Intro
Discover the role of Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) in regulating calcium levels, bone health, and hyperparathyroidism, exploring its functions, symptoms, and treatment options for related disorders.
The parathyroid hormone, also known as PTH, plays a crucial role in maintaining the body's calcium and phosphorus levels. Produced by the parathyroid glands, which are four small glands located in the neck, PTH is essential for regulating various bodily functions. In this article, we will delve into the importance of PTH, its functions, and the consequences of imbalances in PTH levels.
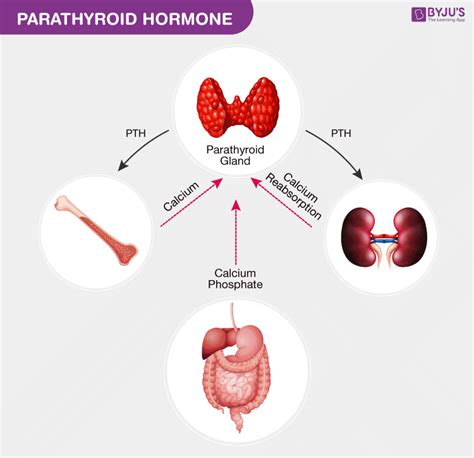
PTH is often referred to as the "calcium regulator" because it helps maintain the body's calcium levels within a narrow range. When calcium levels drop, the parathyroid glands release PTH, which stimulates the bones to release calcium into the bloodstream. This process helps maintain strong bones and teeth, as well as supports muscle and nerve function. Additionally, PTH helps regulate the amount of phosphorus in the body, which is essential for the formation of bones and teeth.
The parathyroid glands are responsible for producing PTH, and they work in conjunction with the thyroid gland to maintain hormonal balance. While the thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism, the parathyroid glands produce PTH to regulate calcium and phosphorus levels. This delicate balance is essential for maintaining overall health, and imbalances in PTH levels can lead to various health issues.
Understanding Parathyroid Hormone Regulation
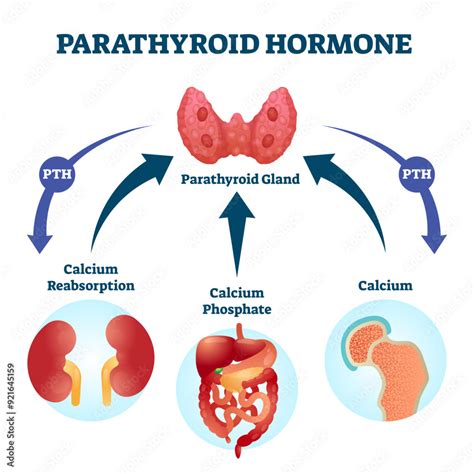
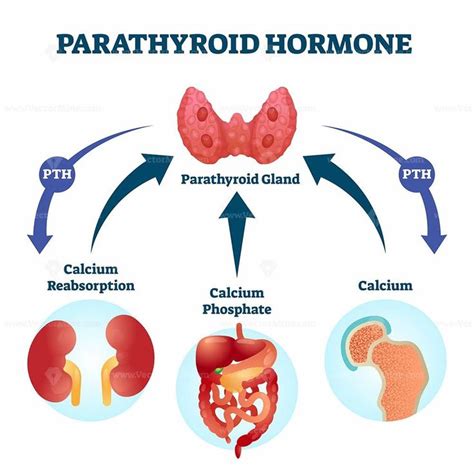
The regulation of PTH is a complex process that involves various feedback mechanisms. When calcium levels in the blood drop, the parathyroid glands are stimulated to release PTH. This hormone then binds to receptors on the surface of bone cells, stimulating them to release calcium into the bloodstream. As calcium levels rise, the parathyroid glands reduce PTH production, and the cycle repeats. This feedback mechanism ensures that calcium levels remain within a narrow range, which is essential for maintaining strong bones and supporting various bodily functions.
Functions of Parathyroid Hormone
The primary functions of PTH include: * Regulating calcium levels in the blood * Stimulating the release of calcium from bones * Enhancing the absorption of calcium from food in the gut * Reducing the excretion of calcium in the urine * Regulating phosphorus levels in the bloodThese functions are crucial for maintaining strong bones and teeth, as well as supporting muscle and nerve function. Imbalances in PTH levels can lead to various health issues, including osteoporosis, kidney stones, and muscle weakness.
