Intro
Learn about preeclampsia symptoms, causes, and treatment in our comprehensive guide, covering pregnancy complications, blood pressure management, and prenatal care to ensure a healthy pregnancy and prevent related disorders like eclampsia and gestational hypertension.
Preeclampsia is a pregnancy complication characterized by high blood pressure and signs of damage to another organ system, most often the liver and kidneys. It is a leading cause of maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality worldwide, affecting approximately 2-8% of pregnancies. The condition can be unpredictable and may develop without warning, making it essential for expectant mothers to be aware of the risks and symptoms.
The importance of understanding preeclampsia cannot be overstated, as it can have severe consequences if left untreated. Women with preeclampsia are at risk of developing complications such as stroke, kidney failure, and seizures, which can be life-threatening. Additionally, preeclampsia can also affect the baby, leading to premature birth, low birth weight, and increased risk of stillbirth. By recognizing the signs and symptoms of preeclampsia, expectant mothers can take proactive steps to manage their condition and ensure the best possible outcomes for themselves and their babies.
Preeclampsia is often referred to as a "silent killer" because it can develop without noticeable symptoms. However, there are certain risk factors that increase a woman's likelihood of developing the condition. These include a history of high blood pressure, kidney disease, or autoimmune disorders, as well as certain lifestyle factors such as obesity and smoking. By understanding these risk factors and being aware of the signs and symptoms of preeclampsia, women can take steps to reduce their risk and ensure a healthy pregnancy.
Preeclampsia Symptoms and Diagnosis

Diagnosing preeclampsia typically involves a combination of physical exams, laboratory tests, and medical history. Healthcare providers will monitor blood pressure and urine protein levels, as well as perform tests to assess liver and kidney function. In some cases, additional tests such as ultrasound and non-stress tests may be performed to assess fetal well-being.
Types of Preeclampsia
There are several types of preeclampsia, including mild, moderate, and severe. Mild preeclampsia is characterized by high blood pressure and minimal symptoms, while moderate preeclampsia involves more significant symptoms and increased risk of complications. Severe preeclampsia is the most serious form of the condition, involving severe hypertension, significant proteinuria, and increased risk of life-threatening complications.Preeclampsia Causes and Risk Factors

- History of high blood pressure or kidney disease
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Age over 35
- Multiple pregnancy (twins, triplets, etc.)
- History of autoimmune disorders
- Family history of preeclampsia
Additionally, certain medical conditions such as diabetes, lupus, and rheumatoid arthritis may also increase the risk of developing preeclampsia.
Preeclampsia Prevention
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent preeclampsia, there are several steps that women can take to reduce their risk. These include:- Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise
- Managing chronic medical conditions such as high blood pressure and diabetes
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Getting regular prenatal care to monitor blood pressure and urine protein levels
- Following a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
Preeclampsia Treatment and Management

In more severe cases, women may require hospitalization to receive close monitoring and treatment. This may involve medications to lower blood pressure, corticosteroids to promote fetal lung maturity, and other interventions to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
Preeclampsia and Pregnancy Outcomes
Preeclampsia can have significant effects on pregnancy outcomes, including increased risk of premature birth, low birth weight, and stillbirth. Women with preeclampsia are also at increased risk of developing complications during delivery, such as placental abruption and postpartum hemorrhage.To minimize risks and ensure the best possible outcomes, women with preeclampsia should work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan. This may involve regular prenatal visits, close monitoring of blood pressure and urine protein levels, and lifestyle modifications to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
Preeclampsia and Future Pregnancy Risks
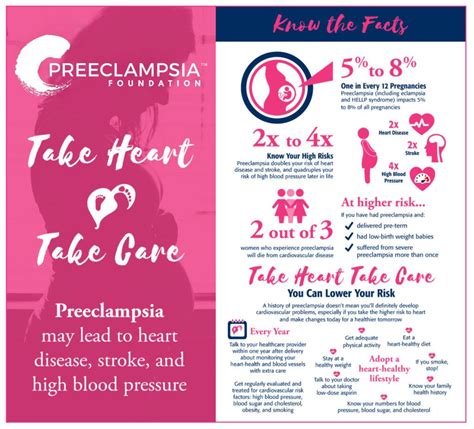
To minimize risks, women with a history of preeclampsia should work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan. This may involve close monitoring of blood pressure and urine protein levels, lifestyle modifications to manage symptoms, and medications to prevent complications.
Preeclampsia Research and Advances
Researchers are working to better understand the causes and mechanisms of preeclampsia, as well as to develop new treatments and prevention strategies. Some promising areas of research include:- The use of biomarkers to predict and diagnose preeclampsia
- The development of new medications to manage symptoms and prevent complications
- The use of lifestyle modifications and alternative therapies to reduce risk and manage symptoms
By staying up-to-date on the latest research and advances, women with preeclampsia can take proactive steps to manage their condition and ensure the best possible outcomes for themselves and their babies.
What are the symptoms of preeclampsia?
+Preeclampsia symptoms can vary from woman to woman, but common signs include high blood pressure, protein in the urine, and swelling in the hands and feet. In some cases, women may experience more severe symptoms such as headaches, vision changes, and abdominal pain.
How is preeclampsia diagnosed?
+Diagnosing preeclampsia typically involves a combination of physical exams, laboratory tests, and medical history. Healthcare providers will monitor blood pressure and urine protein levels, as well as perform tests to assess liver and kidney function.
Can preeclampsia be prevented?
+While there is no guaranteed way to prevent preeclampsia, there are several steps that women can take to reduce their risk. These include maintaining a healthy weight, managing chronic medical conditions, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and getting regular prenatal care.
What are the risks of preeclampsia for the baby?
+Preeclampsia can have significant effects on pregnancy outcomes, including increased risk of premature birth, low birth weight, and stillbirth. Women with preeclampsia are also at increased risk of developing complications during delivery, such as placental abruption and postpartum hemorrhage.
What is the prognosis for women with preeclampsia?
+The prognosis for women with preeclampsia depends on the severity of the condition and the gestational age of the baby. With prompt and proper treatment, most women with preeclampsia can expect a good outcome. However, women with severe preeclampsia or those who develop complications may face a more guarded prognosis.
In conclusion, preeclampsia is a complex and multifaceted condition that requires careful management and attention. By understanding the symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies, women can take proactive steps to reduce their risk and ensure the best possible outcomes for themselves and their babies. If you have any questions or concerns about preeclampsia, we encourage you to reach out to your healthcare provider or share your thoughts in the comments below.
