Intro
Learn about preeclampsia, a pregnancy complication causing high blood pressure, characterized by symptoms like proteinuria, affecting maternal health and fetal development, requiring prompt diagnosis and treatment to prevent eclampsia and preterm birth.
Preeclampsia is a pregnancy complication characterized by high blood pressure and damage to organs such as the liver and kidneys. It is a leading cause of maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality worldwide, affecting approximately 2-8% of pregnancies. Preeclampsia can occur at any time during pregnancy, but it typically develops after 20 weeks of gestation. The exact cause of preeclampsia is still unknown, but research suggests that it may be related to abnormalities in the development of the placenta.
The importance of understanding preeclampsia cannot be overstated, as it can have severe consequences for both the mother and the baby if left untreated. Women who develop preeclampsia are at increased risk of developing other complications, such as preterm labor, fetal growth restriction, and placental abruption. Additionally, preeclampsia can increase the risk of long-term health problems, such as cardiovascular disease and kidney disease, in both the mother and the child.
Despite the risks associated with preeclampsia, it is a condition that can be managed and treated with proper medical care. Early detection and monitoring are critical in preventing complications and ensuring the best possible outcomes for both the mother and the baby. In this article, we will delve into the world of preeclampsia, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. We will also examine the latest research and advancements in the field, as well as provide practical advice and support for women who are affected by this condition.
Preeclampsia Causes and Risk Factors

- Age: Women over 35 years old are at increased risk of developing preeclampsia
- Obesity: Women with a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher are at increased risk
- Pre-existing medical conditions: Women with pre-existing medical conditions, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, or kidney disease, are at increased risk
- Multiple pregnancy: Women carrying twins or other multiples are at increased risk
- History of preeclampsia: Women who have had preeclampsia in a previous pregnancy are at increased risk of developing it again
In addition to these risk factors, research has also identified several potential causes of preeclampsia, including:
- Abnormalities in the development of the placenta
- Imbalances in angiogenic and anti-angiogenic factors
- Inflammation and oxidative stress
- Genetic predisposition
Understanding the causes and risk factors of preeclampsia is critical in developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Preeclampsia Symptoms and Diagnosis
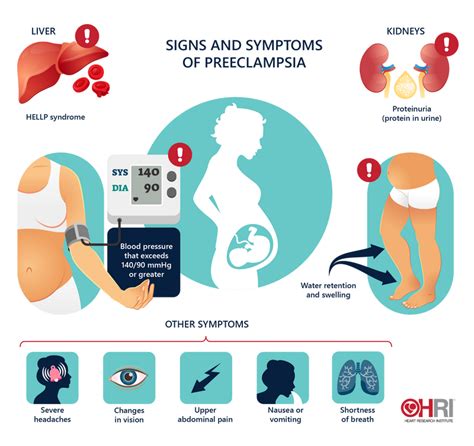
- High blood pressure
- Protein in the urine
- Severe headaches
- Vision changes, such as blurred vision or sensitivity to light
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Sudden weight gain
Diagnosing preeclampsia typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. These tests may include:
- Blood pressure measurements
- Urine tests to detect protein
- Blood tests to detect liver and kidney damage
- Ultrasound to monitor fetal growth and well-being
Early diagnosis and treatment are critical in preventing complications and ensuring the best possible outcomes for both the mother and the baby.
Preeclampsia Classification
Preeclampsia can be classified into several different categories, including:- Mild preeclampsia: Characterized by high blood pressure and minimal organ damage
- Moderate preeclampsia: Characterized by high blood pressure and moderate organ damage
- Severe preeclampsia: Characterized by high blood pressure and significant organ damage
- Eclampsia: Characterized by seizures and coma
Understanding the classification of preeclampsia is important in determining the best course of treatment and management.
Preeclampsia Treatment and Management

- Bed rest
- Close monitoring of blood pressure and organ function
- Medications to control blood pressure
Moderate to severe preeclampsia may require more intensive treatment, including:
- Hospitalization
- Corticosteroids to promote fetal lung maturity
- Magnesium sulfate to prevent seizures
- Blood pressure medications
- Fetal monitoring
In some cases, delivery may be necessary to prevent further complications. The decision to deliver is typically made on a case-by-case basis, taking into account the severity of the preeclampsia and the gestational age of the baby.
Preeclampsia Prevention
While preeclampsia cannot be completely prevented, there are several steps that women can take to reduce their risk. These include:- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Eating a balanced diet
- Managing stress
- Getting enough sleep
Additionally, women who are at high risk of developing preeclampsia may be advised to take:
- Low-dose aspirin
- Calcium supplements
- Antioxidants
Understanding the prevention strategies for preeclampsia is critical in reducing the risk of this condition and promoting a healthy pregnancy.
Preeclampsia Complications

- Preterm labor
- Fetal growth restriction
- Placental abruption
- Eclampsia
- HELLP syndrome
These complications can have serious consequences for both the mother and the baby, and may require intensive medical treatment.
Preeclampsia and Long-Term Health
Preeclampsia can have long-term consequences for both the mother and the baby. Women who develop preeclampsia are at increased risk of developing:- Cardiovascular disease
- Kidney disease
- Hypertension
- Diabetes
Babies born to mothers with preeclampsia may also be at increased risk of developing:
- Low birth weight
- Premature birth
- Respiratory distress syndrome
Understanding the long-term consequences of preeclampsia is critical in promoting healthy outcomes for both the mother and the baby.
What is preeclampsia?
+Preeclampsia is a pregnancy complication characterized by high blood pressure and damage to organs such as the liver and kidneys.
What are the symptoms of preeclampsia?
+The symptoms of preeclampsia can vary widely, but common symptoms include high blood pressure, protein in the urine, severe headaches, and vision changes.
How is preeclampsia diagnosed?
+Preeclampsia is typically diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests, including blood pressure measurements, urine tests, and blood tests.
What is the treatment for preeclampsia?
+The treatment for preeclampsia depends on the severity of the condition and the gestational age of the baby, but may include bed rest, close monitoring, medications to control blood pressure, and delivery.
Can preeclampsia be prevented?
+While preeclampsia cannot be completely prevented, there are several steps that women can take to reduce their risk, including maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and eating a balanced diet.
In conclusion, preeclampsia is a serious pregnancy complication that can have severe consequences for both the mother and the baby. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of preeclampsia is critical in promoting healthy outcomes and reducing the risk of complications. By working together with healthcare providers and taking proactive steps to manage their health, women can reduce their risk of developing preeclampsia and ensure a healthy pregnancy. We encourage readers to share their experiences and ask questions in the comments below, and to explore the many resources available for women who are affected by preeclampsia.