Causes and Symptoms of Parathyroid Hormone Imbalance
An imbalance in PTH levels can occur due to various reasons, including:
- Hyperparathyroidism: Overproduction of PTH, which can lead to high calcium levels in the blood
- Hypoparathyroidism: Underproduction of PTH, which can lead to low calcium levels in the blood
- Parathyroid gland disorders: Tumors, cysts, or other abnormalities in the parathyroid glands can affect PTH production
- Vitamin D deficiency: Low levels of vitamin D can affect PTH production and calcium absorption
Symptoms of PTH imbalance can vary depending on the underlying cause, but common symptoms include:
- Bone pain or tenderness
- Muscle weakness or cramps
- Fatigue or weakness
- Numbness or tingling in the hands and feet
- Kidney stones or other kidney problems
If left untreated, PTH imbalance can lead to serious health complications, including osteoporosis, kidney damage, and cardiovascular disease.
Treatment Options for Parathyroid Hormone Imbalance
Treatment for PTH imbalance depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Common treatment options include: * Medications: To regulate PTH production and calcium levels * Surgery: To remove tumors or other abnormalities in the parathyroid glands * Vitamin D and calcium supplements: To support bone health and calcium absorption * Lifestyle changes: To maintain a healthy diet and exercise routineIt is essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment of PTH imbalance. With proper treatment, it is possible to manage symptoms and prevent long-term complications.
Parathyroid Hormone and Bone Health
PTH plays a crucial role in maintaining bone health by regulating calcium levels and stimulating the release of calcium from bones. When PTH levels are imbalanced, it can lead to various bone-related disorders, including osteoporosis. Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by weak and brittle bones, which can increase the risk of fractures and other bone-related problems.
To maintain strong bones, it is essential to:
- Consume a diet rich in calcium and vitamin D
- Engage in regular exercise, such as weight-bearing activities
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Manage stress and maintain a healthy weight
By maintaining a healthy lifestyle and managing PTH imbalance, it is possible to reduce the risk of osteoporosis and other bone-related disorders.
Parathyroid Hormone and Kidney Function
PTH also plays a role in regulating kidney function by controlling the amount of calcium and phosphorus in the blood. When PTH levels are imbalanced, it can lead to kidney damage and other kidney-related problems. Kidney stones, for example, can form when there is an excess of calcium in the urine.To maintain healthy kidneys, it is essential to:
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water
- Consume a diet low in sodium and phosphorus
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Manage stress and maintain a healthy weight
By maintaining a healthy lifestyle and managing PTH imbalance, it is possible to reduce the risk of kidney damage and other kidney-related problems.
Parathyroid Hormone and Cardiovascular Health
PTH also plays a role in regulating cardiovascular health by controlling the amount of calcium in the blood. When PTH levels are imbalanced, it can lead to cardiovascular disease, including high blood pressure and heart failure.
To maintain a healthy heart, it is essential to:
- Consume a diet low in sodium and saturated fats
- Engage in regular exercise, such as cardio and strength training
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Manage stress and maintain a healthy weight
By maintaining a healthy lifestyle and managing PTH imbalance, it is possible to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease and other heart-related problems.
Parathyroid Hormone and Mental Health
PTH also plays a role in regulating mental health by controlling the amount of calcium in the brain. When PTH levels are imbalanced, it can lead to various mental health disorders, including depression and anxiety.To maintain good mental health, it is essential to:
- Consume a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids and other essential nutrients
- Engage in regular exercise, such as yoga and meditation
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Manage stress and maintain a healthy weight
By maintaining a healthy lifestyle and managing PTH imbalance, it is possible to reduce the risk of mental health disorders and other brain-related problems.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, PTH plays a crucial role in maintaining various bodily functions, including calcium and phosphorus regulation, bone health, kidney function, cardiovascular health, and mental health. Imbalances in PTH levels can lead to various health issues, and it is essential to manage these imbalances through a combination of lifestyle changes, medications, and surgery.
Future research should focus on developing new treatments and therapies for PTH imbalance, as well as improving our understanding of the complex mechanisms involved in PTH regulation. By working together, we can improve our understanding of PTH and develop effective strategies for maintaining optimal health.
What is parathyroid hormone?
+Parathyroid hormone (PTH) is a hormone produced by the parathyroid glands that regulates calcium and phosphorus levels in the blood.
What are the symptoms of parathyroid hormone imbalance?
+Symptoms of PTH imbalance can include bone pain, muscle weakness, fatigue, numbness or tingling in the hands and feet, and kidney stones or other kidney problems.
How is parathyroid hormone imbalance treated?
+Treatment for PTH imbalance depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition, but common treatment options include medications, surgery, vitamin D and calcium supplements, and lifestyle changes.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of parathyroid hormone and its importance in maintaining various bodily functions. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please share it with your friends and family to help spread awareness about the importance of PTH.
