Intro
Discover how radiation therapy for cancer works, using techniques like intensity-modulated radiotherapy, stereotactic body radiotherapy, and proton therapy to target tumors and minimize side effects.
Radiation therapy is a crucial treatment method for cancer, used to destroy or shrink cancer cells. It works by utilizing high-energy particles or waves, such as X-rays, gamma rays, or proton beams, to damage the DNA of cancer cells, preventing them from growing and dividing. This treatment is often used in conjunction with other cancer treatments, such as surgery and chemotherapy, to provide comprehensive care for patients. The importance of radiation therapy lies in its ability to target specific areas of the body, reducing the risk of damage to healthy tissues and cells.
The use of radiation therapy has become increasingly prevalent in cancer treatment, with over half of all cancer patients undergoing some form of radiation therapy during their treatment. This is due to its effectiveness in treating a wide range of cancer types, including breast, lung, prostate, and brain cancers. Radiation therapy can be used as a curative treatment, aiming to eliminate the cancer entirely, or as a palliative treatment, focusing on relieving symptoms and improving quality of life.
Radiation therapy is a complex and highly specialized field, requiring a deep understanding of cancer biology, radiation physics, and treatment planning. Radiation oncologists, medical physicists, and radiation therapists work together to design and deliver personalized treatment plans, taking into account the unique characteristics of each patient's cancer. The goal of radiation therapy is to deliver a precise and effective dose of radiation to the tumor site, while minimizing exposure to surrounding healthy tissues.
How Radiation Therapy Works
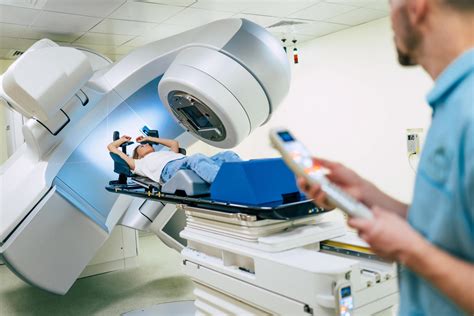
Radiation therapy works by damaging the DNA of cancer cells, which ultimately leads to cell death. There are several types of radiation therapy, including external beam radiation therapy, internal radiation therapy, and systemic radiation therapy. External beam radiation therapy involves directing a beam of radiation from outside the body to the tumor site, while internal radiation therapy involves placing a radioactive source directly into or near the tumor. Systemic radiation therapy uses radioactive substances that are injected into the bloodstream to target cancer cells throughout the body.
The process of radiation therapy typically begins with a simulation session, where the patient is positioned on a treatment table and imaging tests are performed to determine the exact location and size of the tumor. A treatment plan is then created, outlining the dosage and duration of radiation therapy. During each treatment session, the patient is positioned on the treatment table, and the radiation beam is directed at the tumor site. The treatment process can take anywhere from a few minutes to an hour, depending on the type and complexity of the treatment.
Types of Radiation Therapy
There are several types of radiation therapy, each with its own unique characteristics and advantages. These include: * External beam radiation therapy: This is the most common type of radiation therapy, where a beam of radiation is directed at the tumor site from outside the body. * Internal radiation therapy: This involves placing a radioactive source directly into or near the tumor, allowing for a high dose of radiation to be delivered directly to the cancer cells. * Systemic radiation therapy: This uses radioactive substances that are injected into the bloodstream to target cancer cells throughout the body. * Stereotactic body radiation therapy: This is a specialized type of external beam radiation therapy that uses multiple beams of radiation to deliver a high dose of radiation to a small, well-defined tumor.Benefits of Radiation Therapy
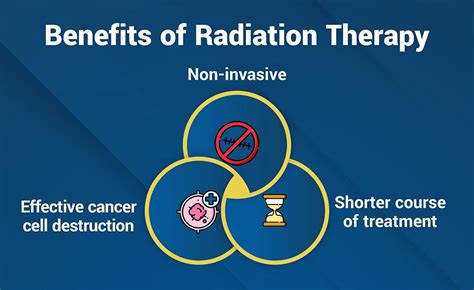
Radiation therapy offers several benefits for cancer patients, including:
- High success rates: Radiation therapy has been shown to be highly effective in treating a wide range of cancer types, with many patients experiencing complete remission.
- Minimally invasive: Radiation therapy is a non-surgical treatment, reducing the risk of complications and scarring.
- Targeted treatment: Radiation therapy allows for precise targeting of the tumor site, reducing the risk of damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
- Improved quality of life: Radiation therapy can help alleviate symptoms such as pain, bleeding, and shortness of breath, improving overall quality of life.
Radiation Therapy Side Effects
While radiation therapy is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects, including: * Fatigue: Radiation therapy can cause feelings of tiredness and exhaustion. * Skin changes: Radiation therapy can cause skin redness, itching, and dryness. * Hair loss: Radiation therapy can cause hair loss in the treatment area. * Nausea and vomiting: Radiation therapy can cause nausea and vomiting, especially when treating the abdomen or pelvis. * Diarrhea: Radiation therapy can cause diarrhea, especially when treating the abdomen or pelvis.Radiation Therapy Technology
Advances in radiation therapy technology have significantly improved treatment outcomes and reduced side effects. Some of the latest technologies include:
- Intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT): This technology allows for precise modulation of the radiation beam, reducing the risk of damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
- Image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT): This technology uses imaging tests to guide the radiation beam, ensuring accurate targeting of the tumor site.
- Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT): This technology uses multiple beams of radiation to deliver a high dose of radiation to a small, well-defined tumor.
- Proton beam therapy: This technology uses protons instead of X-rays to deliver radiation, reducing the risk of damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
Future of Radiation Therapy
The future of radiation therapy is promising, with ongoing research and development aimed at improving treatment outcomes and reducing side effects. Some of the latest advancements include: * Personalized medicine: Radiation therapy is becoming increasingly personalized, with treatment plans tailored to an individual's unique genetic profile and tumor characteristics. * Immunotherapy: Radiation therapy is being combined with immunotherapy, aiming to stimulate the immune system to attack cancer cells. * Nanotechnology: Radiation therapy is being combined with nanotechnology, aiming to deliver radiation directly to cancer cells using nanoparticles.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, radiation therapy is a highly effective treatment for cancer, offering a range of benefits and advantages. While it can cause side effects, advances in technology and treatment planning have significantly improved outcomes and reduced risks. As research and development continue to advance, radiation therapy is likely to become an even more important part of cancer treatment. If you or a loved one is considering radiation therapy, it is essential to discuss the benefits and risks with a healthcare provider, as well as explore the latest treatment options and technologies.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with radiation therapy in the comments below. Have you or a loved one undergone radiation therapy? What were your experiences and outcomes? Share your story and help raise awareness about the importance of radiation therapy in cancer treatment.
What is radiation therapy?
+Radiation therapy is a treatment method that uses high-energy particles or waves to destroy or shrink cancer cells.
How does radiation therapy work?
+Radiation therapy works by damaging the DNA of cancer cells, preventing them from growing and dividing.
What are the benefits of radiation therapy?
+Radiation therapy offers several benefits, including high success rates, minimally invasive treatment, targeted treatment, and improved quality of life.
What are the side effects of radiation therapy?
+Radiation therapy can cause side effects, including fatigue, skin changes, hair loss, nausea and vomiting, and diarrhea.
What is the future of radiation therapy?
+The future of radiation therapy is promising, with ongoing research and development aimed at improving treatment outcomes and reducing side effects.
