Intro
Pulmonary edema is a serious medical condition characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the lungs, making it difficult to breathe. This condition can be life-threatening if not treated promptly and properly. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for pulmonary edema is crucial for individuals who are at risk or have been diagnosed with this condition.
The importance of recognizing pulmonary edema cannot be overstated, as it can arise from various underlying health issues, including heart problems, high altitude, and certain medical treatments. By learning more about pulmonary edema, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their risk factors and seek medical attention if symptoms arise.
Pulmonary edema is not just a condition that affects the lungs; it can have a significant impact on an individual's overall quality of life. The symptoms, which can range from mild to severe, often include shortness of breath, coughing, and fatigue. In severe cases, pulmonary edema can lead to respiratory failure, emphasizing the need for swift and effective treatment.
Definition and Causes of Pulmonary Edema
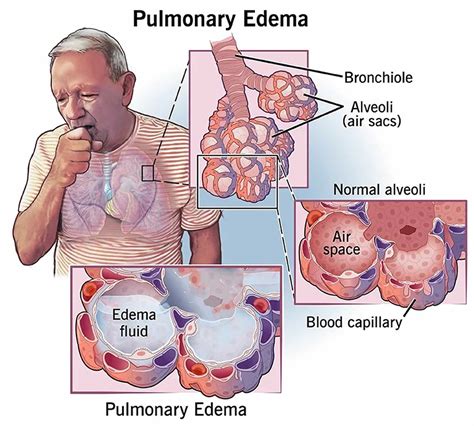
The causes of pulmonary edema can be broadly classified into two categories: cardiogenic and non-cardiogenic. Cardiogenic pulmonary edema is caused by heart problems, such as heart failure or myocardial infarction, while non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema is caused by factors outside the heart, such as high altitude or certain medical conditions. Understanding the underlying cause of pulmonary edema is essential for developing an effective treatment plan.
Types of Pulmonary Edema
There are several types of pulmonary edema, each with distinct characteristics and causes. Cardiogenic pulmonary edema, as mentioned earlier, is caused by heart problems and is the most common type. Non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema, on the other hand, can be caused by a variety of factors, including high altitude, certain medical conditions, and certain medications.Other types of pulmonary edema include hydrostatic pulmonary edema, which is caused by an increase in hydrostatic pressure, and permeability pulmonary edema, which is caused by an increase in vascular permeability. Each type of pulmonary edema requires a different approach to treatment, emphasizing the need for accurate diagnosis and personalized care.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Pulmonary Edema

Diagnosing pulmonary edema typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests. Chest X-rays and computed tomography (CT) scans can help identify fluid buildup in the lungs, while echocardiograms and electrocardiograms (ECGs) can help assess heart function. Blood tests can also be used to rule out other conditions that may be causing symptoms.
Diagnostic Tests for Pulmonary Edema
Diagnostic tests play a crucial role in diagnosing pulmonary edema and determining the underlying cause. Chest X-rays, for example, can show fluid buildup in the lungs, while CT scans can provide more detailed images of the lungs and surrounding tissues. Echocardiograms and ECGs, on the other hand, can help assess heart function and identify any potential heart problems.Other diagnostic tests, such as blood tests and arterial blood gas analysis, can also be used to diagnose pulmonary edema and determine the severity of the condition. By combining the results of these tests, healthcare providers can develop an accurate diagnosis and create an effective treatment plan.
Treatment and Management of Pulmonary Edema
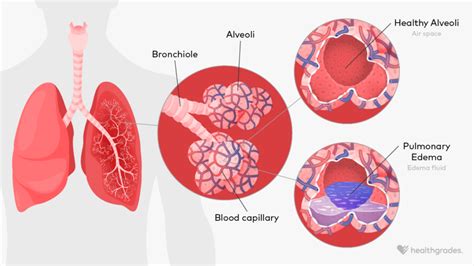
For non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema, treatment typically involves addressing the underlying cause, such as high altitude or certain medical conditions. This may involve supplemental oxygen, medications, and other supportive care. In severe cases, pulmonary edema may require hospitalization and aggressive treatment, including mechanical ventilation and other life-support measures.
