Intro
Discover what Oxybutynin is, an antispasmodic medication treating overactive bladder symptoms, including urinary incontinence and frequency, with related terms like bladder control and muscle relaxants.
Oxybutynin is a medication that has been widely used for several decades to treat various conditions, particularly those related to the urinary system. It belongs to a class of drugs known as anticholinergics or antimuscarinics, which work by blocking the action of a neurotransmitter called acetylcholine in the body. Acetylcholine is involved in the contraction and relaxation of smooth muscle, including the muscle in the wall of the bladder.
The importance of oxybutynin lies in its ability to provide relief from symptoms associated with overactive bladder, such as urinary frequency, urgency, and incontinence. These symptoms can significantly impact an individual's quality of life, causing discomfort, embarrassment, and anxiety. By managing these symptoms, oxybutynin helps patients regain control over their bladder function, allowing them to engage in daily activities with more confidence and less concern about their urinary health.
Oxybutynin's mechanism of action is based on its anticholinergic properties, which help relax the bladder muscle, reducing the frequency of contractions and increasing the bladder's capacity to hold urine. This effect is beneficial for individuals suffering from overactive bladder syndrome, where the bladder muscle contracts too often, leading to the aforementioned symptoms. Understanding how oxybutynin works and its benefits is crucial for patients who are considering this medication as part of their treatment plan.
Benefits of Oxybutynin

The benefits of oxybutynin are multifaceted, offering relief from the bothersome symptoms of overactive bladder. By reducing the frequency of urination and the urgent need to urinate, oxybutynin improves sleep quality, as patients are less likely to wake up during the night to use the bathroom. This improvement in sleep, combined with the reduction in daytime symptoms, significantly enhances the overall quality of life for those taking the medication.
Moreover, oxybutynin has been found to be effective in treating other conditions, such as detrusor overactivity, which is characterized by an overactive bladder muscle leading to urinary incontinence. The medication's ability to relax the bladder muscle makes it a valuable treatment option for patients with this condition.
Common Uses of Oxybutynin
Oxybutynin is commonly prescribed for: - Overactive bladder (OAB) with symptoms of urge urinary incontinence, urgency, and frequency. - Detrusor overactivity. - Neurogenic bladder due to spinal cord injury or other conditions affecting bladder control.How Oxybutynin Works
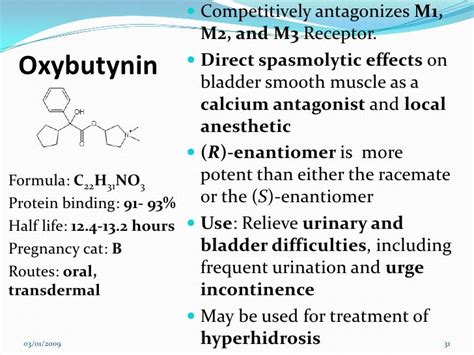
Oxybutynin works by competitively inhibiting the muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, which are found in the smooth muscle of the bladder. By blocking these receptors, oxybutynin decreases the contractility of the detrusor muscle, the smooth muscle in the wall of the bladder. This decrease in muscle contraction leads to an increase in bladder capacity and a reduction in the urgency and frequency of urination.
The medication also has a direct relaxant effect on the smooth muscle of the bladder, further contributing to its therapeutic effects. This dual mechanism of action makes oxybutynin an effective treatment for managing the symptoms of overactive bladder and other related conditions.
Side Effects of Oxybutynin
While oxybutynin is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects due to its anticholinergic properties. Common side effects include: - Dry mouth - Constipation - Dizziness - Blurred vision - Heat intoleranceThese side effects are usually mild and temporary, resolving on their own once the body adjusts to the medication. However, in some cases, they can be bothersome enough to require a dose adjustment or the consideration of alternative treatments.
Dosage and Administration
The dosage of oxybutynin can vary depending on the patient's condition, age, and response to the medication. It is available in various formulations, including immediate-release tablets, extended-release tablets, and a topical gel. The immediate-release form is typically taken two to three times a day, while the extended-release form is taken once daily.
The topical gel formulation is applied to the skin, usually on the abdomen, upper arm, or thigh, once daily. This form can be beneficial for patients who experience gastrointestinal side effects from the oral forms or for those who prefer a non-oral route of administration.
Precautions and Interactions
Before starting oxybutynin, patients should inform their healthcare provider about any other medications they are taking, as well as any medical conditions they have. Oxybutynin can interact with other anticholinergic medications, increasing the risk of side effects. It is also contraindicated in patients with certain conditions, such as urinary retention, gastric retention, or uncontrolled narrow-angle glaucoma.Alternatives to Oxybutynin

For patients who do not respond well to oxybutynin or experience intolerable side effects, there are alternative treatments available. These include other antimuscarinic agents, such as tolterodine, solifenacin, and trospium, as well as beta-3 adrenergic agonists like mirabegron. The choice of alternative medication depends on the patient's specific needs, medical history, and the severity of their symptoms.
Lifestyle Changes
In addition to medication, lifestyle changes can play a significant role in managing overactive bladder symptoms. These changes include: - Maintaining a healthy weight - Avoiding bladder irritants like caffeine and alcohol - Practicing pelvic floor exercises (Kegel exercises) - Managing fluid intakeBy combining medication with these lifestyle modifications, patients can achieve better control over their bladder function and improve their overall quality of life.
Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, oxybutynin is a valuable medication for the treatment of overactive bladder and related conditions. Its effectiveness in reducing symptoms and improving quality of life makes it a widely prescribed and recommended treatment option. As research continues to advance, new formulations and delivery methods for oxybutynin, as well as the development of new therapeutic agents, promise to provide even more effective and tolerable treatments for patients.
For those considering oxybutynin as part of their treatment plan, it is essential to discuss the potential benefits and risks with a healthcare provider. By understanding how oxybutynin works and what to expect from treatment, patients can make informed decisions about their care and work towards achieving better bladder health.
What is oxybutynin used for?
+Oxybutynin is used to treat overactive bladder and its symptoms, such as urinary frequency, urgency, and incontinence.
How does oxybutynin work?
+Oxybutynin works by blocking the action of acetylcholine on the bladder muscle, reducing its contractions and increasing its capacity to hold urine.
What are the common side effects of oxybutynin?
+Common side effects include dry mouth, constipation, dizziness, blurred vision, and heat intolerance.
We invite you to share your experiences or ask questions about oxybutynin in the comments below. Your input can help others who are considering this medication as part of their treatment plan. Additionally, feel free to share this article with anyone who might benefit from the information provided. Together, we can work towards raising awareness and promoting better understanding of overactive bladder and its treatments.
