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Nabumetone Side Effects and Interactions

Nabumetone Contraindications and Precautions
Nabumetone is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to the medication or other NSAIDs. Additionally, nabumetone should be used with caution in patients with a history of gastrointestinal problems, such as ulcers or bleeding, as well as in patients with renal or hepatic impairment. Patients should be monitored closely for signs of adverse effects, and the dose of nabumetone should be adjusted accordingly.Nabumetone Dosage and Administration

Nabumetone Overdose and Toxicity
In cases of overdose or toxicity, patients should be monitored closely for signs of adverse effects, including gastrointestinal problems, renal impairment, and hepatic dysfunction. Treatment should be supportive, with gastric lavage and administration of activated charcoal as needed.Nabumetone Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Nabumetone Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of nabumetone in pediatric patients have not been established. Therefore, its use in children should be avoided unless the benefits outweigh the risks.Nabumetone Geriatric Use
Nabumetone Drug Interactions
Nabumetone can interact with other medications, including anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents, and other NSAIDs, increasing the risk of adverse effects. Patients should be monitored closely for signs of adverse effects, and the dose of nabumetone should be adjusted accordingly.What is nabumetone used for?
+Nabumetone is used to treat various conditions, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and other inflammatory diseases.
How does nabumetone work?
+Nabumetone works by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, which play a key role in the inflammatory process.
What are the side effects of nabumetone?
+Nabumetone can cause side effects, including gastrointestinal problems, such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Can I take nabumetone with other medications?
+Nabumetone can interact with other medications, including anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents, and other NSAIDs, increasing the risk of adverse effects.
Is nabumetone safe for pregnant women?
+Nabumetone is classified as a category C medication in pregnancy, meaning that it should be used with caution in pregnant women.
As we conclude our exploration of nabumetone uses, it is clear that this medication has the potential to improve the lives of many individuals suffering from inflammatory diseases. With its anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic properties, nabumetone has become a valuable treatment option for various conditions, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and other inflammatory diseases. We invite readers to share their experiences with nabumetone, ask questions, and engage in discussions about the benefits and risks of this medication. By working together, we can promote a better understanding of nabumetone uses and improve the management of inflammatory diseases.