Medications for Pulmonary Edema
Medications play a crucial role in the treatment and management of pulmonary edema. Diuretics, for example, can help reduce fluid buildup in the lungs, while vasodilators can help reduce blood pressure and improve heart function. Other medications, such as beta blockers and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, can also be used to manage heart failure and reduce the risk of complications.It is essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the best treatment plan for pulmonary edema. By combining medications with lifestyle changes and other supportive care, individuals can effectively manage their symptoms and reduce their risk of complications.
Prevention and Risk Reduction of Pulmonary Edema
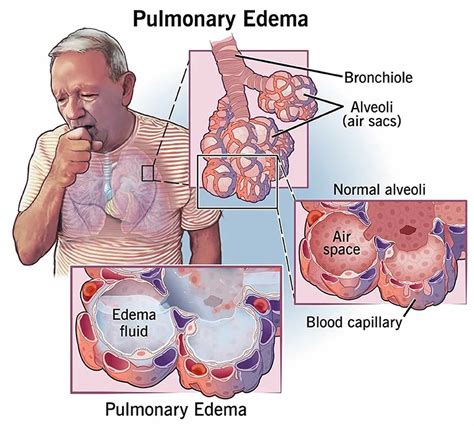
Regular health checkups can also help identify potential heart problems and other conditions early on, allowing for prompt treatment and reducing the risk of complications. Additionally, avoiding high altitudes and certain medications can also help reduce the risk of pulmonary edema.
Risk Factors for Pulmonary Edema
Certain risk factors can increase an individual's likelihood of developing pulmonary edema. These include heart problems, such as heart failure or myocardial infarction, as well as high altitude and certain medical conditions. Other risk factors include older age, obesity, and a history of smoking.By understanding these risk factors, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their risk of developing pulmonary edema. This may involve making lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking or increasing physical activity, as well as working closely with a healthcare provider to manage any underlying medical conditions.
Living with Pulmonary Edema
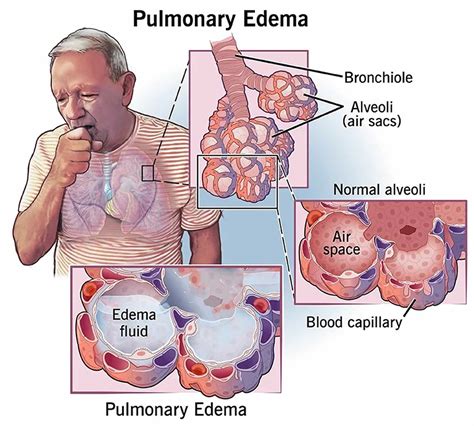
It is also essential to stay informed about pulmonary edema, including its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. This can help individuals make informed decisions about their care and take proactive steps to manage their condition.
Coping with Pulmonary Edema
Coping with pulmonary edema can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. It is essential to seek support from family, friends, and healthcare providers to manage the condition effectively. This may involve joining a support group or seeking counseling to address any emotional or psychological challenges.By staying positive and focused on management, individuals can effectively cope with pulmonary edema and improve their overall quality of life. This may involve setting realistic goals, prioritizing self-care, and staying connected with loved ones.
What are the symptoms of pulmonary edema?
+The symptoms of pulmonary edema can vary in severity and may include shortness of breath, coughing, fatigue, and chest pain.
How is pulmonary edema diagnosed?
+Pulmonary edema is typically diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests, such as chest X-rays, CT scans, and echocardiograms.
What are the treatment options for pulmonary edema?
+The treatment options for pulmonary edema depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition and may include medications, lifestyle changes, and supportive care.
Can pulmonary edema be prevented?
+Yes, pulmonary edema can be prevented by reducing the risk of underlying heart problems and other conditions that can lead to fluid buildup in the lungs, such as maintaining a healthy weight, reducing salt intake, and increasing physical activity.
What is the prognosis for individuals with pulmonary edema?
+The prognosis for individuals with pulmonary edema depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition, as well as the effectiveness of treatment and management.
