Intro
Discover Prozac uses and benefits, including anxiety and depression treatment, obsessive-compulsive disorder management, and mood stabilization, highlighting its efficacy as a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor.
The world of psychiatric medications is vast and complex, with numerous options available for treating various mental health conditions. Among these, Prozac, also known by its generic name fluoxetine, stands out as one of the most widely recognized and prescribed antidepressants. Its impact on mental health treatment has been significant, offering relief to millions of people worldwide suffering from depression, anxiety disorders, and other conditions. Understanding the uses and benefits of Prozac can provide valuable insights into its role in modern psychiatric care.
The discovery and development of Prozac marked a significant milestone in the history of psychiatric medication. Introduced in the late 1980s, it was the first of a new class of drugs known as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), which work by increasing the levels of serotonin in the brain. Serotonin is a neurotransmitter associated with mood regulation, and its imbalance is linked to various mental health disorders. By inhibiting the reuptake of serotonin, Prozac effectively increases its availability in the brain, thereby helping to alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Prozac's applications extend beyond the treatment of major depressive disorder. It is also prescribed for a range of other conditions, including obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), bulimia nervosa, panic disorder, and premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD). Its efficacy in managing symptoms of these conditions has made it a versatile tool in the psychiatric toolkit. Furthermore, Prozac has been studied for its potential benefits in treating other disorders, such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), although its use in these cases may be more controversial and subject to individual patient response.
How Prozac Works
Benefits of Prozac
The benefits of Prozac are multifaceted, reflecting its broad spectrum of applications in psychiatric care. For individuals suffering from depression, Prozac can help alleviate symptoms such as persistent sadness, loss of interest in activities once enjoyed, and changes in appetite or sleep patterns. In the treatment of OCD, it can reduce the frequency and intensity of obsessive thoughts and compulsive behaviors. For those with bulimia nervosa, Prozac has been shown to decrease the frequency of binge-eating and purging behaviors, contributing to a healthier relationship with food and body image.Prozac for Depression
Prozac for Anxiety Disorders
In addition to its antidepressant effects, Prozac has anxiolytic properties, making it effective in the treatment of various anxiety disorders, including OCD, panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder. Its ability to reduce anxiety symptoms can significantly improve patients' daily functioning and overall well-being. For individuals with OCD, Prozac can lead to a substantial decrease in the intrusive thoughts and compulsions that characterize the disorder, while for those with panic disorder, it can reduce the frequency and severity of panic attacks.Side Effects and Considerations

Interactions and Contraindications
Prozac can interact with other medications, including certain antidepressants, leading to a condition known as serotonin syndrome, which can be life-threatening. Therefore, it's essential to inform healthcare providers about all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements, being taken. Prozac is also contraindicated in patients taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) due to the risk of serotonin syndrome.Dosage and Administration
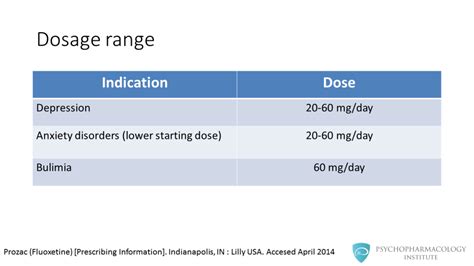
Long-Term Use and Withdrawal
Prozac, like other SSRIs, can be associated with withdrawal symptoms when discontinued, particularly if stopped abruptly. Symptoms may include dizziness, headache, and irritability. To minimize these effects, healthcare providers often recommend gradually tapering the dose over a period of weeks or months when discontinuing Prozac.Conclusion and Future Directions
To further understand the implications and applications of Prozac, readers are encouraged to engage with the content, sharing their thoughts and experiences. The discussion around mental health and its treatment is ongoing, and every perspective contributes to a deeper understanding of these critical issues.
What is Prozac used for?
+Prozac, or fluoxetine, is used to treat depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder, bulimia nervosa, panic disorder, and premenstrual dysphoric disorder.
How does Prozac work?
+Prozac works by selectively inhibiting the reuptake of serotonin, a neurotransmitter associated with mood regulation, thereby increasing its availability in the brain.
What are the common side effects of Prozac?
+Common side effects of Prozac include nausea, headache, dry mouth, and changes in sleep patterns or appetite. More serious side effects can occur, such as an increased risk of suicidal thoughts or behaviors.
