Intro
Discover 5 ways to achieve normal BGL, managing blood glucose levels through lifestyle changes, healthy diets, and exercise routines, improving overall health and preventing diabetes complications.
Maintaining normal blood glucose levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. Blood glucose levels, or blood sugar levels, refer to the amount of glucose present in the blood. Glucose is a simple sugar that serves as the primary source of energy for the body's cells. When we eat, our body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. The pancreas regulates blood glucose levels by releasing insulin, a hormone that facilitates the uptake of glucose by cells, thereby lowering blood sugar levels.
Effective management of blood glucose levels is essential to prevent complications associated with diabetes, a condition characterized by the body's inability to regulate blood sugar levels properly. Diabetes can lead to a range of health issues, including heart disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision problems. Therefore, understanding how to maintain normal blood glucose levels is vital for individuals with diabetes and those at risk of developing the condition.
The importance of maintaining normal blood glucose levels cannot be overstated. It not only helps in managing diabetes but also in preventing the onset of the disease in individuals who are at risk. Normal blood glucose levels are typically between 70 and 140 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) after eating and less than 100 mg/dL when fasting. Achieving and maintaining these levels requires a combination of a healthy diet, regular physical activity, and, in some cases, medication.
Understanding Blood Glucose Levels
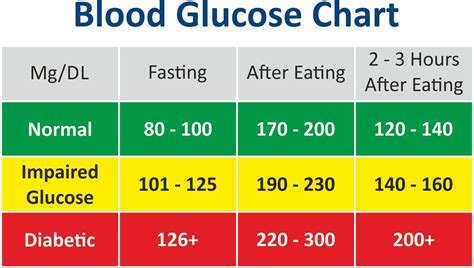
Understanding blood glucose levels is the first step towards managing them effectively. Blood glucose levels can fluctuate throughout the day based on factors such as diet, physical activity, and sleep. Monitoring these levels regularly can provide valuable insights into how the body responds to different foods and activities. For individuals with diabetes, regular monitoring is crucial for adjusting medication, diet, and exercise to maintain blood sugar levels within the target range.
Factors Affecting Blood Glucose Levels
Several factors can affect blood glucose levels, including diet, physical activity, stress, and sleep. Consuming foods high in simple carbohydrates can cause a rapid increase in blood glucose levels, while regular physical activity can help lower blood sugar levels by increasing the body's sensitivity to insulin. Stress and lack of sleep can also impact blood glucose levels by affecting the body's hormonal balance and insulin sensitivity.Dietary Approaches to Managing Blood Glucose Levels

Diet plays a critical role in managing blood glucose levels. Eating a balanced diet that is low in simple carbohydrates and added sugars but rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals can help regulate blood sugar levels. Foods with a low glycemic index, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, are particularly beneficial as they cause a gradual increase in blood glucose levels. Additionally, staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water and limiting intake of sugary drinks can also help in maintaining normal blood glucose levels.
Practical Dietary Tips
- Eat regular, balanced meals to prevent large fluctuations in blood glucose levels. - Include a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables in your diet to ensure adequate intake of vitamins and minerals. - Choose whole grains over refined grains to increase fiber intake. - Limit intake of foods high in added sugars, saturated fats, and sodium.Physical Activity and Blood Glucose Levels

Regular physical activity is another key component of managing blood glucose levels. Exercise helps lower blood sugar levels by increasing the body's sensitivity to insulin, thereby facilitating the uptake of glucose by cells. Additionally, physical activity can help with weight management, which is crucial for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. A combination of aerobic exercises, such as walking or cycling, and strength-training exercises can provide the most benefits.
Benefits of Regular Exercise
- Improves insulin sensitivity, helping to lower blood glucose levels. - Aids in weight management, reducing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. - Enhances cardiovascular health, reducing the risk of heart disease. - Improves mental health and reduces stress levels.Stress Management and Blood Glucose Levels

Stress can have a significant impact on blood glucose levels. When we are under stress, our body releases stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which can cause an increase in blood glucose levels. Engaging in stress-reducing activities can help mitigate this effect. Techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, and yoga can help manage stress levels, thereby supporting the management of blood glucose levels.
Stress Reduction Techniques
- Practice deep breathing exercises to calm the mind and body. - Engage in regular physical activity to reduce stress and improve mood. - Try meditation or yoga to enhance mental well-being and reduce stress. - Ensure adequate sleep to help regulate stress hormones.Sleep and Blood Glucose Levels

Adequate sleep is essential for maintaining normal blood glucose levels. Lack of sleep can disrupt the body's hormonal balance, leading to increased levels of stress hormones, which can cause an increase in blood glucose levels. Furthermore, sleep deprivation can affect the body's sensitivity to insulin, making it harder for glucose to enter cells. Ensuring adequate sleep each night can help regulate blood glucose levels and support overall health.
Importance of Adequate Sleep
- Helps regulate the body's hormonal balance, including insulin and stress hormones. - Supports weight management by affecting appetite hormones. - Enhances physical and mental restoration, improving overall health and well-being. - Improves concentration and cognitive function.Medication and Blood Glucose Levels

For individuals with diabetes, medication may be necessary to manage blood glucose levels. There are several types of diabetes medications, each working in a different way to lower blood sugar levels. Some medications stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin, while others improve the body's sensitivity to insulin or reduce glucose production in the liver. It is essential to follow the prescribed medication regimen and monitor blood glucose levels regularly to adjust medication as needed.
Types of Diabetes Medications
- Metformin: Improves insulin sensitivity and reduces glucose production in the liver. - Sulfonylureas: Stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin. - Meglitinides: Also stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin. - Thiazolidinediones: Improve insulin sensitivity. - DPP-4 inhibitors: Help the body produce more insulin and reduce glucose production in the liver.What are normal blood glucose levels?
+Normal blood glucose levels are typically between 70 and 140 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) after eating and less than 100 mg/dL when fasting.
How can diet affect blood glucose levels?
+Diet plays a critical role in managing blood glucose levels. Eating a balanced diet that is low in simple carbohydrates and added sugars but rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals can help regulate blood sugar levels.
Why is regular physical activity important for blood glucose management?
+Regular physical activity helps lower blood sugar levels by increasing the body's sensitivity to insulin, thereby facilitating the uptake of glucose by cells. It also aids in weight management and improves cardiovascular health.
In conclusion, maintaining normal blood glucose levels is a multifaceted approach that involves dietary changes, regular physical activity, stress management, adequate sleep, and, when necessary, medication. By understanding the factors that affect blood glucose levels and making informed lifestyle choices, individuals can effectively manage their blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications and improving overall health and well-being. We invite our readers to share their experiences and tips on managing blood glucose levels and to engage in a discussion on the importance of this aspect of health management.
